Afrofuturism explores the intersection of African culture, technology, and science fiction to reimagine the future through a Black cultural lens. This movement blends history, art, and speculative narratives to challenge existing social norms and inspire innovative perspectives. Discover how Afrofuturism shapes culture and creativity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
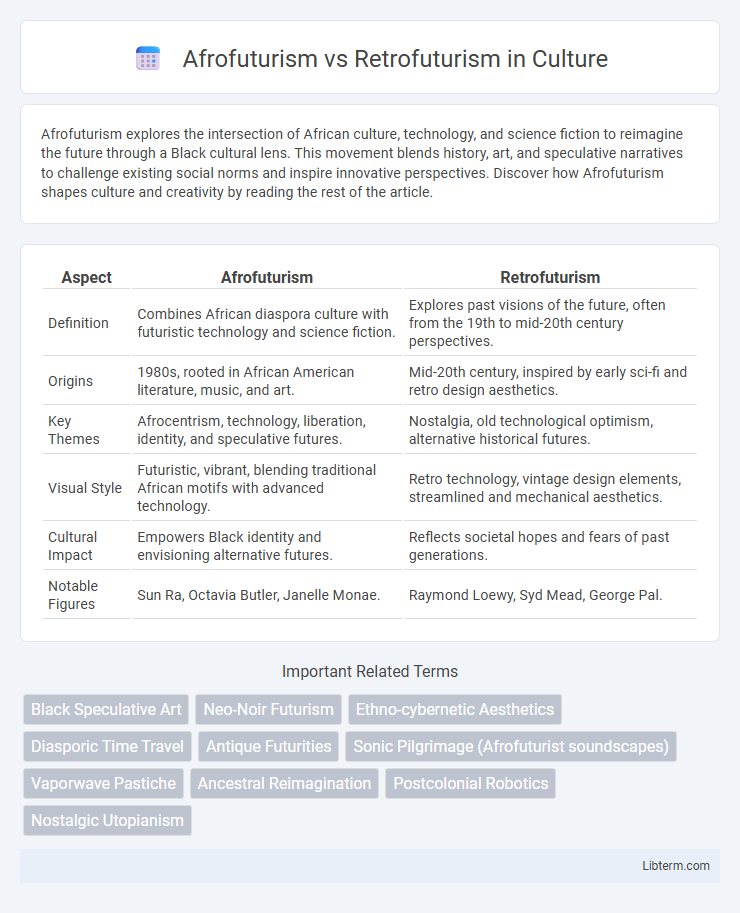
| Aspect | Afrofuturism | Retrofuturism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines African diaspora culture with futuristic technology and science fiction. | Explores past visions of the future, often from the 19th to mid-20th century perspectives. |
| Origins | 1980s, rooted in African American literature, music, and art. | Mid-20th century, inspired by early sci-fi and retro design aesthetics. |
| Key Themes | Afrocentrism, technology, liberation, identity, and speculative futures. | Nostalgia, old technological optimism, alternative historical futures. |
| Visual Style | Futuristic, vibrant, blending traditional African motifs with advanced technology. | Retro technology, vintage design elements, streamlined and mechanical aesthetics. |
| Cultural Impact | Empowers Black identity and envisioning alternative futures. | Reflects societal hopes and fears of past generations. |
| Notable Figures | Sun Ra, Octavia Butler, Janelle Monae. | Raymond Loewy, Syd Mead, George Pal. |
Defining Afrofuturism: Roots and Vision
Afrofuturism combines African culture, history, and futurist themes to reimagine the Black experience through speculative fiction, technology, and art, rooted in the African diaspora's struggle for identity and empowerment. It envisions a future where Black narratives transcend historical oppression, blending science fiction, mysticism, and African traditions to explore new possibilities. Unlike Retrofuturism, which nostalgically revisits past futures often rooted in Western perspectives, Afrofuturism challenges dominant narratives by centering Black voices and innovation in futuristic contexts.
Retrofuturism Explained: Nostalgia Meets Innovation
Retrofuturism explores the intersection of past visions of the future with contemporary innovation, blending nostalgic elements from 20th-century design, such as Art Deco and mid-century modern aesthetics, with futuristic technology concepts. This genre reimagines how the future was once envisioned, often highlighting vintage sci-fi motifs, analog technology, and optimistic space-age themes that contrast sharply with current digital advancements. By merging historical styles and speculative technology, Retrofuturism creates a unique cultural narrative that examines the evolution of societal expectations and technological progress through a lens of both hindsight and forward-thinking creativity.
