Cultural relativism emphasizes understanding and evaluating cultural practices within their own social contexts rather than through the lens of another culture. This perspective fosters tolerance and reduces ethnocentric biases by recognizing that moral and social norms vary widely. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of how cultural relativism shapes cross-cultural interactions and ethical considerations.
Table of Comparison
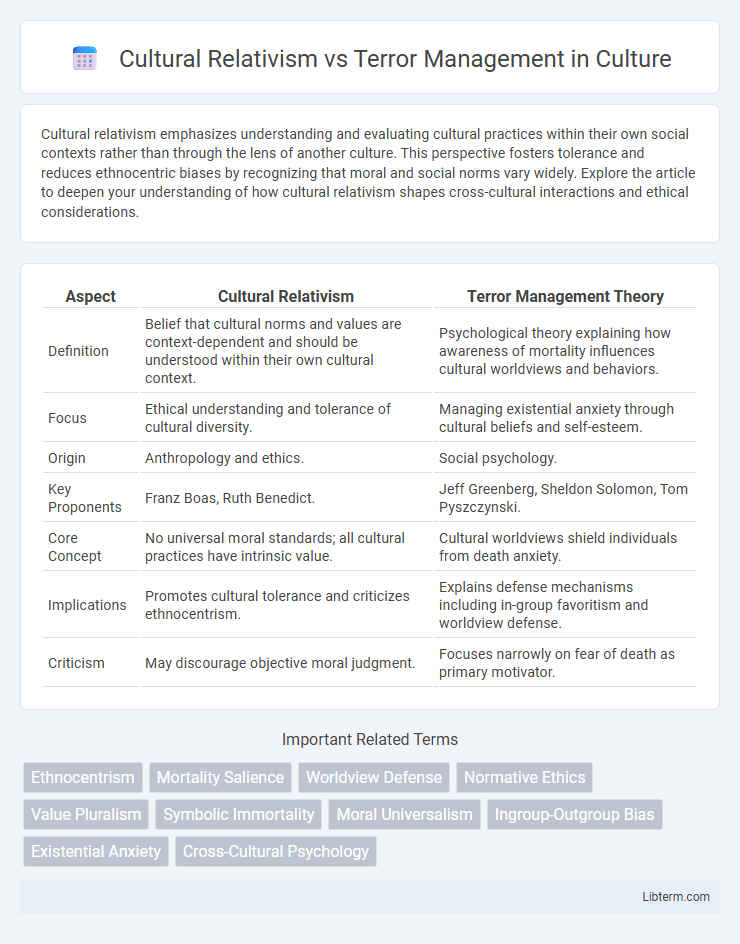
| Aspect | Cultural Relativism | Terror Management Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that cultural norms and values are context-dependent and should be understood within their own cultural context. | Psychological theory explaining how awareness of mortality influences cultural worldviews and behaviors. |
| Focus | Ethical understanding and tolerance of cultural diversity. | Managing existential anxiety through cultural beliefs and self-esteem. |
| Origin | Anthropology and ethics. | Social psychology. |
| Key Proponents | Franz Boas, Ruth Benedict. | Jeff Greenberg, Sheldon Solomon, Tom Pyszczynski. |
| Core Concept | No universal moral standards; all cultural practices have intrinsic value. | Cultural worldviews shield individuals from death anxiety. |
| Implications | Promotes cultural tolerance and criticizes ethnocentrism. | Explains defense mechanisms including in-group favoritism and worldview defense. |
| Criticism | May discourage objective moral judgment. | Focuses narrowly on fear of death as primary motivator. |
Understanding Cultural Relativism: Core Concepts
Cultural relativism emphasizes evaluating beliefs and practices within the context of an individual's own culture, promoting tolerance and avoiding ethnocentric judgments. Core concepts include recognizing cultural norms as shaped by historical, social, and environmental factors, and understanding that moral values are not universal but culturally specific. This framework contrasts with terror management theory by prioritizing cultural context over existential anxiety in interpreting human behavior.
