Nonmaterial culture encompasses the intangible aspects of a society, including beliefs, values, customs, traditions, language, and norms that shape how people interact and understand their world. These cultural elements influence your perceptions, behaviors, and social interactions more profoundly than physical objects. Explore the rest of the article to gain deeper insight into how nonmaterial culture shapes human experience and social identity.
Table of Comparison
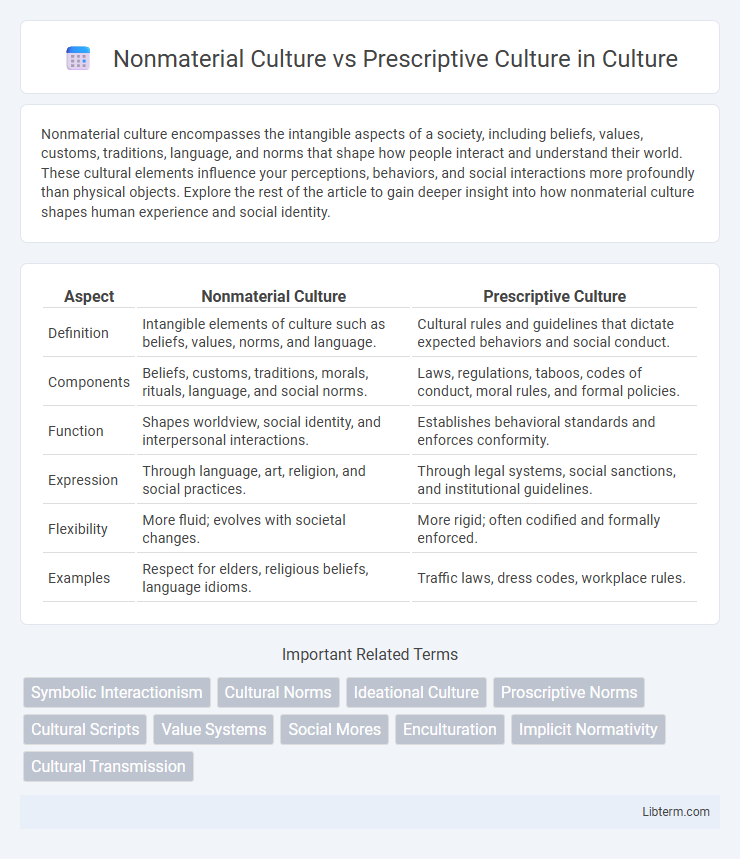
| Aspect | Nonmaterial Culture | Prescriptive Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intangible elements of culture such as beliefs, values, norms, and language. | Cultural rules and guidelines that dictate expected behaviors and social conduct. |
| Components | Beliefs, customs, traditions, morals, rituals, language, and social norms. | Laws, regulations, taboos, codes of conduct, moral rules, and formal policies. |
| Function | Shapes worldview, social identity, and interpersonal interactions. | Establishes behavioral standards and enforces conformity. |
| Expression | Through language, art, religion, and social practices. | Through legal systems, social sanctions, and institutional guidelines. |
| Flexibility | More fluid; evolves with societal changes. | More rigid; often codified and formally enforced. |
| Examples | Respect for elders, religious beliefs, language idioms. | Traffic laws, dress codes, workplace rules. |
Understanding Nonmaterial Culture: Key Concepts
Nonmaterial culture encompasses intangible elements such as beliefs, values, norms, language, and customs that shape social behavior and collective identity. Understanding nonmaterial culture involves recognizing its role in guiding social interactions, influencing perceptions, and transmitting traditions across generations. Prescriptive culture, as a subset, emphasizes norms and rules that dictate acceptable behavior, reinforcing societal order within the broader framework of nonmaterial culture.
