Cross-sectional studies analyze data from a population at a specific point in time, offering valuable insights into prevalence and correlations without requiring long follow-up periods. This research design is efficient for identifying patterns and generating hypotheses about associations between variables. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cross-sectional studies can enhance Your research approach and interpret findings effectively.
Table of Comparison
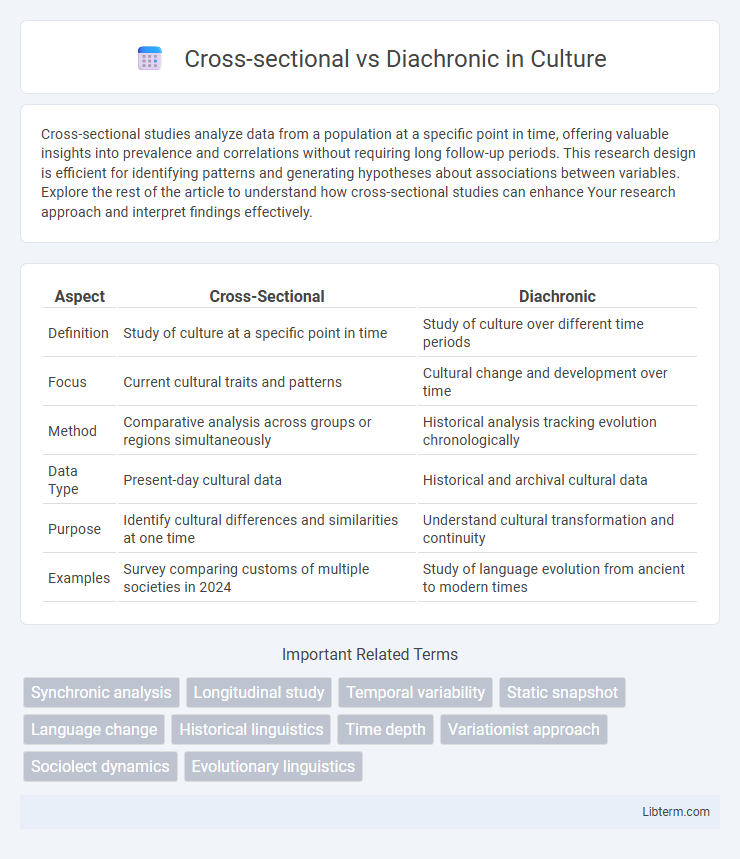
| Aspect | Cross-Sectional | Diachronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of culture at a specific point in time | Study of culture over different time periods |
| Focus | Current cultural traits and patterns | Cultural change and development over time |
| Method | Comparative analysis across groups or regions simultaneously | Historical analysis tracking evolution chronologically |
| Data Type | Present-day cultural data | Historical and archival cultural data |
| Purpose | Identify cultural differences and similarities at one time | Understand cultural transformation and continuity |
| Examples | Survey comparing customs of multiple societies in 2024 | Study of language evolution from ancient to modern times |
Introduction to Cross-sectional and Diachronic Approaches
Cross-sectional and diachronic approaches analyze data from distinct temporal perspectives, with cross-sectional studies examining a specific point in time to capture a snapshot of phenomena, and diachronic studies exploring changes and developments across different periods. Cross-sectional methods are often used in sociolinguistics and psychology to identify patterns and correlations at a particular moment, whereas diachronic approaches trace language evolution, cultural shifts, or historical trends over decades or centuries. Understanding the differences between these approaches helps researchers select appropriate methodologies for studying temporal dynamics in fields such as linguistics, anthropology, and history.
Defining Cross-sectional Analysis
Cross-sectional analysis examines data from multiple subjects or entities at a single point in time, allowing comparisons across different groups or variables. This method is crucial for identifying patterns, correlations, or differences without considering temporal changes. Unlike diachronic analysis, which studies phenomena over time, cross-sectional analysis provides a snapshot that informs assessments of current states or conditions.
Understanding Diachronic Study
Diachronic study examines the evolution of language, culture, or phenomena over time, revealing patterns and changes that cross-sectional approaches cannot capture. By analyzing data from different historical periods, diachronic research uncovers the dynamics and causes behind linguistic shifts or societal transformations. This temporal perspective is essential for understanding development processes and contextualizing current states within their historical trajectories.
Key Differences Between Cross-sectional and Diachronic Methods
Cross-sectional methods analyze data from a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of variables and their relationships, while diachronic methods study data across different time periods to observe changes and trends. Cross-sectional research is ideal for identifying associations and differences among subjects simultaneously, whereas diachronic research excels in examining temporal dynamics and causal developments. Understanding the distinction facilitates selecting appropriate methodologies for studies in linguistics, sociology, and historical analysis.
Advantages of Cross-sectional Analysis
Cross-sectional analysis offers significant advantages by enabling researchers to collect and analyze data from multiple subjects or groups at a single point in time, providing a snapshot that facilitates quick comparison and trend identification. This method is cost-effective and time-efficient compared to diachronic analysis, making it suitable for studies requiring immediate insights or large sample sizes across diverse populations. Cross-sectional studies are particularly advantageous for examining prevalence rates and correlations, supporting robust statistical analysis without the need for prolonged data collection periods.
Benefits of Diachronic Research
Diachronic research offers the benefit of tracking changes and developments over extended periods, providing insights into historical trends and long-term processes that cross-sectional studies cannot capture. This approach enables the analysis of language evolution, cultural shifts, or social transformations by examining data from different time points. Researchers gain a deeper understanding of causality and the dynamics of change through diachronic data, facilitating more accurate predictions and contextual explanations.
Applications in Linguistics
Cross-sectional linguistics analyzes language data from multiple speakers or texts at a single point in time to study variation and synchronic language structure, essential for dialectology and sociolinguistics. Diachronic linguistics examines language evolution and change over time, crucial for historical linguistics and etymological research. Both approaches complement each other by providing insights on language stability and transformation across temporal and social dimensions.
Applications in Social Sciences
Cross-sectional studies in social sciences analyze data from a specific point in time, enabling researchers to identify patterns and correlations among variables across different groups. Diachronic research examines changes over time, providing insights into social trends, cultural shifts, and long-term phenomena. These approaches complement each other by offering snapshots versus trajectories, crucial for understanding social dynamics, policy impacts, and historical development.
Challenges and Limitations
Cross-sectional studies face challenges in capturing temporal dynamics, potentially missing changes over time and causal relationships. Diachronic analysis is limited by data availability and consistency across different time periods, complicating longitudinal comparison and trend accuracy. Both approaches struggle with controlling extraneous variables, which can affect the reliability and validity of findings in linguistic and social research.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Research
Selecting the appropriate research method hinges on the objectives and timeframe of your study, with cross-sectional analysis offering a snapshot of data at a single point, ideal for comparing different groups simultaneously. Diachronic research examines changes over time, providing insights into trends, developments, or causal relationships within longitudinal studies. Researchers must assess their focus on either temporal dynamics or static comparisons to effectively align methodology with data collection and analysis goals.
Cross-sectional Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com