Antonymy is the linguistic relationship between words that have opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold" or "happy" and "sad." Understanding antonymy enhances your vocabulary and improves language comprehension by highlighting semantic contrasts. Explore the rest of the article to discover different types of antonyms and their applications in everyday communication.
Table of Comparison
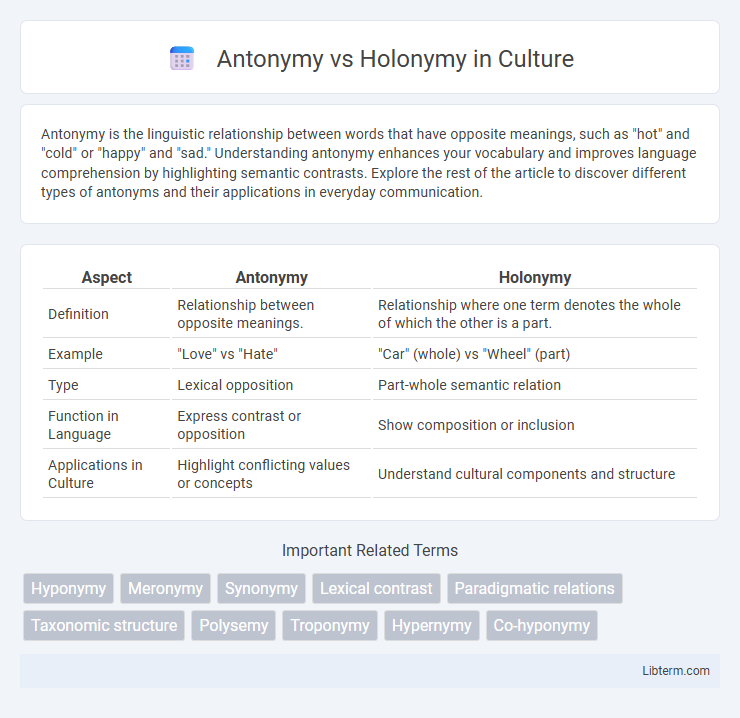
| Aspect | Antonymy | Holonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relationship between opposite meanings. | Relationship where one term denotes the whole of which the other is a part. |
| Example | "Love" vs "Hate" | "Car" (whole) vs "Wheel" (part) |
| Type | Lexical opposition | Part-whole semantic relation |
| Function in Language | Express contrast or opposition | Show composition or inclusion |
| Applications in Culture | Highlight conflicting values or concepts | Understand cultural components and structure |
Introduction to Antonymy and Holonymy
Antonymy involves the relationship between words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," providing essential contrast in language comprehension and lexical semantics. Holonymy, on the other hand, describes the part-whole relationship where a holonym denotes the whole, as in "tree" is the holonym for its parts like "branch" and "leaf." Both antonymy and holonymy are fundamental semantic relationships that enhance the structure and interpretation of vocabulary in natural language processing and linguistics.
Defining Antonymy: Meaning and Examples
Antonymy refers to the semantic relationship between words that have opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold" or "happy" and "sad." This linguistic concept plays a crucial role in vocabulary development and text comprehension by highlighting contrasts in meaning. Common types of antonyms include gradable antonyms, complementary antonyms, and relational antonyms, each demonstrating different oppositional relationships.
Holonymy Explained: Concepts and Illustrations
Holonymy describes the semantic relationship where a term denotes a whole whose parts are represented by other terms; for example, "tree" serves as a holonym for "branch," "leaf," and "trunk." This lexical relationship contrasts with antonymy, which involves words with opposite meanings such as "hot" and "cold." Understanding holonymy is crucial in computational linguistics and natural language processing for tasks like word sense disambiguation and hierarchical semantic analysis.
Key Differences Between Antonymy and Holonymy
Antonymy refers to a semantic relationship where words have opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," emphasizing contrast in meaning. Holonymy describes a part-whole relationship where a term denotes a whole that includes the parts named by other words, like "tree" as a holonym for "branch" and "leaf." The key difference lies in antonymy highlighting opposition between word meanings, while holonymy focuses on hierarchical inclusion and composition within lexical semantics.
Linguistic Functions of Antonymy
Antonymy serves a crucial linguistic function by establishing binary oppositions that enhance semantic clarity and enable precise communication through the expression of contrastive meanings. It facilitates cognitive categorization by allowing speakers to differentiate concepts along dimensions such as direction, quality, or quantity, exemplified by pairs like "hot" versus "cold" or "increase" versus "decrease." Unlike holonymy, which denotes part-whole relationships, antonymy directly impacts synonymic fields by structuring lexical oppositions critical for nuanced language comprehension and vocabulary organization.
Semantic Roles of Holonymy
Holonymy represents a semantic relation where a term denotes a whole whose parts are denoted by other terms, establishing a part-whole relationship essential for understanding the structure of complex concepts. Unlike antonymy, which involves oppositional meanings, holonymy highlights hierarchical organization within lexical semantics, facilitating roles such as meronym identification and contextual inference in language processing. This semantic role contributes significantly to knowledge representation and natural language understanding by enabling precise modeling of entities' components within a domain.
Importance of Understanding Word Relationships
Understanding the distinction between antonymy and holonymy enhances linguistic precision and semantic clarity. Antonymy involves relationships between words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," which is crucial for accurate communication and sentiment analysis. Holonymy refers to whole-part relationships, like "tree" being the holonym of "branch," essential for knowledge representation and natural language processing tasks.
Antonymy in Everyday Language Use
Antonymy, the relationship between words with opposite meanings such as "hot" and "cold," plays a crucial role in everyday language use by enabling clear and precise communication. It helps speakers express contrasts and distinctions, facilitating decision-making and problem-solving in daily interactions. Understanding antonyms enhances vocabulary comprehension and supports language learners in grasping nuanced meanings.
Holonymy in Context: Real-World Applications
Holonymy plays a crucial role in natural language processing applications such as semantic search and knowledge graph construction by linking whole entities to their parts, enhancing information retrieval accuracy. In fields like ontology engineering and taxonomy development, holonymic relationships enable structured representation of complex systems, improving data interoperability. Real-world systems like recommendation engines and digital assistants utilize holonymy to understand user queries contextually, facilitating more relevant and precise responses.
Conclusion: Comparing Antonymy and Holonymy
Antonymy highlights opposition between words with contrasting meanings, such as "hot" versus "cold," emphasizing difference in semantics. Holonymy defines part-whole relationships, exemplified by "wheel" as a part of "car," stressing inclusion and hierarchy in language structure. Understanding both antonymy and holonymy enriches lexical semantic analysis by addressing polarity and compositional relationships among vocabulary items.
Antonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com