Defining Prescriptive Culture in Society
Prescriptive culture in society consists of the explicit norms, rules, and laws that govern behavior and outline accepted practices within a community. It prescribes what actions individuals should or should not perform, establishing clear guidelines for social conduct and order. Unlike nonmaterial culture, which encompasses intangible beliefs, values, and traditions, prescriptive culture directly dictates specific behaviors through formalized codes and regulations.
Core Differences Between Nonmaterial and Prescriptive Culture
Nonmaterial culture encompasses intangible elements such as beliefs, values, norms, and language that shape societal behaviors and worldviews, while prescriptive culture specifically consists of explicit rules and guidelines dictating expected conduct. The core difference lies in nonmaterial culture's broad influence on general social attitudes versus prescriptive culture's focus on formalized mandates and instructions governing social interactions. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify how cultural norms evolve from abstract concepts to concrete behavioral prescriptions within societies.
Examples of Nonmaterial Culture in Everyday Life
Nonmaterial culture encompasses intangible elements such as beliefs, values, norms, language, and customs that shape everyday life, like religious rituals, social etiquette, and spoken language patterns. For instance, greeting customs vary across societies, with phrases like "Hello" in English-speaking countries or bowing in Japan exemplifying nonmaterial culture. Prescriptive culture, in contrast, refers to codified rules or laws dictating behavior, such as legal systems or institutional regulations, emphasizing formalized societal expectations.
The Role of Prescriptive Culture in Shaping Behavior
Prescriptive culture plays a crucial role in shaping behavior by establishing norms, rules, and expectations that guide individuals' actions within a society. Unlike nonmaterial culture, which encompasses beliefs, values, and customs, prescriptive culture provides explicit directives that influence social conduct and decision-making processes. These culturally embedded prescriptions ensure conformity, social order, and predictability in interpersonal interactions and communal life.
Interaction Between Nonmaterial and Prescriptive Cultural Elements
Nonmaterial culture, encompassing beliefs, values, and norms, interacts closely with prescriptive culture, which includes explicit rules and laws guiding behavior in society. This interaction shapes social order by embedding nonmaterial cultural meanings into formal prescriptions, ensuring that regulations reflect deeply held societal values. The dynamic influence between these elements sustains cultural coherence and adaptability amidst social change.
Influence of Nonmaterial Culture on Social Values
Nonmaterial culture, encompassing beliefs, norms, and values, profoundly shapes social values by guiding behavior and establishing shared expectations within society. It influences prescriptive culture by providing the underlying ethical principles that dictate appropriate actions and social prescriptions. This dynamic interaction ensures that social norms evolve in alignment with collective ideals embedded in nonmaterial cultural frameworks.
Prescriptive Culture: Enforcing Norms and Expectations
Prescriptive culture involves enforcing norms and expectations that guide acceptable behavior within a society, ensuring social order and cohesion. These norms are often codified into laws, rules, or formal guidelines that prescribe specific actions, reinforcing conformity and compliance among members. Unlike nonmaterial culture, which encompasses intangible aspects like beliefs and values, prescriptive culture actively shapes behavior through explicit mandates and sanctions.
Challenges in Distinguishing Nonmaterial and Prescriptive Culture
Distinguishing nonmaterial culture, which encompasses intangible elements like beliefs, values, and norms, from prescriptive culture, defined by explicit rules and regulations, presents challenges due to their overlapping influences on behavior. Nonmaterial culture shapes underlying societal attitudes, while prescriptive culture formalizes expected conduct through codified directives, making clear demarcation difficult in practical contexts. The fluidity and interpretation of cultural norms further complicate differentiating implicit cultural beliefs from explicit prescriptive mandates.
The Impact of Culture Types on Modern Society
Nonmaterial culture, encompassing beliefs, values, and norms, shapes social behavior and collective identity in modern society by influencing moral frameworks and communication patterns. Prescriptive culture involves explicit rules and laws, guiding societal order and legal systems critical for governance and institutional functionality. The interaction between these culture types fosters social cohesion while enabling adaptability and innovation in diverse cultural environments.
Nonmaterial Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com