Effective written communication enhances clarity, fosters stronger relationships, and ensures your message is accurately understood across diverse audiences. Mastering this skill is essential for professional success, as it influences collaboration and decision-making. Discover strategies to refine your written communication and elevate your impact by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
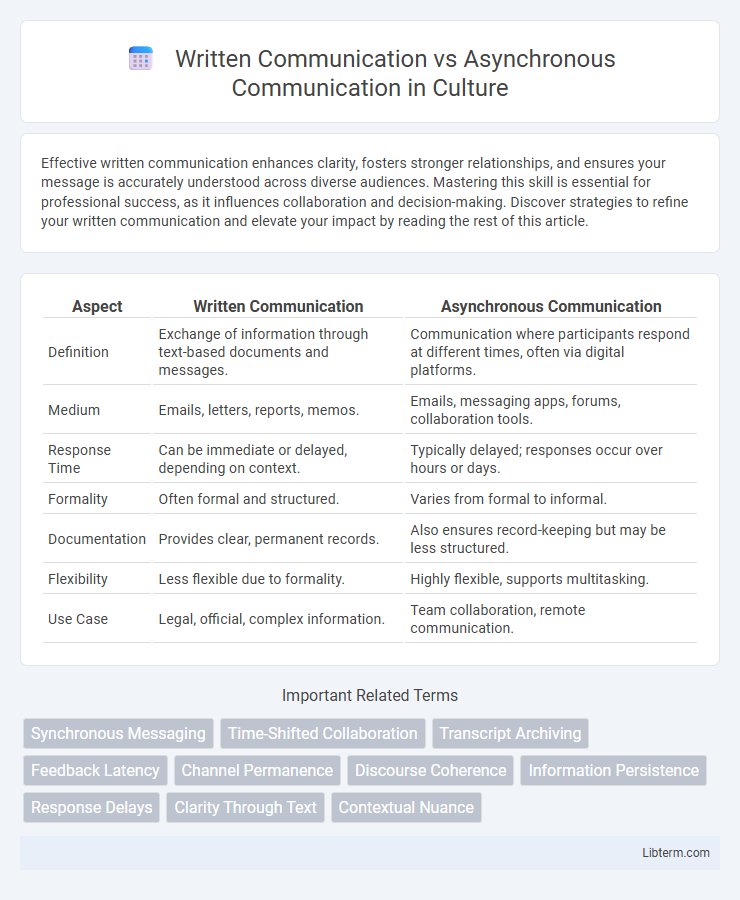
| Aspect | Written Communication | Asynchronous Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of information through text-based documents and messages. | Communication where participants respond at different times, often via digital platforms. |
| Medium | Emails, letters, reports, memos. | Emails, messaging apps, forums, collaboration tools. |
| Response Time | Can be immediate or delayed, depending on context. | Typically delayed; responses occur over hours or days. |
| Formality | Often formal and structured. | Varies from formal to informal. |
| Documentation | Provides clear, permanent records. | Also ensures record-keeping but may be less structured. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to formality. | Highly flexible, supports multitasking. |
| Use Case | Legal, official, complex information. | Team collaboration, remote communication. |
Introduction to Written and Asynchronous Communication
Written communication encompasses the exchange of information through text, including emails, reports, and memos, which provides a clear, documented record ideal for precise and formal interactions. Asynchronous communication allows participants to engage at different times without the need for simultaneous presence, commonly using platforms like email, messaging apps, and collaborative tools to enhance flexibility and reduce scheduling conflicts. Both methods support effective information sharing, with written communication emphasizing clarity and permanence, while asynchronous communication prioritizes convenience and time management in professional and personal contexts.
Defining Written Communication
Written communication involves the exchange of information through text-based messages, including emails, reports, memos, and instant messaging platforms. It enables clear documentation and reference, facilitating detailed and precise communication across different time zones and organizational levels. This mode contrasts with asynchronous communication by allowing recipients to process and respond to messages at their convenience without the need for real-time interaction.
Understanding Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication involves the exchange of information without requiring participants to be engaged simultaneously, allowing messages to be sent and received at different times. This method enhances flexibility and efficiency, especially in remote or distributed work environments, by enabling individuals to respond thoughtfully without the pressure of immediate interaction. Tools like emails, messaging apps, and collaborative platforms exemplify asynchronous communication, facilitating clear documentation and reducing the urgency for real-time responses.
Key Differences Between Written and Asynchronous Communication
Written communication involves exchanging messages through text, such as emails, reports, or letters, where the sender and receiver may not interact simultaneously. Asynchronous communication refers specifically to communication where participants respond at different times, including emails, discussion boards, and recorded messages, allowing flexibility in response time. The key difference lies in that all asynchronous communication is written, but not all written communication is asynchronous; some written exchanges occur in real-time, like instant messaging or live chat.
Advantages of Written Communication
Written communication ensures clear documentation and a permanent record, facilitating accurate information retention and accountability. It allows individuals to carefully craft messages, enhancing clarity and reducing misunderstandings. This form of communication supports detailed and complex information sharing, making it ideal for formal instructions, policies, and legal matters.
Benefits of Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication allows individuals to process information and respond thoughtfully without the pressure of immediate replies, enhancing clarity and reducing errors. It enables flexible scheduling, accommodating different time zones and work habits, which increases productivity and work-life balance. This mode supports better documentation and traceability, as all messages are recorded and easily referenced for future decision-making and collaboration.
Challenges and Limitations
Written communication faces challenges such as lack of immediate feedback, which can lead to misunderstandings and delays in resolving issues. Asynchronous communication limitations include potential information overload and reduced team cohesion due to time lags between messages. Both methods require clear, concise writing and structured protocols to minimize misinterpretation and maintain effective collaboration.
Use Cases in Modern Workplaces
Written communication excels in formal documentation, detailed project specifications, and official announcements where clarity and record-keeping are crucial. Asynchronous communication is ideal for remote teams working across time zones, enabling flexible responses through tools like email, messaging apps, and collaborative platforms such as Slack or Microsoft Teams. Modern workplaces leverage written communication for compliance and knowledge management, while asynchronous methods support continuous workflow and reduce meeting overload.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Choosing the right communication method hinges on the context and urgency of the message. Written communication offers clarity and a permanent record suitable for detailed instructions or formal exchanges, while asynchronous communication, such as emails or messaging apps, allows flexibility in response time, ideal for remote teams and non-urgent collaboration. Assessing factors like time sensitivity, audience, and message complexity ensures effective and efficient communication tailored to specific needs.
Future Trends in Communication Methods
Future trends in communication methods emphasize enhanced integration of written communication with asynchronous platforms to maximize flexibility and efficiency. Advances in AI-powered tools will enable real-time translation, sentiment analysis, and context-aware message refinement, transforming traditional emails and text documents. The rise of cloud-based collaboration environments will further support asynchronous communication by allowing seamless content sharing and version control across global teams.
Written Communication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com