Polytheism refers to the belief in or worship of multiple deities, each often representing different aspects of life, nature, or human experience. This religious framework has shaped cultures and mythologies globally, influencing art, rituals, and societal values throughout history. Explore the rest of the article to understand how polytheism continues to impact various cultures and spiritual practices today.
Table of Comparison
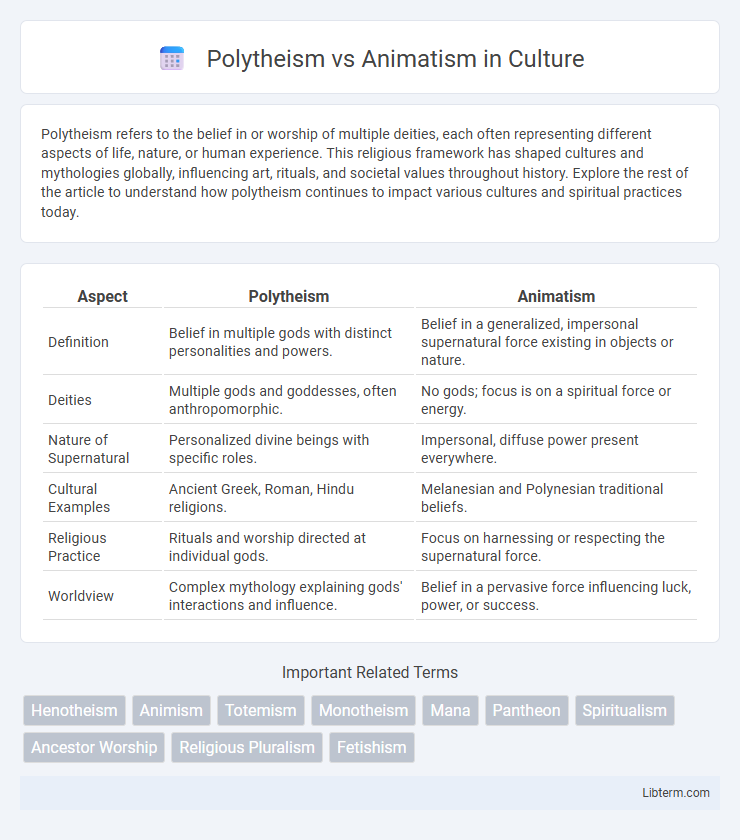
| Aspect | Polytheism | Animatism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in multiple gods with distinct personalities and powers. | Belief in a generalized, impersonal supernatural force existing in objects or nature. |
| Deities | Multiple gods and goddesses, often anthropomorphic. | No gods; focus is on a spiritual force or energy. |
| Nature of Supernatural | Personalized divine beings with specific roles. | Impersonal, diffuse power present everywhere. |
| Cultural Examples | Ancient Greek, Roman, Hindu religions. | Melanesian and Polynesian traditional beliefs. |
| Religious Practice | Rituals and worship directed at individual gods. | Focus on harnessing or respecting the supernatural force. |
| Worldview | Complex mythology explaining gods' interactions and influence. | Belief in a pervasive force influencing luck, power, or success. |
Defining Polytheism: Belief in Multiple Deities
Polytheism is the belief system centered on the existence and worship of multiple deities, each often associated with specific aspects of nature, human experiences, or cosmic phenomena. These gods and goddesses typically possess distinct personalities, powers, and roles within religious narratives, shaping cultural rituals and moral frameworks. Unlike animatism, which attributes spiritual essence to objects or forces without personification, polytheism emphasizes individualized divine beings that interact with the world and its inhabitants.
Understanding Animatism: Spiritual Power in Nature
Animatism refers to the belief in a generalized spiritual power that exists in natural objects, places, and phenomena, rather than worshiping distinct gods as seen in polytheism. This spiritual force is often impersonal, pervasive, and can be harnessed or influenced through rituals and symbols in many indigenous cultures. Understanding animatism highlights its role in shaping human interactions with nature, emphasizing a profound respect and connection to the environment's inherent energy.
