Oral tradition preserves cultural stories, history, and knowledge through spoken word, enabling generations to share wisdom without written texts. This method fosters a strong community bond and ensures the survival of heritage across time. Explore the rest of the article to discover how oral tradition shapes societies and enriches your understanding of human connection.
Table of Comparison
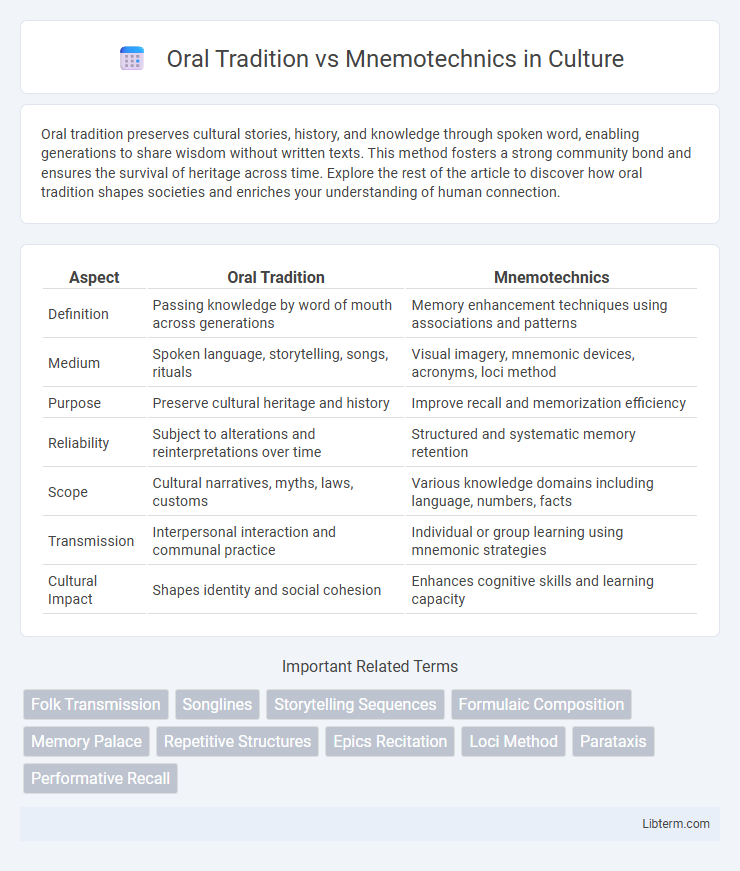
| Aspect | Oral Tradition | Mnemotechnics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passing knowledge by word of mouth across generations | Memory enhancement techniques using associations and patterns |
| Medium | Spoken language, storytelling, songs, rituals | Visual imagery, mnemonic devices, acronyms, loci method |
| Purpose | Preserve cultural heritage and history | Improve recall and memorization efficiency |
| Reliability | Subject to alterations and reinterpretations over time | Structured and systematic memory retention |
| Scope | Cultural narratives, myths, laws, customs | Various knowledge domains including language, numbers, facts |
| Transmission | Interpersonal interaction and communal practice | Individual or group learning using mnemonic strategies |
| Cultural Impact | Shapes identity and social cohesion | Enhances cognitive skills and learning capacity |
Introduction to Oral Tradition and Mnemotechnics
Oral tradition refers to the method of preserving and transmitting knowledge, stories, and cultural practices through spoken word across generations, often relying on repetition and communal participation. Mnemotechnics, or mnemonic techniques, are structured strategies designed to enhance memory retention and recall, using patterns such as visualization, association, and rhythmic patterns. Both oral tradition and mnemotechnics serve as vital tools in cultures lacking written records, enabling the preservation and accurate transmission of information.
Defining Oral Tradition: Ancestral Knowledge Transfer
Oral tradition involves the transmission of ancestral knowledge, stories, customs, and cultural values through spoken word across generations, preserving collective memory without reliance on written records. This method relies on memory, communal participation, and mnemonic structures such as repetition and narrative patterns to ensure accuracy and continuity. Oral traditions serve as foundational frameworks for identity and historical understanding within Indigenous and non-literate societies worldwide.
