Globalism promotes interconnectedness by fostering economic, cultural, and political exchanges across nations, leading to expanded markets and diverse cultural experiences. It also presents challenges such as economic disparities and loss of local traditions, requiring balanced policies to ensure inclusive growth. Discover how globalism shapes your world and what it means for the future in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
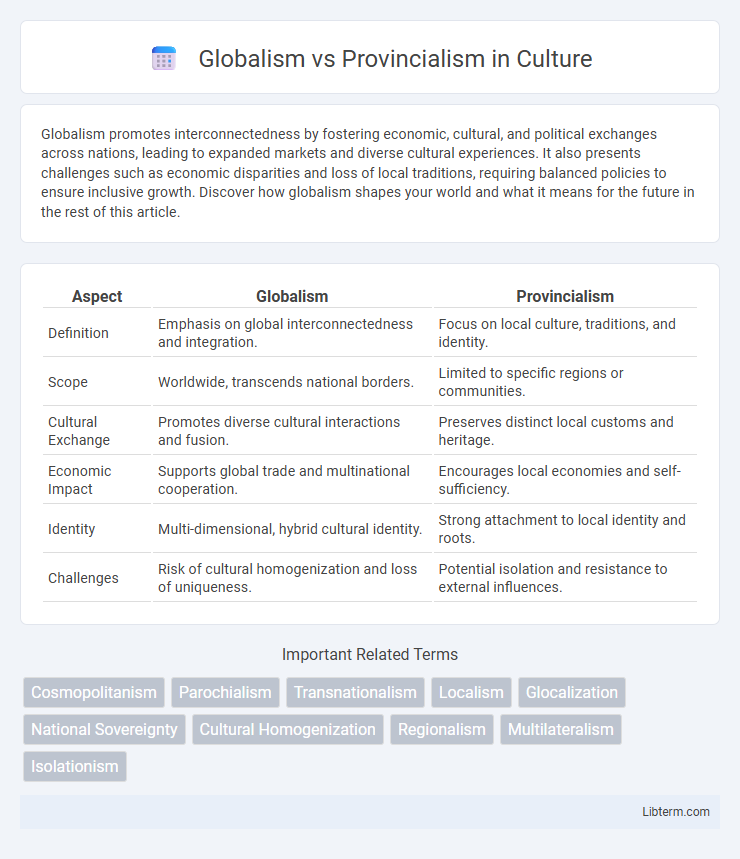
| Aspect | Globalism | Provincialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emphasis on global interconnectedness and integration. | Focus on local culture, traditions, and identity. |
| Scope | Worldwide, transcends national borders. | Limited to specific regions or communities. |
| Cultural Exchange | Promotes diverse cultural interactions and fusion. | Preserves distinct local customs and heritage. |
| Economic Impact | Supports global trade and multinational cooperation. | Encourages local economies and self-sufficiency. |
| Identity | Multi-dimensional, hybrid cultural identity. | Strong attachment to local identity and roots. |
| Challenges | Risk of cultural homogenization and loss of uniqueness. | Potential isolation and resistance to external influences. |
Introduction: Defining Globalism and Provincialism
Globalism emphasizes interconnectedness and the integration of economies, cultures, and policies beyond national borders, promoting international cooperation and shared goals. Provincialism centers on local traditions, values, and interests, prioritizing regional identity and self-reliance over broader global interactions. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing political, economic, and social dynamics in a rapidly changing world.
Historical Context of Globalism and Provincialism
The historical context of globalism traces back to ancient trade routes like the Silk Road, which facilitated cultural exchange and economic interdependence across continents. Provincialism emerged as a counterforce, emphasizing local traditions and governance, often in response to external influences and centralized control. Key events such as the Age of Exploration and the rise of nation-states intensified the dynamic tension between global integration and provincial autonomy.
Key Differences Between Globalist and Provincialist Perspectives
Globalism emphasizes interconnected economies, cultural exchange, and policies promoting international cooperation, whereas provincialism prioritizes local traditions, self-sufficiency, and skepticism toward external influence. Globalists advocate for globalization as a means to address transnational challenges like climate change and economic inequality, while provincialists stress the importance of preserving regional identity and autonomy. The divergence lies in globalists seeking broad integration versus provincialists favoring localized control and cultural preservation.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Globalism
Technology accelerates globalism by connecting economies, cultures, and communication networks worldwide through innovations like the internet, satellite communications, and digital platforms. Advanced technologies enable multinational corporations to manage global supply chains efficiently and foster cross-border collaboration in research and development. Mobile technology and social media platforms facilitate cultural exchange and information sharing, diminishing provincial barriers and promoting a more interconnected global society.
Cultural Impacts: Blending vs. Preservation
Globalism fosters cultural blending by promoting the exchange of ideas, traditions, and values across borders, leading to the emergence of hybrid identities and multicultural societies. Provincialism emphasizes cultural preservation, safeguarding local customs, languages, and heritage from external influences to maintain distinct community identities. The tension between globalism and provincialism shapes cultural dynamics, influencing social cohesion, identity formation, and the resilience of indigenous practices in an interconnected world.
Economic Implications: Global Markets vs. Local Economies
Globalism accelerates economic integration by expanding access to international markets, increasing trade volume, and fostering cross-border investment, which drives GDP growth and technological innovation. Provincialism emphasizes protecting local economies through tariffs, subsidies, and support for small businesses, aiming to preserve cultural identity and employment but often limiting scalability and global competitiveness. Balancing global market participation with local economic resilience remains critical for sustainable development and reducing vulnerabilities to external shocks.
Political Influence: International Cooperation vs. National Sovereignty
Globalism promotes international cooperation by encouraging countries to work together on issues like trade, climate change, and security, fostering interdependence among nations. Provincialism emphasizes national sovereignty, prioritizing self-governance and local interests over global agreements to protect cultural identity and political autonomy. The political influence of globalism often manifests in multinational organizations like the United Nations and World Trade Organization, while provincialism finds expression in movements advocating for stricter border controls and reduced international commitments.
Social Dynamics: Inclusion vs. Exclusion
Globalism promotes social inclusion by encouraging cultural exchange, diversity, and cooperation across national borders, fostering broader social networks and mutual understanding. Provincialism, in contrast, often leads to social exclusion by prioritizing local traditions, identities, and interests, which can result in resistance to external influences and marginalization of outsiders. These opposing social dynamics shape the extent to which communities embrace pluralism or reinforce boundaries that limit social cohesion.
Challenges and Criticisms of Globalism and Provincialism
Globalism faces challenges such as cultural homogenization, economic inequality, and loss of local identities, with critics arguing it prioritizes multinational corporations over community needs. Provincialism's main criticisms include resistance to beneficial global cooperation and economic stagnation due to limited openness to international trade and innovation. Balancing global integration with local autonomy remains a complex issue, as both perspectives present economic, social, and political trade-offs.
Future Outlook: Balancing Globalism and Provincialism
Balancing globalism and provincialism requires integrating local cultures and economies within broader international frameworks to foster sustainable development. Emphasizing technological innovation and cross-border collaboration can drive economic growth while preserving regional identities. Future outlooks suggest adaptive governance models that harmonize global connectivity with local resilience will be essential for addressing complex challenges like climate change and social inequality.
Globalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com