Social practices shape how communities interact, establish norms, and transmit cultural values across generations. These behaviors influence everything from communication styles to conflict resolution and collective decision-making. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your participation in social practices impacts society and personal relationships.
Table of Comparison
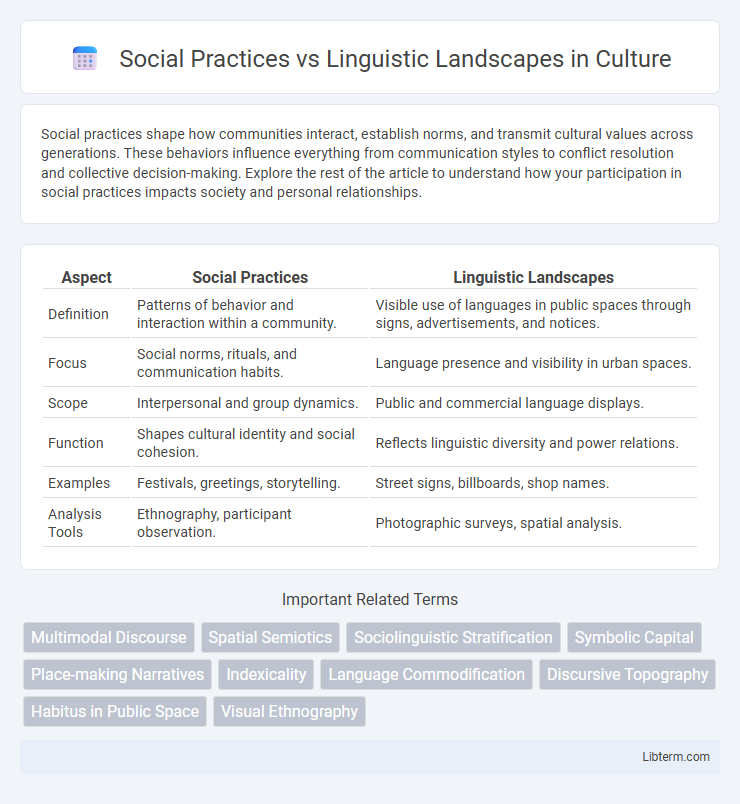
| Aspect | Social Practices | Linguistic Landscapes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Patterns of behavior and interaction within a community. | Visible use of languages in public spaces through signs, advertisements, and notices. |
| Focus | Social norms, rituals, and communication habits. | Language presence and visibility in urban spaces. |
| Scope | Interpersonal and group dynamics. | Public and commercial language displays. |
| Function | Shapes cultural identity and social cohesion. | Reflects linguistic diversity and power relations. |
| Examples | Festivals, greetings, storytelling. | Street signs, billboards, shop names. |
| Analysis Tools | Ethnography, participant observation. | Photographic surveys, spatial analysis. |
Understanding Social Practices in Society
Social practices shape daily interactions, cultural norms, and identity formation within society by influencing how language is used and perceived. These practices provide context for interpreting linguistic landscapes, which consist of visible language displays in public spaces reflecting power dynamics and social relationships. Understanding social practices enables deeper insight into the meanings, functions, and implications of multilingual signs, advertisements, and public texts in diverse communities.
Defining Linguistic Landscapes
Linguistic landscapes refer to the visible display of language on public and commercial signs in a specific geographic area, reflecting the sociolinguistic environment and the presence of various languages. This concept captures the interplay between language use, identity, and power, revealing how languages coexist, compete, or dominate within urban or rural spaces. Analyzing linguistic landscapes provides valuable insights into social practices by illustrating language attitudes, policies, and community dynamics embedded in everyday public communication.
The Intersection of Language and Social Behavior
The intersection of language and social behavior reveals that social practices shape and are shaped by linguistic landscapes, which serve as visible markers of cultural identity and power dynamics in public spaces. Linguistic landscapes, encompassing multilingual signs and public texts, reflect ongoing social interactions and highlight the societal norms governing language use. Studying this intersection uncovers how language policies and community practices influence communication patterns and social inclusion within diverse urban environments.
Public Spaces as Sites of Social Interaction
Public spaces serve as dynamic sites of social interaction where social practices shape and are shaped by linguistic landscapes, reflecting community identities and power relations. The presence of multilingual signage, graffiti, and digital displays in these areas exemplifies how language use negotiates social inclusion and exclusion. Analysis of linguistic landscapes in public spaces reveals the interdependence between language visibility and everyday social behavior.
Visual Language: Signs, Symbols, and Meaning
Visual language within linguistic landscapes is a dynamic interplay of signs and symbols that convey social meanings embedded in cultural contexts. These visual elements function as communicative tools reflecting social practices, revealing power relations, identity expressions, and community values through their placement, style, and frequency. Understanding the semiotics of signs and symbols enables deeper insight into how public spaces become sites of social negotiation and cultural representation.
Social Identity and Language Use in Public Domains
Social practices in public domains shape and are shaped by linguistic landscapes, reflecting the dynamic interplay between social identity and language use. Language choices in public signage, advertisements, and graffiti serve as markers of group identity, power relations, and community belonging within specific social contexts. Examining these linguistic landscapes reveals how marginalized or dominant groups assert their presence and negotiate social inclusion through visible language strategies.
Power Dynamics Reflected in Linguistic Landscapes
Linguistic landscapes serve as visible representations of power dynamics within social practices, showcasing which languages are privileged or marginalized in public spaces. Dominant groups often inscribe their language in signage, advertising, and official texts, reinforcing socio-political hierarchies and influencing identity construction. These landscapes reveal underlying struggles over linguistic legitimacy and cultural authority, reflecting broader societal inequalities.
Multilingualism in Urban Environments
Multilingualism in urban environments shapes both social practices and linguistic landscapes by reflecting diverse language use in public spaces such as signage, advertisements, and street art. Social practices involve the dynamic interaction and communication patterns among multilingual communities, influencing language choice and language visibility in everyday urban life. Linguistic landscapes serve as a visual representation of these multilingual interactions, showcasing the coexistence and competition of languages that mirror the city's cultural and social diversity.
Shaping Community Narratives through Language Displays
Social practices shape community narratives by embedding cultural values and collective identities within linguistic landscapes, where language displays such as signs, graffiti, and public texts visually articulate local histories and power dynamics. These linguistic markers serve as tangible reflections of social interactions and ideological frameworks, influencing how community members perceive and engage with their environment. Consequently, the interplay between social practices and linguistic landscapes fosters a dynamic space for negotiating belonging, memory, and social change.
Future Implications for Social Practices and Linguistic Landscapes
The future implications for social practices and linguistic landscapes involve the dynamic interplay between digital communication technologies and language use in public spaces. Emerging trends indicate that augmented reality and geotagging will transform linguistic landscapes into interactive, data-rich environments, reshaping how communities engage with languages and cultural identities. These shifts will influence social practices by promoting multilingualism and altering power relations embedded in language visibility and accessibility.
Social Practices Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com