Reductionism simplifies complex phenomena by breaking them down into their fundamental parts, aiming to understand the whole through its individual components. This approach is widely used in science and philosophy but often faces criticism for overlooking the interactions and emergent properties that arise from these components. Explore the rest of this article to discover how reductionism impacts various fields and what it means for your understanding of complexity.
Table of Comparison
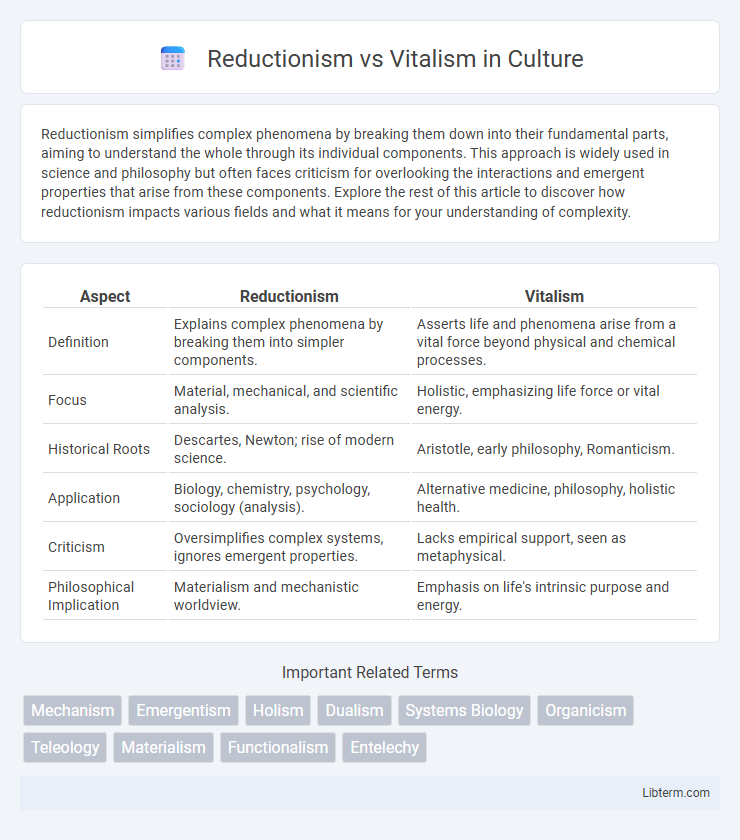
| Aspect | Reductionism | Vitalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explains complex phenomena by breaking them into simpler components. | Asserts life and phenomena arise from a vital force beyond physical and chemical processes. |
| Focus | Material, mechanical, and scientific analysis. | Holistic, emphasizing life force or vital energy. |
| Historical Roots | Descartes, Newton; rise of modern science. | Aristotle, early philosophy, Romanticism. |
| Application | Biology, chemistry, psychology, sociology (analysis). | Alternative medicine, philosophy, holistic health. |
| Criticism | Oversimplifies complex systems, ignores emergent properties. | Lacks empirical support, seen as metaphysical. |
| Philosophical Implication | Materialism and mechanistic worldview. | Emphasis on life's intrinsic purpose and energy. |
Understanding Reductionism: A Scientific Overview
Reductionism in science emphasizes analyzing complex systems by breaking them down into their fundamental components, such as molecules or cells, to understand their functions and interactions. This approach relies on empirical evidence and mechanistic explanations, often employed in fields like molecular biology and genetics to explain physiological phenomena. Understanding reductionism is crucial for advancing biomedical research by isolating specific variables and elucidating underlying biological mechanisms.
The Core Principles of Vitalism
Vitalism centers on the belief that living organisms possess a vital force beyond physical and chemical processes, which drives biological functions and cannot be fully explained by reductionist methods. This core principle asserts that life is fundamentally different from non-living matter due to this unique, non-measurable energy or essence. Vitalism challenges the mechanistic view by emphasizing holistic properties and the irreducibility of living systems to merely their constituent parts.