Cultural Contexts: Afrofuturism and Retrofuturism Compared
Afrofuturism reimagines Black culture and history through futuristic narratives that challenge traditional Western perspectives, emphasizing technology, spirituality, and identity in a post-colonial context. Retrofuturism nostalgically explores past visions of the future, often reflecting Western industrial progress and Cold War anxieties, blending vintage aesthetics with speculative technology. Both movements engage with cultural memory but diverge in their focus: Afrofuturism centers marginalized voices to reclaim and empower, while Retrofuturism critiques mainstream historical optimism and technological progress.
Visual Aesthetics: Contrasts in Style and Symbolism
Afrofuturism's visual aesthetics blend African cultural motifs with futuristic technology, emphasizing vibrant colors, organic patterns, and symbolic references to African heritage and cosmic identity. In contrast, Retrofuturism draws inspiration from mid-20th-century visions of the future, featuring sleek metallic surfaces, streamlined designs, and nostalgic elements like vintage space-age technology and neon lighting. The symbolism in Afrofuturism often challenges historical narratives and reclaims Black identity through speculative futures, while Retrofuturism nostalgically reflects past hopes and anxieties about technological progress.
Technology and Science in Both Movements
Afrofuturism harnesses advanced technology and speculative science to reimagine Black futures through a blend of African culture and futuristic innovation, often emphasizing empowerment, space exploration, and cybernetics. Retrofuturism explores past visions of the future, integrating vintage technology aesthetics with modern scientific concepts, evoking nostalgia while questioning the evolution of technology and its societal impact. Both movements use technology and science as central motifs to challenge contemporary narratives, but Afrofuturism foregrounds cultural reclamation and liberation, while Retrofuturism critiques and romanticizes technological progress through the lens of history.
Representation and Identity: Who Gets the Future?
Afrofuturism reclaims Black identity by envisioning futures centered on Black experiences, technology, and culture, challenging dominant narratives that have historically excluded or marginalized these voices. Retrofuturism, by contrast, often revisits and reinterprets past visions of the future, sometimes reinforcing Eurocentric and mainstream perspectives, which can limit diverse representation. The critical question of "Who Gets the Future?" underscores the need for inclusive storytelling that empowers historically underrepresented groups to shape their own futures and cultural identities.
Music, Literature, and Film: Manifestations in Art
Afrofuturism in music, literature, and film blends African diasporic culture with futuristic themes, evident in artists like Sun Ra and authors like Octavia Butler, who reimagine Black identity through speculative narratives and cosmic soundscapes. Retrofuturism, contrastingly, embraces a nostalgic vision of the future influenced by mid-20th-century aesthetics, visible in films like "Metropolis" and literature that explore outdated technological optimism and altered histories. Both movements use distinct visual and thematic motifs to challenge and expand cultural understandings of time, technology, and identity in their artistic expressions.
Social Commentary: Challenging or Reinforcing Norms
Afrofuturism employs futuristic narratives and African diaspora culture to challenge racial and social norms, envisioning empowered black identities beyond historical oppression. Retrofuturism blends past and future aesthetics, sometimes reinforcing nostalgia-driven ideals that uphold traditional social structures while critiquing modernity's impact. Both genres serve as social commentaries that question power dynamics but differ in their focus: Afrofuturism disrupts systemic inequalities, whereas Retrofuturism reflects on societal change through historical reinterpretation.
Global Impact: Influence Across Continents
Afrofuturism reshapes global perceptions by merging African culture, technology, and speculative fiction, inspiring art, music, and fashion across Africa, the Americas, and Europe. Retrofuturism influences worldwide design and media by envisioning futuristic technology through the lens of past eras, impacting industries from automotive to cinema in North America, Europe, and Asia. Both movements spark cross-continental dialogues on identity, innovation, and cultural memory, shaping diverse creative landscapes around the world.
The Future Imagined: Diverging Paths Forward
Afrofuturism envisions the future by blending African culture, technology, and speculative fiction to reclaim identity and reshape narratives through empowerment and innovation. Retrofuturism revisits past visions of the future from the mid-20th century, often highlighting nostalgia and the aesthetics of vintage technology with futuristic elements. These paths diverge in their cultural focus and purpose: Afrofuturism aims to create new, inclusive futures rooted in Black experiences, while Retrofuturism reflects on historical hopes and anxieties about progress and technology.
Afrofuturism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com