Homogeneity refers to the uniformity and consistency within a material, group, or dataset, ensuring that its components share similar characteristics or properties. In various fields, achieving homogeneity is crucial for accurate analysis, reliable results, and efficient processes. Explore how understanding homogeneity can enhance your approach and decision-making by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
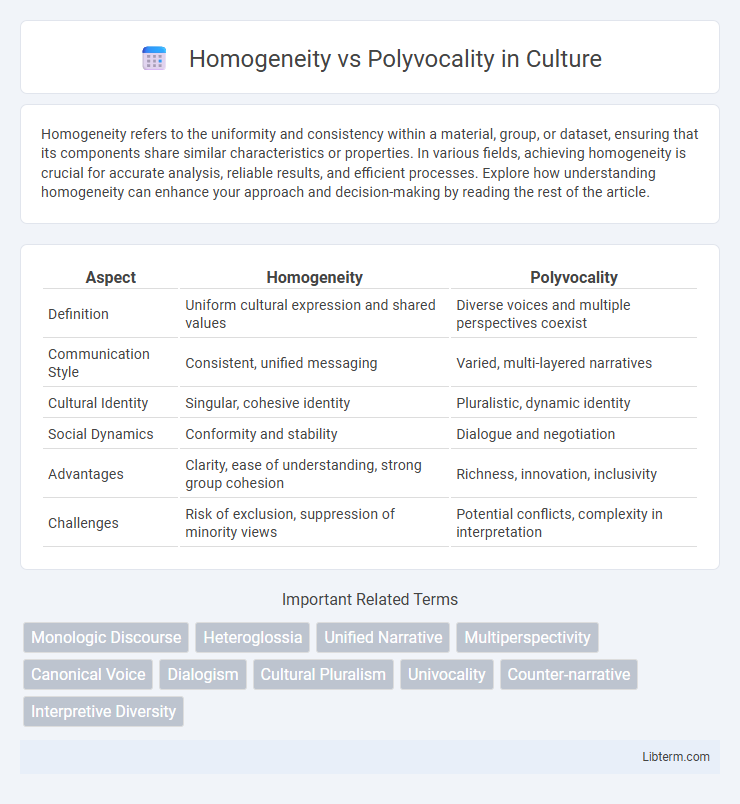
| Aspect | Homogeneity | Polyvocality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform cultural expression and shared values | Diverse voices and multiple perspectives coexist |
| Communication Style | Consistent, unified messaging | Varied, multi-layered narratives |
| Cultural Identity | Singular, cohesive identity | Pluralistic, dynamic identity |
| Social Dynamics | Conformity and stability | Dialogue and negotiation |
| Advantages | Clarity, ease of understanding, strong group cohesion | Richness, innovation, inclusivity |
| Challenges | Risk of exclusion, suppression of minority views | Potential conflicts, complexity in interpretation |
Introduction to Homogeneity and Polyvocality
Homogeneity refers to the uniformity and consistency of ideas, themes, or voices within a text or group, emphasizing a singular perspective. Polyvocality highlights the presence of multiple, diverse voices, perspectives, or interpretations, enriching the discourse with varied viewpoints. Understanding the balance between homogeneity and polyvocality is crucial in analyzing narrative structures, cultural representations, and communication dynamics.
Defining Homogeneity in Communication
Homogeneity in communication refers to the uniformity and consistency of messages, where all participants share common language, cultural references, and values, creating a cohesive and easily interpretable discourse. This standardization simplifies understanding and reinforces shared identities within a group or community. In contrast, polyvocality embraces multiple voices and perspectives, leading to diverse interpretations and richer dialogues.
Understanding Polyvocality and Its Significance
Polyvocality refers to the presence of multiple voices or perspectives within a single text or discourse, enriching its meaning and fostering inclusive representation. Understanding polyvocality is crucial for analyzing complex narratives in literature, media, and social contexts, where diverse viewpoints contribute to a deeper, more nuanced interpretation. Emphasizing polyvocality enhances critical thinking, challenges dominant ideologies, and supports cultural diversity by valuing heterogeneous expressions over homogeneity.
Historical Perspectives on Discourse Diversity
Historical perspectives on discourse diversity reveal that homogeneity often enforced a singular dominant narrative, marginalizing alternative voices and limiting pluralistic expression. Polyvocality emerged as a critical response, emphasizing the inclusion of multiple perspectives and fostering richer, more nuanced understandings within social and cultural contexts. This shift from homogeneity to polyvocality reflects evolving attitudes towards power, identity, and representation in historical discourse analysis.
Benefits of Homogeneous Narratives
Homogeneous narratives foster clarity and coherence by presenting a unified perspective that enhances audience understanding and retention. They streamline communication, reducing ambiguity and conflicting interpretations, which is particularly effective in educational and corporate settings. This singular voice strengthens brand identity and reinforces consistent messaging across diverse platforms.
Strengths and Challenges of Polyvocal Approaches
Polyvocal approaches enhance inclusivity by integrating diverse perspectives, fostering innovation and richer understanding through the collaboration of multiple voices. This multiplicity can challenge coherence and complicate consensus-building, requiring sophisticated coordination and interpretive frameworks. Despite these complexities, polyvocality promotes resilience and adaptability in knowledge production by embracing complexity and contestation.
Homogeneity vs Polyvocality in Media and Culture
Homogeneity in media and culture refers to the dominance of a single, unified perspective that minimizes diversity, often resulting in standardized content and limited representation of different voices. Polyvocality embraces multiple, diverse perspectives and narratives, enriching media and cultural expressions by incorporating varied identities, experiences, and viewpoints. The tension between homogeneity and polyvocality shapes contemporary media landscapes, influencing audience engagement, cultural inclusivity, and the democratization of content creation.
Impact on Audience Engagement and Interpretation
Homogeneity in communication often limits audience engagement by presenting a singular, unified perspective that can restrict diverse interpretations and reduce emotional connection. Polyvocality encourages multiple voices and viewpoints, enriching the audience's experience through layered meanings and fostering deeper engagement by allowing individuals to find personal relevance. This multiplicity enhances interpretive complexity, making content more inclusive and resonant across varied cultural and cognitive backgrounds.
Case Studies: Homogeneous vs Polyvocal Examples
Case studies of homogeneous communication models often emphasize uniformity in messaging, exemplified by corporate branding strategies like Apple's consistent product narrative, which reinforces a singular, cohesive identity. In contrast, polyvocal case studies highlight diverse perspectives and voices, such as participatory journalism platforms like Medium, where multiple authors contribute varied viewpoints, enriching the discourse. These examples illustrate how homogeneous approaches prioritize clarity and consistency, while polyvocal models foster inclusivity and multifaceted interpretations.
Future Directions in Discourse Dynamics
Future directions in discourse dynamics emphasize integrating homogeneity and polyvocality to enhance semantic richness and interaction. Researchers explore adaptive frameworks that balance unified narratives with diverse perspectives, improving contextual understanding in communication technologies. Advanced AI models are being developed to dynamically detect and synthesize multiple voices, fostering more inclusive and responsive discourse environments.
Homogeneity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com