Understanding consumption patterns reveals how individuals and societies allocate resources, influencing economic growth and sustainability. Analyzing your consumption habits can lead to more informed decisions that benefit both personal finances and the environment. Explore the rest of the article to uncover practical strategies for optimizing your consumption.
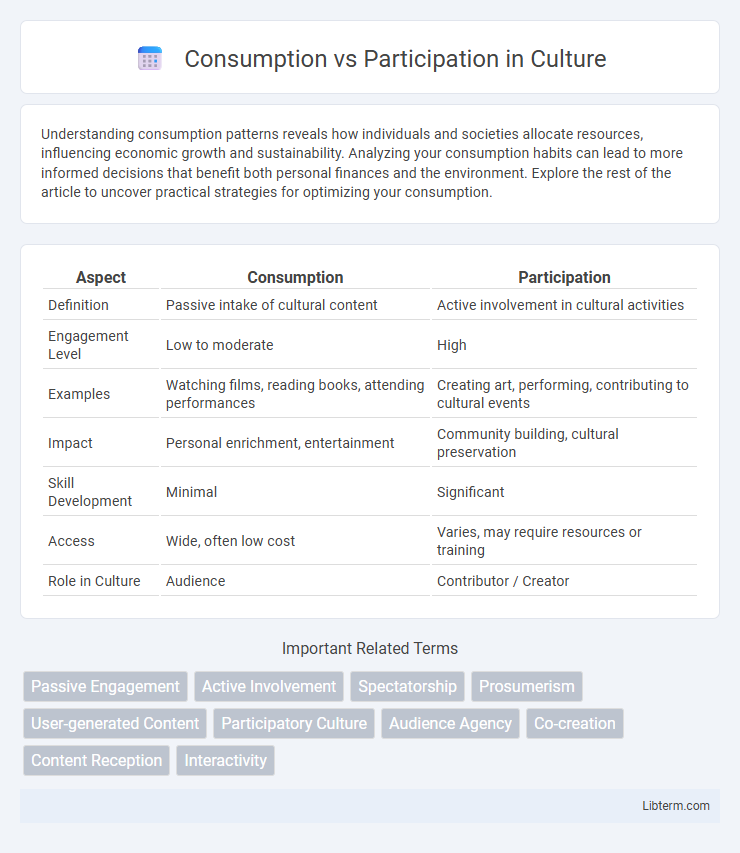
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consumption | Participation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passive intake of cultural content | Active involvement in cultural activities |
| Engagement Level | Low to moderate | High |
| Examples | Watching films, reading books, attending performances | Creating art, performing, contributing to cultural events |
| Impact | Personal enrichment, entertainment | Community building, cultural preservation |
| Skill Development | Minimal | Significant |
| Access | Wide, often low cost | Varies, may require resources or training |
| Role in Culture | Audience | Contributor / Creator |
Understanding Consumption and Participation
Understanding consumption involves recognizing it as the act of using or absorbing products, services, or content, reflecting individual preferences and needs. Participation emphasizes active engagement and interaction within communities, events, or activities, fostering collaboration and shared experiences. Both consumption and participation shape cultural dynamics by influencing how audiences connect with and contribute to various contexts.
Key Differences Between Consumption and Participation
Consumption refers to the passive act of using or absorbing content, products, or services, while participation involves active engagement or contribution within a system or community. Key differences include the level of interaction, with consumption being one-directional and participation requiring two-way involvement or collaboration. Participation often leads to deeper personal investment and influence over outcomes, unlike consumption which primarily centers on receiving value.
Historical Perspectives on Consumption and Participation
Historical perspectives on consumption and participation highlight the evolving relationship between individuals and cultural, economic, and social activities. In early societies, consumption was often passive, centered on acquiring goods for survival, while participation involved communal cooperation in rituals and decision-making. Over time, industrialization and mass media transformed consumption into a more active, symbolic act, increasing consumer influence and participation in shaping cultural trends and market dynamics.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Consumption and Participation
Technology revolutionizes consumption and participation by enabling instant access to diverse content and interactive platforms that foster user engagement. Digital tools such as social media, streaming services, and virtual reality create immersive experiences that transform passive consumption into active participation. Data analytics and personalized algorithms further tailor content, enhancing user involvement and shaping consumption behaviors dynamically.
Psychological Factors Influencing Consumption vs Participation
Psychological factors influencing consumption versus participation hinge on motivation, perceived self-efficacy, and social identity. Consumption often satisfies emotional needs such as comfort, status, or instant gratification, driven by intrinsic motivations and external cues like advertising. Participation, conversely, is typically motivated by a sense of competence, autonomy, and relatedness, fostering deeper engagement and long-term psychological rewards through active involvement and social connection.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Consumption and Participation
Consumption shapes social identity and cultural norms by influencing preferences, lifestyle choices, and access to resources, often reflecting socioeconomic status and reinforcing social stratification. Participation in cultural and social activities fosters community cohesion, promotes shared values, and encourages active engagement, which can challenge existing power dynamics and create inclusive spaces. Both consumption and participation impact cultural evolution, with consumption driving market trends and individual expression, while participation sustains traditions and collective meaning.
Advantages of Active Participation Over Passive Consumption
Active participation enhances cognitive engagement and retention by involving individuals directly in the learning or experience process. It promotes critical thinking, creativity, and skill development through practical application and real-time feedback. Unlike passive consumption, active participation fosters a deeper connection and personal investment, leading to greater motivation and long-term benefits.
Balancing Consumption and Participation in Daily Life
Balancing consumption and participation in daily life involves managing time and resources between passive activities like media consumption and active engagement in social, physical, or creative pursuits. Effective balance supports mental well-being, promotes personal growth, and enhances social connections by encouraging meaningful interactions over excessive screen time. Prioritizing participation through hobbies, community involvement, and exercise can reduce overconsumption and improve overall life satisfaction.
Case Studies: Consumption and Participation in Modern Society
Case studies in modern society reveal the shifting dynamics between consumption and participation, highlighting how digital platforms transform passive consumers into active contributors. Research shows platforms like YouTube and TikTok foster user-generated content, blurring the line between consumption and participation by empowering individuals to create and share media. Data indicates this participatory culture enhances community engagement and reshapes marketing strategies, driving brands to prioritize interactive experiences over traditional consumption patterns.
Future Trends and Predictions: Shifting from Consumption to Participation
Future trends indicate a significant shift from passive consumption to active participation in digital media and entertainment, driven by advancements in interactive technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality, and blockchain-based platforms. Predictions highlight increased user engagement through co-creation, immersive experiences, and decentralized communities, transforming traditional consumer roles into collaborative contributors. This evolution fosters personalized content, greater audience empowerment, and new economic models centered on participation rather than mere consumption.
Consumption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com