Terror Management Theory: An Overview
Terror Management Theory (TMT) explores how humans cope with the existential anxiety caused by the awareness of mortality by reinforcing cultural worldviews and self-esteem. It posits that cultural belief systems provide a symbolic buffer against death-related fear, motivating individuals to uphold values that offer a sense of meaning and permanence. Empirical studies reveal that reminders of mortality increase adherence to cultural norms, enhance in-group favoritism, and intensify efforts to bolster self-worth as psychological defense mechanisms.
Origins and Historical Perspectives
Cultural relativism originated in the early 20th century through anthropologists like Franz Boas, emphasizing understanding cultures on their own terms without ethnocentric bias. Terror management theory, developed in the late 20th century by social psychologists Jeff Greenberg, Sheldon Solomon, and Tom Pyszczynski, builds on Ernest Becker's work on mortality salience and human fear of death. Both frameworks emerged from distinct academic traditions--cultural anthropology versus social psychology--shaping their divergent approaches to human behavior and cultural interpretation.
Comparing Worldview Defense Mechanisms
Cultural relativism emphasizes understanding beliefs and practices within specific cultural contexts, promoting tolerance by recognizing diverse worldviews as equally valid. Terror management theory explains how individuals defend their worldview to mitigate existential anxiety, leading to heightened in-group favoritism and out-group derogation when confronted with mortality reminders. Comparing these defense mechanisms reveals that cultural relativism fosters cognitive flexibility and acceptance, whereas terror management triggers rigid, protective responses to uphold self-esteem and symbolic immortality.
Culture, Morality, and Meaning-Making
Cultural relativism asserts that moral values and practices are deeply embedded within specific cultural contexts, shaping meaning-making processes unique to each society. Terror management theory examines how individuals uphold cultural worldviews and moral frameworks to mitigate existential anxiety and foster a sense of meaning and security. Both perspectives highlight culture's pivotal role in constructing morality and providing individuals with frameworks for understanding existence and managing fear of death.
Cultural Relativism and Fear of the Unknown
Cultural relativism emphasizes understanding and evaluating cultures based on their own values and norms, avoiding ethnocentric judgments. This approach helps mitigate the fear of the unknown by promoting openness and acceptance of diverse cultural practices and beliefs. Embracing cultural relativism reduces anxiety triggered by unfamiliar cultural differences, fostering tolerance and social cohesion.
Death Anxiety and Cultural Norms
Cultural relativism emphasizes understanding death anxiety within the context of varying cultural norms, where beliefs and rituals shape how societies cope with mortality. Terror management theory explores how death anxiety drives individuals to uphold cultural worldviews as a defense mechanism against existential fear. The interplay between cultural relativism and terror management highlights that death anxiety's manifestation is deeply influenced by culturally specific practices and values.
Conflict and Tolerance Between Cultures
Cultural Relativism promotes understanding and tolerance by interpreting cultural practices within their own context, reducing ethnocentric conflicts between diverse groups. Terror Management Theory explains intergroup conflict as a defense mechanism against existential anxiety, often intensifying in-group favoritism and out-group hostility. Balancing these theories enhances conflict resolution by fostering empathy while addressing deep-rooted fears that fuel cultural intolerance.
Implications for Global Ethics
Cultural relativism emphasizes understanding ethical practices within cultural contexts, challenging universal moral standards, while terror management theory highlights how mortality awareness influences cultural worldviews and ethical behavior. These frameworks impact global ethics by revealing tensions between respecting cultural diversity and promoting shared human values to address existential anxieties. Balancing cultural sensitivity with universal human rights remains a critical challenge for ethical discourse in global contexts.
Bridging the Gap: Toward Mutual Understanding
Bridging the gap between Cultural Relativism and Terror Management Theory involves recognizing the importance of respecting diverse cultural values while addressing existential anxieties that shape human behavior. Emphasizing open dialogue and empathy fosters mutual understanding, allowing societies to navigate cultural differences without undermining core psychological needs related to mortality awareness. Integrating insights from both perspectives promotes social cohesion and tolerance amid global cultural diversity.
Cultural Relativism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com