Hyponymy refers to the relationship between a more specific term (hyponym) and a more general category (hypernym), such as "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." Understanding hyponymy can enhance your vocabulary and improve semantic clarity in language processing tasks. Explore the rest of the article to learn how hyponymy shapes meaning and aids communication.
Table of Comparison
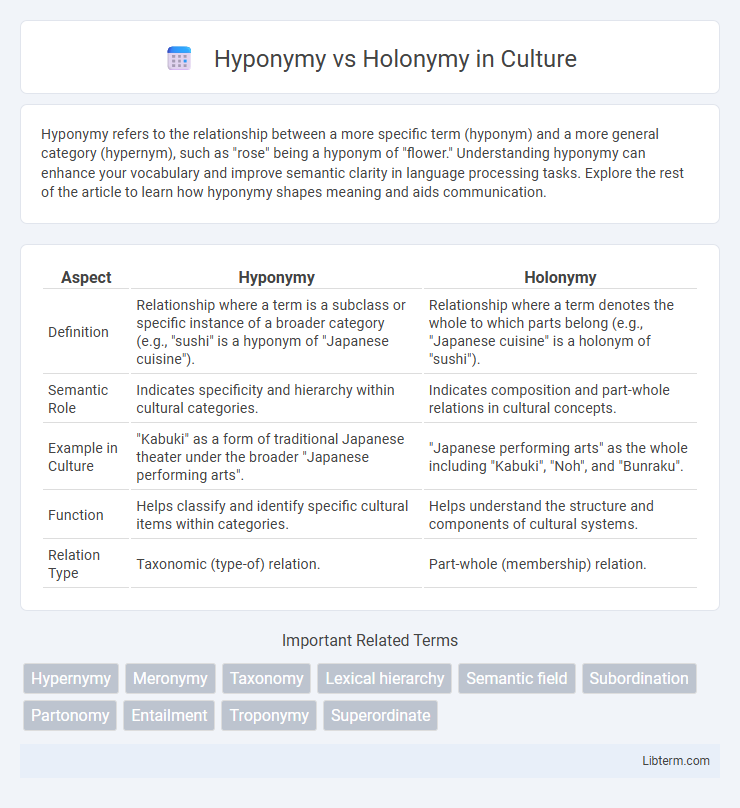
| Aspect | Hyponymy | Holonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relationship where a term is a subclass or specific instance of a broader category (e.g., "sushi" is a hyponym of "Japanese cuisine"). | Relationship where a term denotes the whole to which parts belong (e.g., "Japanese cuisine" is a holonym of "sushi"). |
| Semantic Role | Indicates specificity and hierarchy within cultural categories. | Indicates composition and part-whole relations in cultural concepts. |
| Example in Culture | "Kabuki" as a form of traditional Japanese theater under the broader "Japanese performing arts". | "Japanese performing arts" as the whole including "Kabuki", "Noh", and "Bunraku". |
| Function | Helps classify and identify specific cultural items within categories. | Helps understand the structure and components of cultural systems. |
| Relation Type | Taxonomic (type-of) relation. | Part-whole (membership) relation. |
Understanding Hyponymy and Holonymy
Hyponymy refers to the relationship where a specific term (hyponym) denotes a subtype of a more general category (hypernym), such as "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." Holonymy involves a whole-part relationship where a term (holonym) represents the whole, and its parts (meronyms) are components of that whole, like "tree" as the holonym for "branch" and "leaf." Understanding hyponymy and holonymy enhances semantic analysis by clarifying hierarchical and part-whole connections between words.
Defining Hyponymy in Semantics
Hyponymy in semantics refers to the relationship where the meaning of one word (the hyponym) is included within the meaning of another (the hypernym), such as "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." This hierarchical structure facilitates precise categorization in lexical databases and enhances natural language processing tasks, like word sense disambiguation. Holonymy, by contrast, relates to part-whole associations, exemplified by "tree" as a holonym of "branch.
Exploring the Concept of Holonymy
Holonymy defines a semantic relationship where a term denotes the whole to which other terms (its meronyms) belong, such as "tree" being the holonym for "branch" and "leaf." This concept contrasts with hyponymy, where the focus is on hierarchical inclusion from specific instances to general categories, for example, "oak" as a hyponym of "tree." Understanding holonymy enhances lexical semantics by clarifying part-whole relationships crucial for natural language processing and knowledge representation.
Key Differences Between Hyponymy and Holonymy
Hyponymy refers to a semantic relationship where a word's meaning is included within a broader category, such as "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." Holonymy involves a part-whole relationship where a term denotes the whole to which parts belong, like "car" being a holonym for "engine." The key difference lies in hyponymy expressing subclass relations, while holonymy specifies whole-part associations.
Examples of Hyponymy in Language
Hyponymy exemplifies the relationship where a specific term (hyponym) falls under a broader category (hypernym), such as "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." Other examples include "poodle" as a hyponym of "dog" and "oak" as a hyponym of "tree." This hierarchical semantic structure enables precise categorization and retrieval in natural language processing and lexicography.
Examples of Holonymy in Semantics
Holonymy in semantics refers to the relationship where one term denotes a whole that includes the other as a part, such as "car" being a holonym of "wheel," "engine," and "door." Other examples include "tree" as a holonym for "branch" and "leaf," and "house" as a holonym for "room," "roof," and "window." Understanding holonymy helps in grasping how entities are structured and related through part-whole associations in language.
Importance of Hyponymy and Holonymy in Linguistics
Hyponymy and holonymy are crucial semantic relations in linguistics, with hyponymy defining hierarchical relationships where a hyponym represents a specific instance of a broader category, as seen in "rose" being a hyponym of "flower." Holonymy, on the other hand, captures part-whole relationships, such as "wheel" being a holonym of "car." Understanding hyponymy and holonymy enhances lexical organization, improves natural language processing tasks like word sense disambiguation and ontology construction, and aids in developing more accurate language models.
Applications in Natural Language Processing
Hyponymy plays a crucial role in natural language processing (NLP) by enabling systems to understand hierarchical relationships between concepts, improving tasks like semantic search, text classification, and knowledge representation. Holonymy supports NLP applications by facilitating the identification of part-whole relationships, essential for enhanced entity recognition, information extraction, and context-aware language models. Leveraging both hyponymy and holonymy enriches word sense disambiguation and ontology construction, advancing more accurate and nuanced machine understanding of human language.
Challenges in Identifying Hyponyms and Holonyms
Identifying hyponyms involves challenges such as polysemy and context variability, which make discerning specific subcategories within a broader class difficult. Holonym identification struggles with ambiguous part-whole relationships and varying levels of granularity, complicating precise mapping between parts and wholes. Both require advanced natural language processing techniques and robust ontologies to accurately capture semantic hierarchies and dependencies.
Future Research and Trends in Lexical Semantics
Future research in lexical semantics is likely to explore the integration of hyponymy and holonymy with advanced machine learning models to improve natural language understanding and automated text analysis. Emerging trends emphasize the creation of larger, more nuanced lexical databases that capture hierarchical and part-whole relationships with greater precision and contextual awareness. Innovations in embedding techniques and knowledge graphs are expected to enhance the representation and disambiguation of semantic relations, driving progress in applications such as information retrieval and knowledge extraction.
Hyponymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com