Historical Perspectives on Reductionism vs Vitalism
Historical perspectives on reductionism vs vitalism reveal a fundamental debate in the philosophy of biology and medicine. Reductionism, tracing back to Descartes and Newton, posits that complex biological phenomena can be explained by analyzing their simplest components, such as atoms and molecules. In contrast, vitalism, prominent in the 18th and 19th centuries through figures like Hans Driesch, asserts that living organisms possess a non-physical vital force that cannot be reduced to mechanical parts, emphasizing the distinctiveness of life processes.
Key Differences Between Reductionism and Vitalism
Reductionism explains complex biological phenomena by breaking them down into simpler components, emphasizing physical and chemical processes, while Vitalism asserts that life cannot be fully understood through these mechanisms alone, proposing a distinct vital force unique to living organisms. Reductionism relies on empirical evidence and mechanistic explanations prevalent in molecular biology and biochemistry, whereas Vitalism highlights the irreducibility of life's qualities, often linked to historical perspectives in biology and philosophy. The key difference lies in Reductionism's emphasis on material causation versus Vitalism's focus on an intrinsic life principle that transcends physical laws.
Influence of Reductionism in Modern Science
Reductionism, emphasizing the analysis of complex phenomena into simpler components, has profoundly influenced modern science by enabling precise experimentation and specialization across disciplines such as molecular biology, neuroscience, and physics. This approach has facilitated groundbreaking discoveries, including the decoding of the human genome and understanding cellular processes at the molecular level. However, the reductionist paradigm often faces criticism for overlooking systemic interactions and emergent properties, which holistic approaches like vitalism attempt to address.
Vitalism’s Role in Traditional and Alternative Medicine
Vitalism plays a central role in traditional and alternative medicine by emphasizing the presence of a vital force or life energy that governs physiological processes and healing, contrasting sharply with the mechanistic view of reductionism. Practices such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine, and homeopathy rely on the principle that this vital energy must be balanced for health maintenance and disease prevention. The vitalist perspective informs holistic treatment approaches that integrate mind, body, and spirit, promoting natural healing mechanisms beyond purely biochemical interactions.
Notable Figures Associated with Each Theory
Reductionism has been championed by figures like Rene Descartes, who emphasized the mechanical aspects of nature, and Francis Crick, known for his work on molecular biology explaining life through physical processes. Vitalism found support among thinkers such as Hans Driesch, who argued for an immaterial life force beyond physical and chemical explanations, and Henri Bergson, who introduced the concept of elan vital as a vital impetus animating living beings. These opposing perspectives highlight foundational debates in philosophy of biology about whether life can be fully understood through material components or requires acknowledging non-physical forces.
Criticisms and Limitations of Reductionism
Reductionism faces criticism for oversimplifying complex biological phenomena by reducing them solely to molecular or physical components, often neglecting emergent properties and holistic interactions that are essential to understanding living systems. It struggles to explain phenomena such as consciousness, life force, and biological organization, which vitalism attributes to intrinsic, non-material principles beyond mere chemical and physical processes. These limitations highlight the inadequacy of reductionism in capturing the full complexity of life, prompting calls for more integrative approaches that combine empirical science with a recognition of emergent biological properties.
Contemporary Relevance of Vitalism
Vitalism persists in contemporary debates as a counterpoint to reductionism, emphasizing the unique, irreducible qualities of life that cannot be fully explained by physical and chemical processes alone. Modern fields like systems biology and holistic medicine resonate with vitalist principles by highlighting emergent properties and complex interactions within living organisms. This perspective influences current research on consciousness, regenerative medicine, and bioethics, underscoring the importance of non-material factors in understanding life.
Integrative Approaches: Bridging Reductionism and Vitalism
Integrative approaches in the study of biological systems combine reductionism's focus on molecular and cellular mechanisms with vitalism's emphasis on the holistic and emergent properties of life. Systems biology and complexity science exemplify this bridge by analyzing interactions within biological networks while acknowledging the significance of life's intrinsic qualities beyond mere physical components. These methodologies enable a comprehensive understanding that respects both the biochemical details and the dynamic organization inherent in living organisms.
Reductionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com