Nonverbal communication conveys emotions and intentions through body language, facial expressions, and gestures, often revealing more than spoken words. Understanding these cues enhances your ability to interpret messages accurately in personal and professional interactions. Explore the full article to master the art of reading and using nonverbal signals effectively.
Table of Comparison
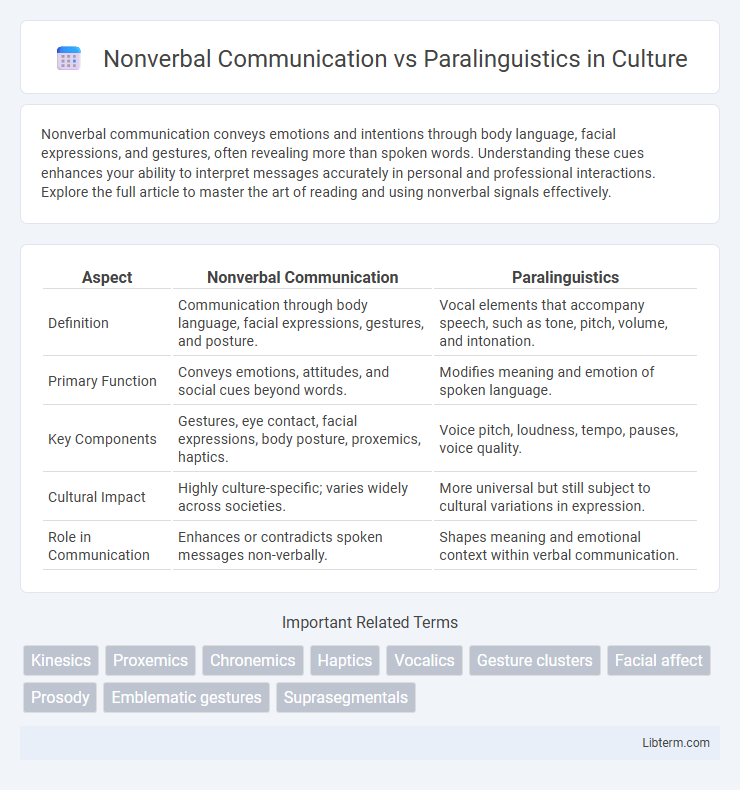
| Aspect | Nonverbal Communication | Paralinguistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication through body language, facial expressions, gestures, and posture. | Vocal elements that accompany speech, such as tone, pitch, volume, and intonation. |
| Primary Function | Conveys emotions, attitudes, and social cues beyond words. | Modifies meaning and emotion of spoken language. |
| Key Components | Gestures, eye contact, facial expressions, body posture, proxemics, haptics. | Voice pitch, loudness, tempo, pauses, voice quality. |
| Cultural Impact | Highly culture-specific; varies widely across societies. | More universal but still subject to cultural variations in expression. |
| Role in Communication | Enhances or contradicts spoken messages non-verbally. | Shapes meaning and emotional context within verbal communication. |
Introduction to Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication encompasses all forms of conveying messages without spoken words, including body language, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact. Paralinguistics refer to the vocal elements that accompany speech, such as tone, pitch, volume, and speaking rate, which modify or reinforce the message. Understanding nonverbal communication is essential for interpreting emotions, intentions, and social cues beyond verbal language.
Defining Paralinguistics
Paralinguistics refers to the vocal elements of communication that accompany speech, such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate, which convey emotions and attitudes beyond the literal meaning of words. Unlike nonverbal communication, which includes gestures, facial expressions, and body language, paralinguistics specifically involves the auditory aspects of how something is said rather than what is said. These vocal cues play a critical role in shaping interpersonal interactions and interpreting speaker intent.
Key Differences Between Nonverbal Communication and Paralinguistics
Nonverbal communication encompasses all forms of conveying messages without words, including facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact, while paralinguistics specifically refers to vocal elements such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that modify spoken language. The key difference lies in the modality: nonverbal communication is primarily visual and physical, whereas paralinguistics is auditory and related to how something is said, not what is said. Understanding these distinctions enhances interpretation of interpersonal interactions by clarifying how meaning is constructed through both bodily cues and vocal nuances.
Components of Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication encompasses a variety of components including facial expressions, gestures, posture, eye contact, and proxemics, which convey meaning without spoken words. Paralinguistics, a subset of nonverbal communication, specifically involves vocal elements such as tone, pitch, loudness, and speech rate that accompany verbal messages. Understanding these components enhances interpersonal communication by providing context and emotional nuance beyond the literal content of speech.
Elements of Paralinguistic Cues
Paralinguistic cues encompass vocal elements such as pitch, tone, volume, speech rate, and pauses that modify or enhance spoken language without altering its literal meaning. Unlike nonverbal communication, which includes gestures, facial expressions, and body language, paralinguistics specifically refers to voice-related features that convey emotions and intentions. Understanding elements like intonation patterns and vocal stress is crucial for interpreting speaker attitude and engagement in interpersonal communication.
Cultural Influences on Nonverbal Communication and Paralinguistics
Cultural influences profoundly shape nonverbal communication and paralinguistics, dictating how gestures, facial expressions, and vocal tones are interpreted across societies. Variations in eye contact, personal space, and intonation patterns reflect deep-rooted cultural norms that govern social interactions and emotional expression. Understanding these cultural nuances enhances effective cross-cultural communication and prevents misinterpretations in global contexts.
Impact on Interpersonal Relationships
Nonverbal communication, including body language, facial expressions, and gestures, significantly influences interpersonal relationships by conveying emotions and intentions beyond words. Paralinguistics, such as tone, pitch, and vocal intensity, shapes how messages are interpreted and can alter the emotional impact of spoken language. Both elements contribute to trust, empathy, and understanding, playing critical roles in effective social interactions and relationship dynamics.
Role in Workplace Communication
Nonverbal communication in the workplace includes body language, facial expressions, gestures, and physical proximity, which convey emotions and attitudes, enhancing interpersonal understanding and team cohesion. Paralinguistics involves vocal elements such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate, influencing how verbal messages are perceived and can modulate the speaker's intent or emotional state. Both nonverbal communication and paralinguistics play critical roles in effective workplace interactions by reinforcing or contradicting spoken words, impacting trust, clarity, and collaboration.
Common Misinterpretations and Challenges
Nonverbal communication often faces challenges due to cultural differences, causing gestures or facial expressions to be misinterpreted as hostile or disinterested when they might signal something entirely different. Paralinguistics, which includes tone, pitch, and pace of speech, can lead to misunderstandings if listeners incorrectly infer emotions such as anger or sarcasm from vocal cues that are neutral or context-specific. Both modes require contextual awareness to accurately decode messages, as misinterpretations frequently arise from overlooking situational factors and individual communication styles.
Conclusion: Integrating Nonverbal and Paralinguistic Skills
Integrating nonverbal communication with paralinguistic skills significantly enhances interpersonal understanding by combining body language cues with vocal tone variations. Mastery of both elements allows individuals to convey emotions and intentions more accurately, reducing misunderstandings in personal and professional interactions. Effective communication arises from the dynamic interplay between facial expressions, gestures, voice pitch, and speech rhythm, creating a holistic message delivery system.
Nonverbal Communication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com