Historical Origins of Polytheism and Animatism
Polytheism traces its historical origins to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece, where the belief in multiple gods personifying natural and social forces was central to religious practice and societal organization. Animatism, a concept identified in the study of indigenous and prehistoric religions, refers to the belief in a generalized, impersonal spiritual force permeating objects and phenomena, predating organized polytheistic systems. Archaeological evidence from Paleolithic sites suggests animatism as an early religious expression, which later evolved into the complex mythologies characteristic of polytheistic traditions.
Key Differences Between Polytheism and Animatism
Polytheism involves the belief in multiple gods, each with distinct personalities and domains, whereas animatism centers on the belief in a generalized spiritual force or power that pervades objects and living beings. Polytheistic religions often feature structured mythologies and rituals dedicated to individual deities, while animatism emphasizes the presence of an impersonal, supernatural essence without personal deities. Key differences include the nature of supernatural entities--personal gods in polytheism versus an impersonal force in animatism--and the complexity of worship practices.
Core Beliefs and Worldviews Compared
Polytheism centers around the worship of multiple deities, each with distinct personalities and domains, reflecting a structured pantheon that governs aspects of the natural world and human experience. Animatism emphasizes an impersonal spiritual force or power permeating objects, creatures, and locations, suggesting a more diffuse and generalized sacred presence. Polytheistic belief systems often include rituals and myths explaining divine interactions, whereas animatism assigns spiritual vitality to material elements without individualized gods.
Influence on Rituals and Religious Practices
Polytheism influences rituals by centering devotion on multiple deities, each with specific domains, leading to diverse ceremonies and offerings tailored to individual gods or goddesses. Animatism emphasizes the presence of impersonal spiritual forces in objects or natural phenomena, resulting in rituals aimed at harnessing or appeasing these forces to ensure luck, protection, or harmony. Both belief systems shape religious practices by directing the purpose and method of ceremonies, reflecting their distinct understandings of supernatural power and its interaction with the material world.
Examples of Polytheistic and Animatistic Traditions
Ancient Greek and Hindu religions exemplify polytheistic traditions, worshiping multiple deities like Zeus and Vishnu who govern various aspects of life and nature. Animatism is seen in Melanesian and Polynesian cultures, where spiritual power, or mana, is believed to inhabit objects, places, and living beings without personification. These traditions reflect diverse worldviews: polytheism centers on gods with distinct personalities, while animatism emphasizes impersonal spiritual forces.
Polytheism and Animatism in Modern Society
Polytheism, the belief in multiple deities with distinct attributes and roles, continues to influence modern society through vibrant religious practices in Hinduism, Shinto, and various neopagan movements. Animatism, the belief in impersonal spiritual forces present in natural objects and phenomena, is evident in indigenous traditions and contemporary ecological spirituality emphasizing harmony with nature. Both belief systems contribute to cultural diversity, shaping rituals, ethical worldviews, and environmental attitudes in contemporary communities worldwide.
Intersections and Overlaps in Belief Systems
Polytheism and animatism intersect in their attribution of supernatural powers to multiple entities, with polytheism worshipping distinct gods while animatism sees spiritual forces in objects or phenomena. Both belief systems emphasize a world imbued with spiritual presence, influencing human life and natural events through divine or mystical powers. Overlaps occur as some polytheistic traditions incorporate animatistic elements, recognizing spirits in nature alongside deities, creating a complex spiritual hierarchy.
Cultural Impact and Significance Today
Polytheism, characterized by belief in multiple deities with distinct personalities and domains, shapes cultural traditions through ritualistic festivals, temples, and mythologies that reinforce community identity and moral values worldwide. In contrast, animatism, the belief in a generalized, impersonal spiritual force present in all things, influences contemporary environmental ethics and indigenous practices by fostering a deep connection with nature and promoting sustainable living. Both belief systems continue to impact modern society, with polytheism sustaining religious diversity and animatism inspiring ecological awareness and cultural heritage preservation.
Polytheism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com