Scientific rationalism emphasizes understanding the world through reason, empirical evidence, and the scientific method, rejecting superstition and dogma. It promotes critical thinking and continuous inquiry as tools to uncover objective truths and solve complex problems. Explore the article to discover how scientific rationalism shapes knowledge and influences your daily decisions.
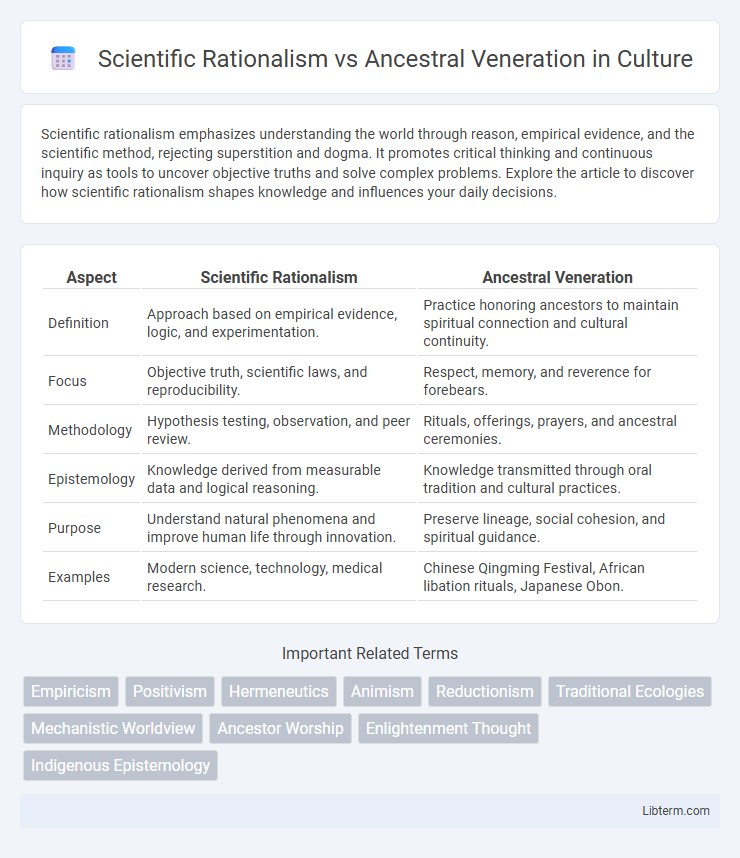
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Scientific Rationalism | Ancestral Veneration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Approach based on empirical evidence, logic, and experimentation. | Practice honoring ancestors to maintain spiritual connection and cultural continuity. |
| Focus | Objective truth, scientific laws, and reproducibility. | Respect, memory, and reverence for forebears. |
| Methodology | Hypothesis testing, observation, and peer review. | Rituals, offerings, prayers, and ancestral ceremonies. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge derived from measurable data and logical reasoning. | Knowledge transmitted through oral tradition and cultural practices. |
| Purpose | Understand natural phenomena and improve human life through innovation. | Preserve lineage, social cohesion, and spiritual guidance. |
| Examples | Modern science, technology, medical research. | Chinese Qingming Festival, African libation rituals, Japanese Obon. |
Introduction to Scientific Rationalism and Ancestral Veneration
Scientific rationalism emphasizes empirical evidence and logical reasoning as the foundation for knowledge, relying on observation, experimentation, and skepticism to understand natural phenomena. Ancestral veneration centers on honoring deceased forebears through rituals and traditions, reflecting a cultural belief in the continuing influence of ancestors on the living community. Both frameworks offer distinct approaches to interpreting the world: one grounded in scientific inquiry, the other rooted in spiritual and cultural continuity.
