Popular culture shapes everyday life through music, movies, fashion, and social media trends that reflect and influence societal values and identities. Understanding these phenomena helps you navigate the dynamic landscape of modern entertainment and communication. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how popular culture impacts your world.
Table of Comparison
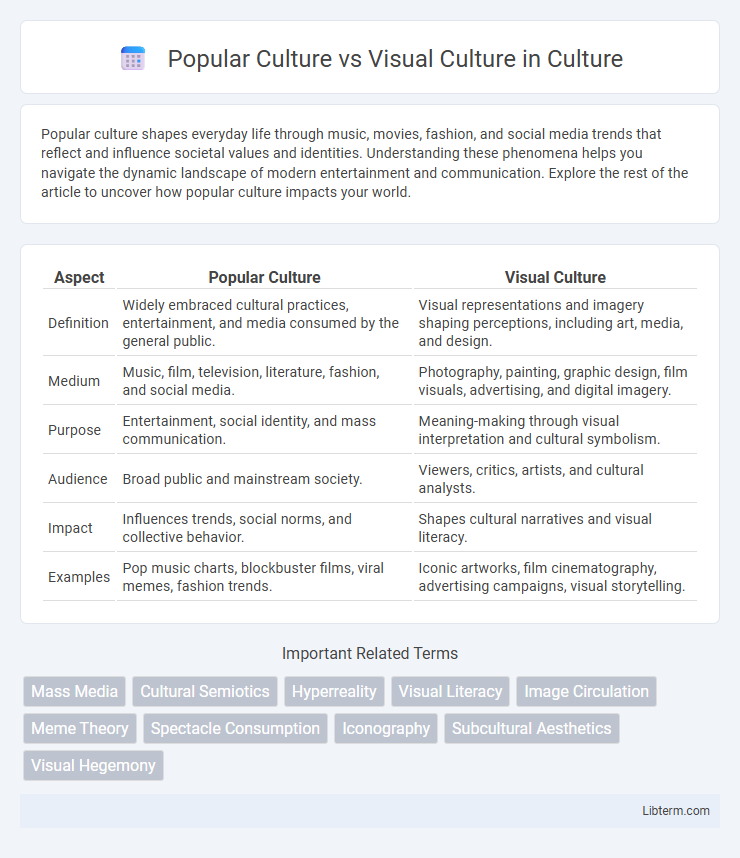
| Aspect | Popular Culture | Visual Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Widely embraced cultural practices, entertainment, and media consumed by the general public. | Visual representations and imagery shaping perceptions, including art, media, and design. |
| Medium | Music, film, television, literature, fashion, and social media. | Photography, painting, graphic design, film visuals, advertising, and digital imagery. |
| Purpose | Entertainment, social identity, and mass communication. | Meaning-making through visual interpretation and cultural symbolism. |
| Audience | Broad public and mainstream society. | Viewers, critics, artists, and cultural analysts. |
| Impact | Influences trends, social norms, and collective behavior. | Shapes cultural narratives and visual literacy. |
| Examples | Pop music charts, blockbuster films, viral memes, fashion trends. | Iconic artworks, film cinematography, advertising campaigns, visual storytelling. |
Defining Popular Culture and Visual Culture
Popular culture encompasses the everyday practices, beliefs, and objects that are widely accepted and disseminated within a society, including music, film, fashion, and social media trends that reflect mass consumption and shared values. Visual culture refers to the study and analysis of visual images and artifacts such as art, photography, advertisements, and digital media, emphasizing how these visual elements communicate meaning and influence perception. Both fields explore societal norms and identity, but popular culture focuses on widespread cultural expressions while visual culture centers on the interpretation and impact of visual representation.
Historical Evolution of Popular and Visual Culture
Popular culture emerged from oral traditions, mass media, and consumerism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, reflecting societal shifts and technological advancements. Visual culture, encompassing art, imagery, and digital media, evolved from early cave paintings to Renaissance art and gained prominence with photography, film, and digital technology. Both cultures have influenced each other, reshaping perceptions and social narratives throughout history.
Key Theoretical Frameworks
Popular culture encompasses everyday practices and media consumed by large audiences, analyzed through frameworks like cultural studies and critical theory emphasizing ideology, identity, and power relations. Visual culture focuses on images and visual media, employing theories from semiotics, visual rhetoric, and media archaeology to decode meaning, representation, and spectatorship. Both frameworks intersect in exploring how visual artifacts shape social narratives and negotiate cultural identities.
The Interplay Between Mass Media and Visual Representation
The interplay between mass media and visual representation shapes popular culture by disseminating images that influence societal norms and identities. Visual culture relies on mass media platforms such as television, social media, and advertising to circulate iconic symbols, celebrity imagery, and visual narratives that reflect and construct cultural values. This dynamic interaction amplifies the cultural resonance of visual content, making it a critical force in shaping public perception and collective memory.
Iconic Symbols: From Pop Art to Digital Memes
Iconic symbols in popular culture, such as Andy Warhol's Campbell's Soup Cans, have evolved into visual culture's digital memes, serving as rapid, widespread vehicles for social commentary and identity expression. Pop art's bold, accessible imagery laid the groundwork for meme culture's emphasis on replication and remixing, transforming static symbols into dynamic, participatory phenomena. The transition from printed icons to digital symbols illustrates the shift in cultural consumption from passive observation to active engagement within global networks.
Globalization’s Impact on Popular and Visual Culture
Globalization accelerates the exchange and hybridization of popular culture, spreading music, fashion, and entertainment across borders, while simultaneously reshaping visual culture through diverse aesthetic influences and digital media. The widespread accessibility of global platforms like social media enhances visual culture's dynamism by enabling instant sharing and consumption of images, videos, and art from around the world. This interconnectedness fosters cross-cultural dialogues, transforming both popular and visual culture into fluid, ever-evolving phenomena shaped by global networks and localized interpretations.
Subcultures and Identity Formation
Subcultures play a crucial role in popular culture by fostering unique identities and community belonging, often expressed through music, fashion, and language. Visual culture enhances this identity formation by providing symbols, imagery, and media representations that subcultures adopt and adapt to communicate their distinct values and narratives. The intersection of popular culture and visual culture shapes how individuals negotiate self-expression and group affiliation in a media-saturated society.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Visual Narratives
Technology profoundly impacts visual narratives by enabling innovative forms of storytelling through digital media, virtual reality, and augmented reality. Visual culture leverages advancements like high-resolution imaging and interactive platforms to create immersive experiences that reshape audience engagement. In popular culture, technology accelerates the dissemination and remixing of visual content, fostering dynamic, participatory narratives across global digital networks.
Critiques: Commercialization and Cultural Authenticity
Critiques of popular culture often center on commercialization, where mass media and corporate interests shape content, diluting cultural authenticity for profit-driven motives. Visual culture faces similar challenges, as visual media increasingly prioritize marketable aesthetics over genuine cultural expressions, raising concerns about commodification. Both fields debate the tension between preserving authentic cultural identities and navigating pervasive commercial influences in shaping public perception.
Future Trends and Emerging Paradigms
Future trends in popular culture emphasize the integration of immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), reshaping how audiences engage with entertainment and social narratives. Visual culture is increasingly driven by AI-generated content and data visualization, fostering new paradigms that blur the line between art, information, and digital experience. Emerging paradigms highlight the convergence of interactive storytelling and personalized media, transforming cultural consumption into dynamic, participatory experiences shaped by real-time user input and algorithmic influence.
Popular Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com