Classicism emphasizes harmony, clarity, and proportion, drawing inspiration from the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. This movement values balance and disciplined expression, influencing architecture, literature, and visual arts with timeless principles. Explore the rest of the article to discover how classicism shapes our understanding of beauty and order.
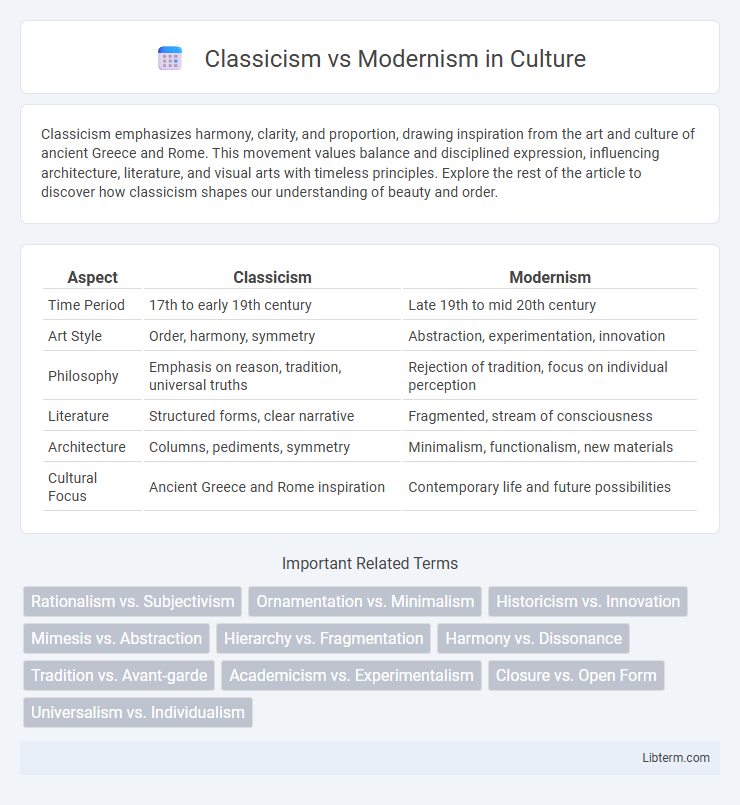
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Classicism | Modernism |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 17th to early 19th century | Late 19th to mid 20th century |
| Art Style | Order, harmony, symmetry | Abstraction, experimentation, innovation |
| Philosophy | Emphasis on reason, tradition, universal truths | Rejection of tradition, focus on individual perception |
| Literature | Structured forms, clear narrative | Fragmented, stream of consciousness |
| Architecture | Columns, pediments, symmetry | Minimalism, functionalism, new materials |
| Cultural Focus | Ancient Greece and Rome inspiration | Contemporary life and future possibilities |
Introduction to Classicism and Modernism
Classicism, emerging in the 17th and 18th centuries, emphasizes harmony, clarity, and adherence to traditional forms inspired by ancient Greek and Roman art and literature. Modernism, rooted in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, breaks from classical conventions by prioritizing innovation, abstraction, and subjective experience in art and culture. Both movements reflect distinct responses to historical contexts, with Classicism valuing order and Modernism embracing experimentation.
Historical Origins of Classicism
Classicism originated in ancient Greece and Rome, emphasizing harmony, proportion, and adherence to established artistic rules. Its historical roots lie in the Renaissance revival of classical antiquity, where artists and thinkers sought inspiration from classical literature, philosophy, and art forms. This tradition influenced European art and architecture profoundly until the 18th century, setting a benchmark for balance and order against which later movements like Modernism reacted.
Emergence and Principles of Modernism
Modernism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a reaction against the rigid formulas, ornamentation, and historical references characteristic of Classicism. It prioritized innovation, abstract forms, and the exploration of new materials and technologies to reflect the rapidly changing industrial society. Key principles of Modernism include a focus on function, simplicity, and the rejection of traditional aesthetics in favor of individual expression and experimentation.
Core Philosophies: Order vs. Innovation
Classicism emphasizes order, balance, and harmony rooted in tradition, valuing timeless principles derived from ancient Greek and Roman art and literature. Modernism prioritizes innovation, experimentation, and breaking away from classical conventions to reflect contemporary life and subjective experience. The philosophical divide highlights Classicism's commitment to structured form and Modernism's pursuit of creative freedom and avant-garde expression.
Artistic Expressions: Architecture, Art, and Literature
Classicism in architecture emphasizes symmetry, proportion, and use of classical orders, reflecting harmony and order inspired by ancient Greek and Roman models, while Modernism breaks traditional forms, favoring minimalism, functionalism, and innovative materials like steel and glass. In art, Classicism pursues idealized beauty and balanced compositions with clear narratives, contrasting Modernism's abstract forms, experimentation, and rejection of representational accuracy. Literary expressions in Classicism highlight structured genres, clarity, and moral themes, whereas Modernist literature uses stream of consciousness, fragmented narratives, and explores psychological depth and existentialism.
Influential Figures in Classicism and Modernism
Classicism features influential figures like Johann Sebastian Bach and Michelangelo, whose works emphasize harmony, balance, and adherence to traditional forms. Modernism is defined by pioneers such as Pablo Picasso and Virginia Woolf, who challenged conventional norms with innovative techniques and experimental styles. These figures profoundly shaped their respective movements, reflecting the evolving cultural and artistic landscapes of their eras.
Societal and Cultural Impact
Classicism emphasized harmony, order, and tradition, shaping societies through reinforced cultural norms and hierarchical values that promoted stability and continuity. Modernism challenged these conventions by embracing innovation, individualism, and social progress, leading to transformative shifts in art, architecture, and social thought that questioned established authority and encouraged cultural experimentation. The tension between these movements influenced the evolution of societal identities, fostering debates about modernity, tradition, and the role of culture in shaping collective experiences.
Key Differences in Aesthetic Values
Classicism emphasizes harmony, balance, and adherence to traditional forms inspired by ancient Greece and Rome, valuing symmetry and restrained emotion. Modernism rejects these conventions, embracing experimentation, abstraction, and unconventional techniques to express subjective experiences and innovation. The aesthetic difference lies in Classicism's idealized realism versus Modernism's fragmented, often ambiguous representations.
Enduring Legacy in Contemporary Culture
Classicism's enduring legacy in contemporary culture manifests through its emphasis on harmony, proportion, and restrained aesthetics, influencing architecture, literature, and art that value balance and timeless beauty. Modernism's legacy persists in its celebration of innovation, abstraction, and the rejection of traditional forms, shaping avant-garde movements and contemporary design principles focused on function and experimentation. Both movements continue to inform cultural expressions by providing contrasting yet complementary frameworks that drive artistic and intellectual exploration.
Conclusion: Relevance of Classicism and Modernism Today
Classicism continues to influence contemporary design and architecture through its emphasis on symmetry, proportion, and harmony, providing a timeless aesthetic valued in cultural heritage and education. Modernism's focus on innovation, functionality, and minimalism drives advancements in technology, urban planning, and visual arts, reflecting today's dynamic and fast-paced society. Both movements remain relevant by shaping current creative practices and informing diverse artistic expressions worldwide.
Classicism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com