Mainstream culture shapes society's collective values, behaviors, and trends, influencing everything from fashion to entertainment. It reflects the dominant ideals and practices embraced by the majority, often driving social norms and expectations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how mainstream culture impacts your daily life and identity.
Table of Comparison
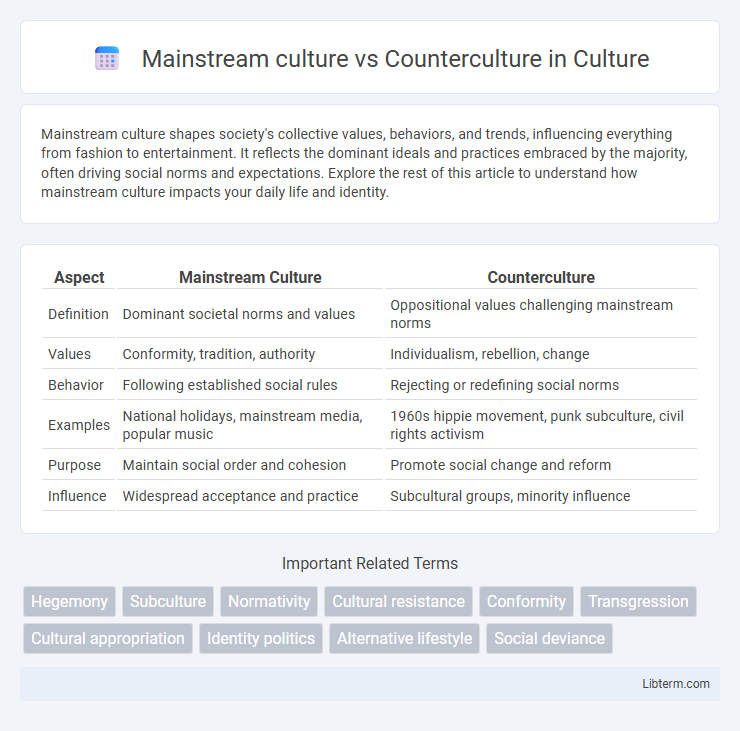
| Aspect | Mainstream Culture | Counterculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dominant societal norms and values | Oppositional values challenging mainstream norms |
| Values | Conformity, tradition, authority | Individualism, rebellion, change |
| Behavior | Following established social rules | Rejecting or redefining social norms |
| Examples | National holidays, mainstream media, popular music | 1960s hippie movement, punk subculture, civil rights activism |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and cohesion | Promote social change and reform |
| Influence | Widespread acceptance and practice | Subcultural groups, minority influence |
Defining Mainstream Culture
Mainstream culture encompasses the dominant values, norms, beliefs, and practices widely accepted and promoted by a society's majority, often reflected in media, education, and government institutions. It shapes collective identity by influencing behaviors, language, fashion, and consumer habits that align with societal expectations. This cultural framework maintains social cohesion by reinforcing commonly held views and marginalizing alternative or dissenting perspectives found in countercultures.
Understanding Counterculture
Counterculture represents a social movement that actively challenges and opposes mainstream culture's norms, values, and practices, often advocating for radical change and alternative lifestyles. It fosters distinct identities through unique language, art, and political beliefs, emphasizing community and resistance to dominant societal structures. Understanding counterculture involves analyzing its role in shaping social innovation, cultural diversity, and political discourse, highlighting its impact on both social progress and cultural conflict.
Historical Origins of Counterculture
The historical origins of counterculture trace back to the 1960s, a period marked by widespread social upheaval and opposition to mainstream norms focused on civil rights, anti-war protests, and the quest for personal freedom. Counterculture emerged as a reaction against dominant values, rejecting materialism, traditional social structures, and established political institutions. Influenced by Beat Generation writers, psychedelic music, and alternative lifestyles, this movement significantly shaped societal changes in art, politics, and social consciousness.
Key Differences Between Mainstream and Counterculture
Mainstream culture represents the dominant societal norms, values, and practices widely accepted and promoted by the majority, while counterculture challenges and opposes these established conventions. Key differences include their contrasting attitudes toward authority, with mainstream culture often endorsing social institutions and counterculture advocating for radical change or rebellion. Furthermore, mainstream culture emphasizes conformity and tradition, whereas counterculture prioritizes innovation, alternative lifestyles, and often seeks to redefine social narratives.
Influences of Mainstream Culture on Society
Mainstream culture shapes societal norms, values, and behaviors by promoting widely accepted beliefs and practices that influence education, media, and politics. This pervasive influence reinforces social cohesion and stability, guiding individuals' identities and interactions within the community. The dominance of mainstream culture often marginalizes alternative viewpoints, impacting how counterculture movements emerge and challenge established conventions.
How Counterculture Challenges Norms
Counterculture challenges mainstream culture by rejecting widely accepted social norms, values, and practices, promoting alternative lifestyles and ideologies that question the status quo. It often manifests through art, music, political activism, and communal living, creating spaces for innovation and social critique. This resistance to conformity encourages societal reflection and can lead to transformative changes in cultural attitudes and policies.
Iconic Counterculture Movements
Iconic counterculture movements like the 1960s Hippie movement and the punk subculture challenged mainstream culture by promoting anti-establishment values, social liberation, and alternative lifestyles. These movements used distinctive symbols such as the peace sign, tie-dye clothing, and punk rock music to express dissent against conformity and consumerism. Their influence persists in contemporary art, music, and social activism, highlighting the enduring impact of countercultural ideals on societal norms and cultural evolution.
Mainstream Assimilation of Counterculture
Mainstream culture often assimilates countercultural elements by adopting their fashion, language, and values into popular trends, transforming initially radical ideas into commercially viable products. This process dilutes the original political or social messages of countercultures, aligning them with dominant societal norms to maintain cultural stability. Such assimilation reinforces mainstream ideologies while neutralizing potential challenges posed by countercultural movements.
Impact on Art, Music, and Fashion
Mainstream culture shapes art, music, and fashion by promoting widely accepted styles, genres, and trends that appeal to large audiences, often driven by commercial interests and mass media. Counterculture challenges these norms by introducing innovative, rebellious, and alternative expressions that question societal values, influencing underground art movements, experimental music genres like punk and hip-hop, and anti-establishment fashion styles such as DIY and vintage wear. The dynamic interaction between mainstream culture and counterculture fuels creative evolution, with elements from subcultures gradually integrating into popular culture, thereby reshaping artistic standards and consumer preferences.
The Future Relationship Between Mainstream and Counterculture
The future relationship between mainstream culture and counterculture is likely to be increasingly dynamic, where countercultural movements continue to inspire shifts in social norms, fashion, technology, and political attitudes within mainstream society. Emerging trends in sustainability, digital innovation, and social justice often originate from countercultural groups before gaining widespread acceptance. As mainstream culture adapts to these influences, the boundaries between the two will blur, fostering a cyclical exchange that drives cultural evolution.
Mainstream culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com