Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of one culture by another, often without understanding or respecting the original meaning and context. This practice can lead to misrepresentation, perpetuation of stereotypes, and harm to the originating community's identity. Explore the rest of the article to understand the complexities of cultural appropriation and how it impacts societies worldwide.
Table of Comparison
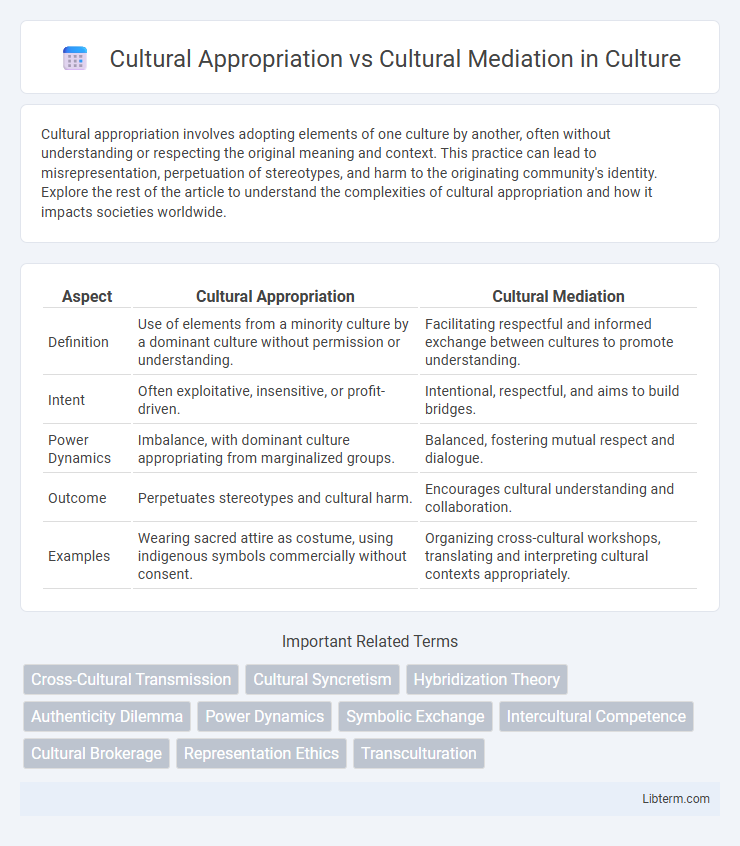
| Aspect | Cultural Appropriation | Cultural Mediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of elements from a minority culture by a dominant culture without permission or understanding. | Facilitating respectful and informed exchange between cultures to promote understanding. |
| Intent | Often exploitative, insensitive, or profit-driven. | Intentional, respectful, and aims to build bridges. |
| Power Dynamics | Imbalance, with dominant culture appropriating from marginalized groups. | Balanced, fostering mutual respect and dialogue. |
| Outcome | Perpetuates stereotypes and cultural harm. | Encourages cultural understanding and collaboration. |
| Examples | Wearing sacred attire as costume, using indigenous symbols commercially without consent. | Organizing cross-cultural workshops, translating and interpreting cultural contexts appropriately. |
Understanding Cultural Appropriation
Understanding cultural appropriation involves recognizing the adoption of elements from one culture by another, often without permission or proper acknowledgment, leading to misrepresentation or exploitation. This concept highlights power imbalances where dominant groups borrow from marginalized cultures, resulting in harm or disrespect to the original communities. Differentiating cultural appropriation from cultural mediation requires emphasizing respect, consent, and the ethical exchange of cultural expressions.
Defining Cultural Mediation
Cultural mediation involves facilitating meaningful dialogue and understanding between diverse cultural groups, promoting respect and exchange rather than exploitation. It serves as a bridge that enables individuals to navigate and appreciate cultural differences without appropriating elements in a disrespectful or commercialized manner. Unlike cultural appropriation, which often involves taking cultural symbols without permission, cultural mediation emphasizes consent, context, and mutual learning.
Historical Contexts: Appropriation and Mediation
Cultural appropriation involves the adoption of elements from one culture by another, often without permission and rooted in historical power imbalances, leading to misrepresentation or exploitation. In contrast, cultural mediation facilitates respectful exchange and understanding between cultures, fostering dialogue and collaboration across historical contexts of conflict or colonization. Historical analysis reveals that mediation seeks to bridge cultural divides by acknowledging past injustices and promoting equitable interactions.
Key Differences Between Appropriation and Mediation
Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of a marginalized culture without understanding or respecting their original context, often leading to misrepresentation and exploitation. Cultural mediation, by contrast, emphasizes respectful exchange and interpretation of cultural elements, promoting mutual understanding and dialogue between cultures. Key differences lie in intent, respect, and power dynamics, where appropriation tends to reinforce inequality, while mediation fosters inclusion and cultural sensitivity.
Power Dynamics in Cross-Cultural Exchanges
Cultural appropriation involves dominant groups exploiting elements of marginalized cultures without permission, reinforcing unequal power dynamics and often leading to misrepresentation and exploitation. Cultural mediation, by contrast, fosters respectful dialogue and mutual understanding, aiming to balance power relations through collaborative exchange and active listening. Power dynamics in cross-cultural exchanges are critical, determining whether interactions perpetuate dominance or promote equity and cultural appreciation.
Examples of Cultural Appropriation
Cultural appropriation occurs when elements of a minority culture, such as traditional clothing, symbols, or rituals, are used by members of a dominant culture without understanding or respect, often leading to misrepresentation and commodification. Examples include wearing Native American headdresses as fashion accessories at music festivals or adopting sacred religious symbols like the Hindu bindi purely as trendy decorations. This practice contrasts with cultural mediation, which promotes respectful exchange, education, and mutual understanding between cultures.
Successful Instances of Cultural Mediation
Successful instances of cultural mediation highlight respectful exchange and mutual understanding between diverse cultural groups, fostering collaboration without exploitation. Effective cultural mediators, such as museums promoting indigenous art with authentic narratives, help preserve heritage while educating broader audiences. These practices contrast with cultural appropriation by emphasizing consent, context, and empowerment rather than misrepresentation or commodification.
Impact on Marginalized Communities
Cultural appropriation often results in the exploitation and misrepresentation of marginalized communities, leading to the erosion of their cultural identity and perpetuation of stereotypes. In contrast, cultural mediation facilitates respectful exchange and mutual understanding, empowering these communities by promoting authenticity and self-representation. The impact of cultural mediation fosters social inclusion and supports the preservation of cultural heritage within marginalized groups.
Promoting Ethical Cultural Engagement
Promoting ethical cultural engagement requires distinguishing cultural appropriation, which involves the unauthorized or insensitive use of cultural elements, from cultural mediation, characterized by respectful exchange and mutual understanding. Emphasizing cultural mediation fosters empathy, honors the origin communities, and supports authentic representation through dialogue and collaboration. Ethical engagement encourages learning and sharing while preserving cultural integrity and addressing power imbalances.
Moving Toward Respectful Cultural Dialogue
Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of a culture without permission, often leading to misrepresentation and disrespect, while cultural mediation fosters mutual understanding and respect by facilitating open dialogue between cultural groups. Moving toward respectful cultural dialogue requires recognizing power imbalances and engaging in active listening to honor cultural origins and meanings. Effective cultural mediation promotes collaboration, empathy, and the preservation of cultural identity through shared experiences and context-sensitive communication.
Cultural Appropriation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com