Historical Context: Origins and Evolution
Scientific rationalism emerged during the Scientific Revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries, emphasizing empirical evidence and logical reasoning as the foundations of knowledge. Ancestral veneration, rooted in ancient traditions across cultures like East Asia and Africa, centers on honoring forebears through rituals that maintain social cohesion and spiritual continuity. The evolution of scientific rationalism challenged ancestral veneration by prioritizing observable phenomena over metaphysical beliefs, reshaping intellectual and cultural paradigms over time.
Core Principles of Scientific Rationalism
Scientific rationalism centers on the use of empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and the scientific method to understand natural phenomena. It emphasizes skepticism, reproducibility, and the continual questioning of hypotheses to build reliable knowledge. This approach contrasts with ancestral veneration, which relies on traditions, spiritual beliefs, and cultural rituals to explain existence and guide behavior.
Fundamentals of Ancestral Veneration
Ancestral veneration centers on the belief that ancestors maintain an active presence and influence over the lives of their descendants, fostering a reciprocal relationship through rituals and offerings. Its fundamentals include honoring lineage, maintaining family harmony, and seeking guidance or protection from forebears, which strengthens cultural identity and continuity. This practice contrasts with scientific rationalism, which relies on empirical evidence and logical reasoning instead of spiritual or supernatural beliefs.
Methodologies: Empiricism vs. Tradition
Scientific rationalism relies on empiricism, emphasizing observation, experimentation, and evidence-based methodologies to understand natural phenomena. In contrast, ancestral veneration depends on tradition, utilizing rituals, oral histories, and inherited wisdom to maintain cultural continuity and interpret the world. The empirical approach seeks reproducible results through controlled studies, while traditional methods prioritize communal values and spiritual connections passed down through generations.
Knowledge Transmission: Data vs. Oral Heritage
Scientific rationalism prioritizes empirical data, experimentation, and systematic documentation to ensure precise and reproducible knowledge transmission. In contrast, ancestral veneration relies on oral heritage, storytelling, and ritual practices to pass down cultural wisdom and values across generations. The tension between these approaches highlights the contrast between quantifiable evidence and lived experiential knowledge in preserving collective understanding.
Worldview and Cosmology Comparison
Scientific Rationalism emphasizes empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and falsifiability as foundations for understanding reality, promoting a worldview grounded in observable phenomena and testable hypotheses. Ancestral Veneration centers on spiritual continuity, sacred traditions, and interconnectedness with forebears, supporting a cosmology where ancestral spirits influence the living world and communal harmony. The contrast highlights a materialistic, human-centered interpretation of existence in Scientific Rationalism versus a relational, metaphysical worldview rooted in lineage and ritual in Ancestral Veneration.
Societal Impact and Cultural Relevance
Scientific rationalism promotes societal progress through empirical evidence and technological innovation, fostering critical thinking and scientific literacy across modern communities. Ancestral veneration strengthens cultural identity and social cohesion by preserving traditions, rituals, and intergenerational values that shape communal harmony. The tension between these paradigms influences how societies balance modernization with heritage, impacting education, governance, and cultural continuity worldwide.
Contemporary Debates: Harmony or Conflict?
Contemporary debates on Scientific Rationalism versus Ancestral Veneration often highlight a perceived conflict between empirical evidence and traditional beliefs, where scientific methods prioritize observable data while ancestral veneration emphasizes cultural heritage and spiritual connections. Scholars argue for potential harmony by integrating indigenous knowledge systems with scientific approaches, fostering respect for ancestral wisdom alongside technological progress. This ongoing discourse underscores the challenge of balancing rational inquiry with cultural continuity in modern societies.
Future Perspectives: Integration and Dialogue
Scientific rationalism emphasizes empirical evidence and systematic inquiry to drive technological and medical advancements, while ancestral veneration preserves cultural heritage and spiritual identity through ritual practices. Future perspectives highlight the potential for integration, where scientific methodologies can complement ancestral knowledge systems, fostering holistic approaches to health, environmental stewardship, and community resilience. Dialogue between these worldviews encourages mutual respect and innovation, creating pathways for sustainable development that honor tradition alongside modernity.
Scientific Rationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com