Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities for all individuals regardless of race, gender, or social status, emphasizing fairness and justice in society. This philosophy challenges systemic inequalities and advocates for the redistribution of resources to create a more balanced social environment. Explore the rest of the article to understand how egalitarian principles can impact your community and daily life.
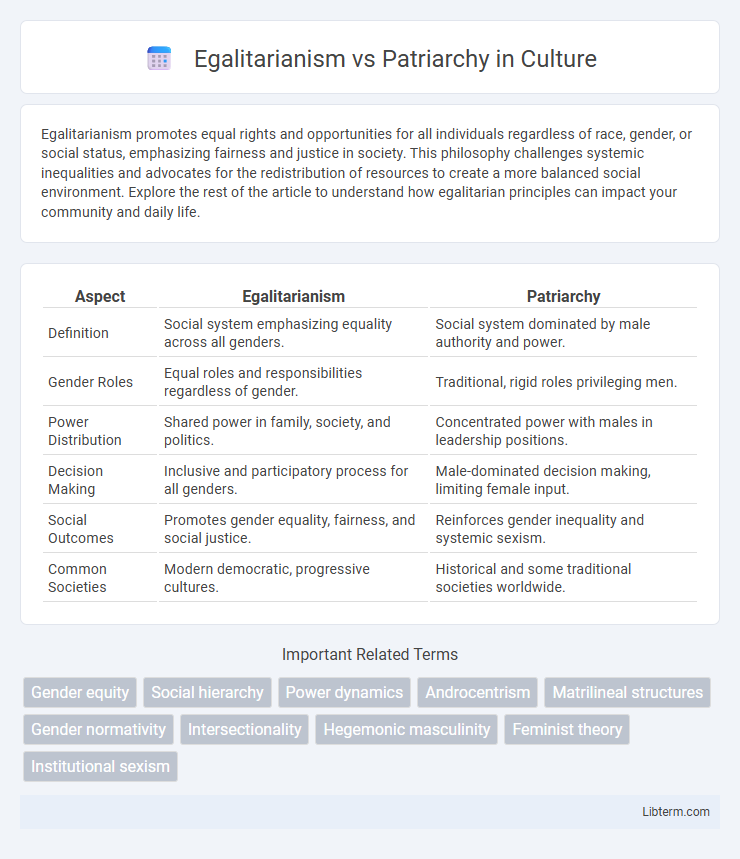
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Patriarchy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system emphasizing equality across all genders. | Social system dominated by male authority and power. |
| Gender Roles | Equal roles and responsibilities regardless of gender. | Traditional, rigid roles privileging men. |
| Power Distribution | Shared power in family, society, and politics. | Concentrated power with males in leadership positions. |
| Decision Making | Inclusive and participatory process for all genders. | Male-dominated decision making, limiting female input. |
| Social Outcomes | Promotes gender equality, fairness, and social justice. | Reinforces gender inequality and systemic sexism. |
| Common Societies | Modern democratic, progressive cultures. | Historical and some traditional societies worldwide. |
Introduction to Egalitarianism and Patriarchy
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights, opportunities, and status across genders, emphasizing fairness and social justice. Patriarchy is a social system where men hold primary power, dominating political leadership, moral authority, and control over property. Understanding these contrasting frameworks highlights ongoing debates about gender roles and societal organization.
Historical Roots of Patriarchy
Patriarchy's historical roots trace back to ancient agrarian societies where male dominance emerged due to physical strength and control over resources, shaping social hierarchies and inheritance laws. This system institutionalized male authority, influencing political structures, family roles, and property rights for millennia, limiting gender equality. Egalitarianism arises as a counter-ideology, advocating equal rights and opportunities irrespective of gender, challenging the deeply embedded patriarchal norms.
Principles of Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism is grounded in the principle that all individuals possess equal worth and deserve equal rights, opportunities, and treatment regardless of gender, race, or social status. This philosophy promotes fairness, social justice, and the dismantling of hierarchical structures that perpetuate discrimination and inequality. By advocating for equal distribution of power and resources, egalitarianism challenges the systemic privileges upheld by patriarchal systems.
Social Structures: Hierarchy vs Equality
Egalitarianism promotes social structures based on equality, where power and resources are distributed evenly across all members, minimizing hierarchical distinctions. Patriarchy reinforces a hierarchical system dominated by male authority, often resulting in unequal access to opportunities and influence. These contrasting frameworks shape societal norms, impacting gender roles, decision-making processes, and social inclusion.
Gender Roles in Patriarchal Societies
In patriarchal societies, gender roles are strictly defined, assigning men as dominant figures responsible for leadership and decision-making, while women are often relegated to domestic duties and caregiving. This rigid division reinforces male authority and limits women's access to opportunities in education, employment, and politics. Egalitarianism challenges these norms by advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, promoting shared responsibilities and dismantling systemic gender-based hierarchies.
Egalitarian Movements and Their Impact
Egalitarian movements advocate for equal rights and opportunities across gender, challenging the systemic inequalities upheld by patriarchy. These movements have significantly influenced legal reforms, such as equal pay legislation and anti-discrimination laws, promoting gender equity worldwide. Socially, they have shifted cultural norms towards inclusivity, empowering marginalized groups and fostering diverse leadership in various sectors.
Economic Disparities: Patriarchy vs Egalitarianism
Patriarchy often reinforces economic disparities by limiting women's access to higher-paying jobs, leadership positions, and financial resources, perpetuating gender wage gaps and economic dependency. Egalitarianism promotes equal economic opportunities regardless of gender, advocating for policies such as equal pay, parental leave, and anti-discrimination laws to reduce income inequality. Data from the World Economic Forum shows countries with stronger egalitarian policies typically have narrower wage gaps and higher female labor force participation rates compared to patriarchal societies.
Cultural Narratives and Power Dynamics
Cultural narratives in egalitarian societies emphasize equality, mutual respect, and shared responsibilities, challenging traditional power hierarchies embedded in patriarchal systems. Patriarchy perpetuates power dynamics that prioritize male authority and dominance, often reinforcing gender roles through social norms, media representation, and institutional practices. Shifting these narratives is crucial for dismantling systemic inequalities and promoting inclusive power structures that reflect diverse experiences and voices.
Challenges to Achieving Egalitarian Societies
Patriarchy presents deep-rooted cultural and institutional challenges to achieving egalitarian societies, often perpetuating gender-based power imbalances and systemic inequalities. Resistance to dismantling patriarchal norms manifests in discriminatory practices, unequal access to education and employment opportunities, and biased legal frameworks. Overcoming these obstacles requires comprehensive policy reforms, widespread societal shifts, and active promotion of gender equity and inclusion.
Future Prospects: Toward Gender Equality
Future prospects for gender equality suggest a gradual decline in patriarchal structures as egalitarian principles gain global traction through policy reform, education, and technology-driven empowerment. Empowering women economically and politically accelerates societal shifts, fostering inclusive governance and equitable resource distribution. Continued advocacy and systemic change remain critical to dismantling entrenched gender hierarchies and achieving full gender parity.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com