Multiculturalism embraces the coexistence of diverse cultures, fostering mutual respect and understanding within societies. It enriches communities by promoting cultural exchange, inclusion, and social cohesion. Discover how multiculturalism shapes your world and the benefits it can bring by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
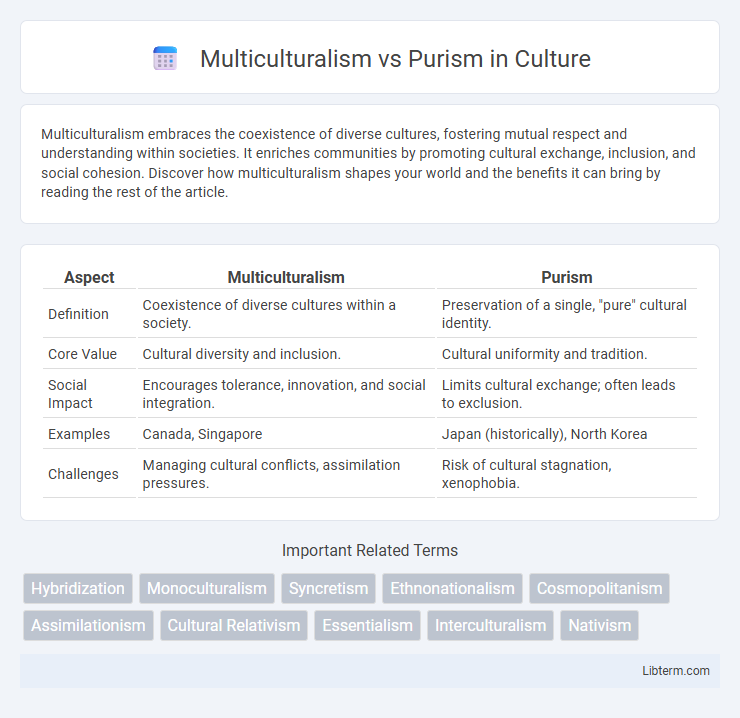
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Purism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures within a society. | Preservation of a single, "pure" cultural identity. |
| Core Value | Cultural diversity and inclusion. | Cultural uniformity and tradition. |
| Social Impact | Encourages tolerance, innovation, and social integration. | Limits cultural exchange; often leads to exclusion. |
| Examples | Canada, Singapore | Japan (historically), North Korea |
| Challenges | Managing cultural conflicts, assimilation pressures. | Risk of cultural stagnation, xenophobia. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Definition and Principles
Multiculturalism is a social and political philosophy promoting the recognition and celebration of diverse cultural identities within a unified society. It emphasizes principles such as cultural pluralism, mutual respect, and equal opportunities for all ethnic and cultural groups. Understanding multiculturalism involves acknowledging the coexistence of multiple cultural traditions and fostering inclusivity without requiring assimilation into a dominant cultural norm.
Purism Explained: Roots and Key Concepts
Purism, rooted in linguistic and cultural preservation, emphasizes maintaining the authenticity and original form of a language or tradition by resisting external influences and changes. Its key concepts include protecting heritage languages from foreign borrowings, promoting standardized norms, and fostering a unified cultural identity. Purism often arises as a reaction to globalization and multiculturalism, aiming to safeguard cultural purity and historical continuity.
Historical Contexts: The Emergence of Both Ideologies
Multiculturalism emerged in the mid-20th century as a response to globalization and increased migration, promoting cultural diversity and coexistence within societies. Purism, rooted in earlier nationalist movements of the 19th century, emphasizes cultural homogeneity and the preservation of a singular cultural identity. Historical contexts reflect how post-colonial shifts and civil rights movements fueled multiculturalism, while purism often arose during periods of nation-building and ethnic consolidation.
Cultural Integration vs Cultural Preservation
Cultural integration promotes the blending of diverse traditions and values, fostering social cohesion and mutual understanding within multicultural societies. Purism emphasizes preserving distinct cultural identities and heritage, safeguarding historical customs and languages from dilution. Balancing integration and preservation challenges policymakers to create inclusive environments that respect diversity while maintaining cultural uniqueness.
The Social Impact of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism fosters social cohesion by promoting inclusivity, mutual respect, and cultural exchange among diverse communities, leading to enhanced social harmony and innovation. Embracing multiculturalism reduces racial and ethnic tensions, supports minority rights, and encourages equitable participation in society. In contrast, purism often leads to social fragmentation, exclusion, and cultural homogeneity, which can hinder diversity-driven economic growth and social resilience.
Purism’s Influence on Identity and Society
Purism emphasizes maintaining cultural or linguistic purity, shaping identity by reinforcing traditional values and resisting external influences. This approach often fosters a strong collective identity but can lead to social fragmentation and exclusion of diverse groups. Societies influenced by purism may experience limited cultural exchange and reduced social cohesion in an increasingly globalized world.
Case Studies: Multiculturalism Around the World
Case studies of multiculturalism around the world reveal diverse approaches to managing cultural diversity, such as Canada's official multicultural policy promoting inclusion and the UK's emphasis on multicultural citizenship rights. In contrast, purism-focused nations like France prioritize cultural assimilation and the preservation of a singular national identity through policies like laicite. These contrasting models illustrate the balance between fostering cultural pluralism and maintaining national cohesion in varying sociopolitical contexts.
The Challenges of Navigating Cultural Differences
Navigating cultural differences in multiculturalism involves addressing language barriers, conflicting values, and varying social norms that influence communication and collaboration. Purism aims to maintain cultural homogeneity, often leading to resistance against hybrid identities and practices, which can create tension and exclusion. Effective management of these challenges requires fostering cultural competence, empathy, and inclusive policies that respect diversity while recognizing shared goals.
The Debate: Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Multiculturalism promotes diversity and inclusion by valuing multiple cultural identities, which enhances social cohesion and fosters innovation through varied perspectives. Purism emphasizes preserving a singular cultural heritage, ensuring tradition continuity and stability but may limit exposure to diverse ideas, potentially leading to social fragmentation. The debate centers on balancing cultural preservation with the enrichment that inter-cultural exchange brings to societies.
Towards a Balanced Future: Reconciling Multiculturalism and Purism
Multiculturalism fosters diversity and inclusion by embracing multiple cultural identities, while purism emphasizes preserving cultural homogeneity and traditions. Effective reconciliation involves promoting intercultural dialogue and adaptive policies that respect heritage without inhibiting social cohesion. Balanced approaches integrate cultural preservation with openness, enhancing societal resilience in a globalized world.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com