Understanding Mnemotechnics: The Science of Memory Aids
Mnemotechnics, the science of memory aids, employs systematic techniques such as visualization, association, and structured patterns to enhance recall and retention of information. Unlike oral tradition, which relies on repetitive storytelling and communal reinforcement to transmit knowledge, mnemotechnics utilizes cognitive principles to create long-lasting mental cues. These methods improve memory efficiency by leveraging the brain's natural ability to connect new information with familiar concepts and sensory imagery.
Historical Context: Evolution of Knowledge Preservation
Oral tradition served as the primary method for preserving and transmitting knowledge across generations in early societies, relying on storytelling, song, and ritual to maintain cultural history and collective memory. Mnemotechnics emerged as a deliberate cognitive technique during the classical era, employing structured memory aids such as loci and visual imagery to enhance recall accuracy and intellectual organization. The evolution from oral tradition to mnemotechnics reflects a shift from communal, narrative-based knowledge preservation toward systematic, individual cognitive strategies optimized for educational and philosophical advancement.
Techniques and Methods: Storytelling vs. Memory Devices
Oral tradition relies on storytelling techniques such as repetition, rhyme, and narrative structure to transmit cultural knowledge across generations, enhancing recall through vivid imagery and emotional engagement. In contrast, mnemotechnics employs systematic memory devices like acronyms, visualization, and the method of loci to encode and retrieve information efficiently. Both methods optimize memory retention but differ in approach: storytelling leverages natural human connection and context, while mnemotechnics uses structured cognitive strategies for precise recall.
Accuracy and Reliability: Comparing Preservation Methods
Oral tradition relies on human memory and communal repetition, often leading to variations but maintaining cultural narratives through generations. Mnemotechnics employs structured techniques like mnemonic devices to enhance memory precision, significantly improving accuracy and reliability in information retention. Studies show that mnemotechnics outperforms pure oral transmission by reducing errors and standardizing recall processes.
Cultural Impact: Shaping Societies Through Memory
Oral tradition has profoundly shaped societies by transmitting cultural values, histories, and social norms through generations, embedding collective identity within community narratives. Mnemotechnics enhances individual and group memory capabilities, allowing complex information to be preserved and accessed with precision, thereby supporting the continuity of knowledge beyond verbal storytelling. Both methods have played crucial roles in maintaining cultural cohesion, influencing educational systems, and reinforcing social structures across diverse civilizations.
Strengths and Limitations of Oral Traditions
Oral traditions excel in preserving cultural identity and communal knowledge through storytelling, songs, and rituals, enabling intergenerational transmission without written records. Their strengths include adaptability, emotional engagement, and accessibility for illiterate populations, while limitations involve vulnerability to memory distortion, loss over time, and challenges in preserving precise details. The reliance on human recall makes oral traditions susceptible to alterations, contrasting with mnemotechnics that use structured memory aids to enhance accuracy and retention.
Modern Applications of Mnemotechnics
Modern applications of mnemotechnics include enhanced learning techniques in education, memory improvement tools for professionals, and cognitive therapies for memory impairments. Digital platforms and apps utilize mnemonic strategies such as spaced repetition and visualization to optimize information retention and recall. These methods surpass traditional oral traditions by integrating neuroscience principles and technology for efficient, scalable memory training.
The Future of Memory: Integration and Innovation
The future of memory lies in the integration of oral tradition's narrative richness with the precision of mnemotechnics, fostering innovative cognitive tools that enhance information retention. Advances in digital technology and neuroscience enable the development of hybrid memory systems, combining storytelling techniques with mnemonic devices to support learning and cultural preservation. This synergy promises to revolutionize educational methods and memory enhancement strategies, blending time-honored practices with cutting-edge innovations.
Oral Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com