Originality drives innovation and sets your work apart in a competitive landscape, highlighting unique ideas and authentic perspectives. Embracing originality fosters creativity, encourages fresh thinking, and enhances the value of your contributions. Explore the rest of the article to unlock strategies for cultivating and showcasing originality in your projects.
Table of Comparison
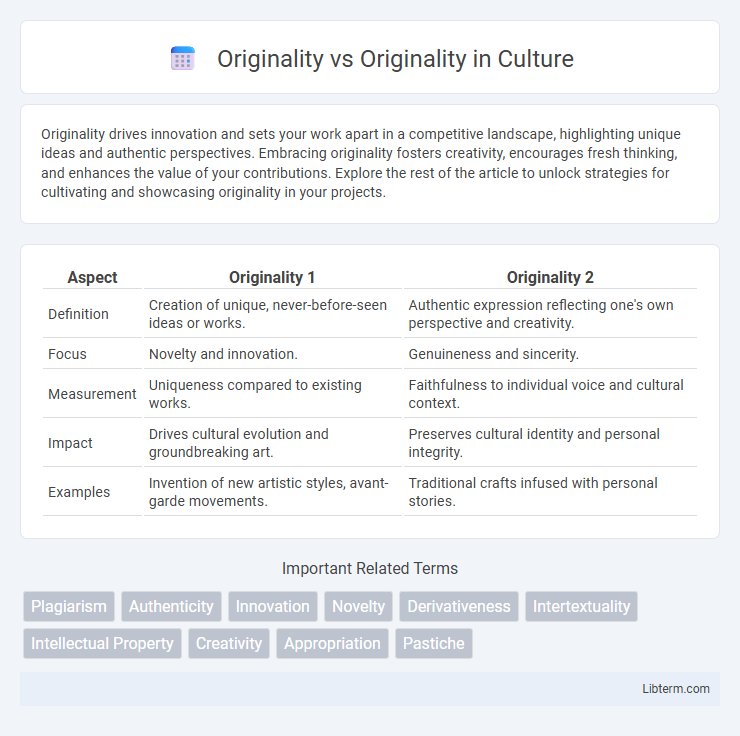
| Aspect | Originality 1 | Originality 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of unique, never-before-seen ideas or works. | Authentic expression reflecting one's own perspective and creativity. |
| Focus | Novelty and innovation. | Genuineness and sincerity. |
| Measurement | Uniqueness compared to existing works. | Faithfulness to individual voice and cultural context. |
| Impact | Drives cultural evolution and groundbreaking art. | Preserves cultural identity and personal integrity. |
| Examples | Invention of new artistic styles, avant-garde movements. | Traditional crafts infused with personal stories. |
Understanding the Concept of Originality
Originality refers to the quality of being novel, unique, and not derived from something else, emphasizing the creation of truly new ideas or works. Understanding originality involves recognizing the difference between genuine innovation and mere imitation or slight modification of existing concepts. The concept underscores the importance of creativity and authenticity in fields ranging from art to technology, where originality drives progress and distinguishes pioneering contributions.
Historical Perspectives on Originality
Historical perspectives on originality reveal evolving definitions influenced by cultural and technological contexts, with Renaissance thinkers emphasizing individual creativity and Enlightenment scholars valuing novel ideas grounded in reason. The Romantic era shifted focus to the primal and emotional authenticity of original works, contrasting with earlier emphasis on classical imitation. In contemporary discourse, originality integrates both uniqueness and intertextuality, reflecting historical transformations in the conceptualization of creative innovation.
Originality in Art and Literature
Originality in art and literature embodies the creation of novel ideas, perspectives, and expressions that break away from traditional conventions and cliches. It thrives on unique narrative voices, innovative techniques, and authentic emotional depth, distinguishing works that influence cultural evolution and inspire future creators. Emphasizing originality fosters intellectual freedom and drives the continual reinvention of artistic and literary paradigms.
Originality in Scientific Innovation
Originality in scientific innovation drives breakthroughs by introducing novel hypotheses, experimental designs, and methodologies that challenge established paradigms. Emphasizing originality leads to unique discoveries and advancements in fields such as biotechnology, quantum physics, and artificial intelligence. This creative aspect fosters transformative research that propels science beyond incremental improvements.
The Role of Imitation in Cultivating Originality
Imitation serves as a foundational mechanism in cultivating originality by allowing individuals to internalize existing ideas and techniques, which can then be transformed into unique expressions. Cognitive neuroscience research reveals that the brain's mirror neuron system facilitates learning through imitation, supporting creative development. Historical analysis of artistic and scientific breakthroughs demonstrates that many original works are rooted in the innovative reinterpretation of prior knowledge rather than spontaneous invention.
Measuring Originality: Subjectivity and Standards
Measuring originality involves navigating significant subjectivity due to varying cultural, academic, and industry standards that define what constitutes novel work. Objective metrics often fall short as originality heavily relies on context, creativity, and the reinterpretation of existing ideas rather than mere novelty. Effective assessment balances qualitative judgments with standardized criteria, ensuring originality reflects meaningful innovation rather than superficial uniqueness.
Digital Age Challenges to Originality
Digital age challenges to originality stem from the rapid proliferation of content through social media, making it difficult to distinguish unique ideas from widespread reproductions. Algorithms often promote repetitive or derivative works that generate higher engagement, reducing incentives for genuine innovation. Intellectual property concerns and digital plagiarism further complicate maintaining originality in creative industries.
Creativity vs Originality: Key Differences
Creativity involves generating novel and valuable ideas by combining existing concepts in unique ways, while originality emphasizes producing ideas or works that are entirely new and unprecedented. Creativity is a broader cognitive process that includes originality as one of its components, focusing on practical application and innovation. Originality is often measured by the uniqueness and rarity of an idea, whereas creativity evaluates both novelty and usefulness within a given context.
Intellectual Property and Protecting Original Work
Intellectual Property laws play a crucial role in distinguishing true originality by protecting creators' unique ideas, inventions, and artistic works from unauthorized use or reproduction. Safeguarding original work through patents, copyrights, and trademarks ensures legal recognition and exclusive rights, which incentivize innovation and creative expression. Proper protection of intellectual property prevents plagiarism and counterfeiting, preserving the integrity and value of genuinely original contributions in various industries.
Fostering Originality in Education and Work
Fostering originality in education and work environments cultivates innovative thinking by encouraging experimentation, critical analysis, and diverse perspectives. Implementing project-based learning and collaborative problem-solving enhances students' and employees' ability to generate unique solutions. Organizations and educators who support a culture of creativity and risk-taking see increased engagement, productivity, and breakthrough ideas.
Originality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com