Integration streamlines processes by combining disparate systems into a unified platform, enhancing efficiency and data accuracy. It enables seamless communication across departments, reducing errors and accelerating workflow. Explore the rest of the article to learn how integration can transform your business operations.
Table of Comparison
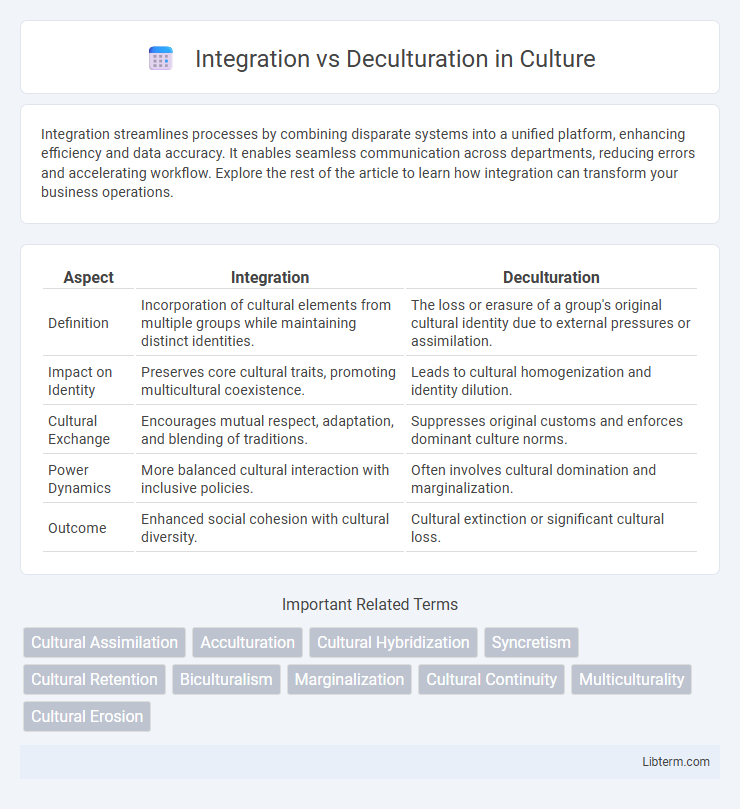
| Aspect | Integration | Deculturation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporation of cultural elements from multiple groups while maintaining distinct identities. | The loss or erasure of a group's original cultural identity due to external pressures or assimilation. |
| Impact on Identity | Preserves core cultural traits, promoting multicultural coexistence. | Leads to cultural homogenization and identity dilution. |
| Cultural Exchange | Encourages mutual respect, adaptation, and blending of traditions. | Suppresses original customs and enforces dominant culture norms. |
| Power Dynamics | More balanced cultural interaction with inclusive policies. | Often involves cultural domination and marginalization. |
| Outcome | Enhanced social cohesion with cultural diversity. | Cultural extinction or significant cultural loss. |
Understanding Integration and Deculturation: Key Definitions
Integration involves individuals maintaining their original cultural identity while adapting to the dominant society, promoting multicultural coexistence and social inclusion. Deculturation refers to the process where individuals lose or abandon their native cultural traits, often leading to cultural assimilation and identity erosion. Understanding these key definitions highlights the distinction between preserving cultural heritage and the complete absorption into a new cultural environment.
Historical Context: How Societies Have Merged or Lost Cultures
Integration in historical contexts often involved societies merging distinct cultural elements to create hybrid identities, exemplified by the Roman Empire's assimilation of conquered peoples while preserving local traditions. Deculturation, conversely, occurred through colonization and forced assimilation, where dominant powers imposed their culture, leading to the erosion or loss of indigenous practices, such as Native American communities during European settlement. These processes are critical in understanding how power dynamics shaped cultural continuity and transformation across global history.
The Psychological Impact of Integration on Individuals
Integration fosters a sense of belonging and identity by allowing individuals to maintain their cultural heritage while adapting to a new environment, promoting psychological well-being. The process reduces feelings of alienation and cultural dissonance, enhancing self-esteem and social connectedness. In contrast, deculturation often leads to identity confusion and emotional distress due to loss of cultural roots and support systems.
Deculturation: Causes and Consequences in Modern Societies
Deculturation occurs when individuals or groups lose their original cultural identity due to external pressures such as globalization, migration, or colonialism, leading to the erosion of traditional customs, languages, and social norms. This phenomenon often results in psychological distress, identity crises, and social fragmentation as individuals struggle to reconcile competing cultural influences. In modern societies, the consequences of deculturation include weakened community cohesion, loss of cultural diversity, and challenges in maintaining intergenerational cultural transmission.
Cultural Identity: Navigating the Spectrum Between Preservation and Change
Integration fosters a dynamic cultural identity by blending traditions with new influences, promoting adaptation without complete loss of heritage. Deculturation involves the erosion of original cultural traits as dominant norms overshadow minority practices, often leading to identity fragmentation. Balancing preservation and change is crucial for sustaining cultural integrity while embracing social evolution.
The Role of Education in Promoting Integration without Deculturation
Education plays a critical role in fostering integration by promoting cultural awareness and mutual respect without compromising individual cultural identities. Curricula that include multicultural content and language preservation help students appreciate diversity while maintaining their heritage. Schools serve as inclusive spaces where students from different backgrounds collaborate, reinforcing social cohesion and reducing the risk of deculturation.
Social Policy Approaches: Balancing Multiculturalism and Assimilation
Social policy approaches to integration versus deculturation grapple with balancing multiculturalism's recognition of diverse cultural identities and assimilation's emphasis on uniform societal norms. Effective strategies prioritize inclusive policies that support cultural expression while promoting social cohesion and equal access to resources. This balance helps prevent marginalization, fostering a cohesive society where diverse backgrounds coexist within a shared framework of rights and responsibilities.
Integration Success Stories: Models from Around the World
Integration success stories highlight effective models from countries such as Canada, Germany, and Sweden, where inclusive policies and community engagement foster social cohesion. Canada's multiculturalism approach emphasizes language acquisition, employment support, and cultural recognition, resulting in higher immigrant retention and economic contribution. Germany's vocational training programs and Sweden's expansive social welfare systems serve as replicable frameworks for empowering newcomers and promoting equitable integration outcomes.
Managing Cultural Conflict: Strategies to Prevent Deculturation
Effective management of cultural conflict involves strategies that prioritize integration over deculturation by fostering mutual respect and understanding among diverse groups. Emphasizing cultural competence training, open communication, and inclusive policies enables organizations to preserve distinct cultural identities while promoting collaboration. Implementing these approaches reduces the risk of cultural erosion and supports a harmonious multicultural environment.
Future Trends: Preserving Heritage in a Globalized World
Future trends in integration versus deculturation emphasize balancing cultural preservation with global interconnectedness, focusing on policies that support multicultural education and heritage conservation. Technological advancements enable digital archiving and virtual cultural exchanges, enhancing awareness and appreciation of diverse traditions while fostering global dialogue. Efforts prioritize inclusive cultural representation to combat homogenization, ensuring that marginalized communities maintain their unique identities within increasingly globalized societies.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com