Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, self-reliance, and the importance of individual rights over collective control. It fosters creativity, innovation, and personal growth by encouraging people to express their unique identities. Dive deeper into this article to explore how individualism shapes society and your own life.
Table of Comparison
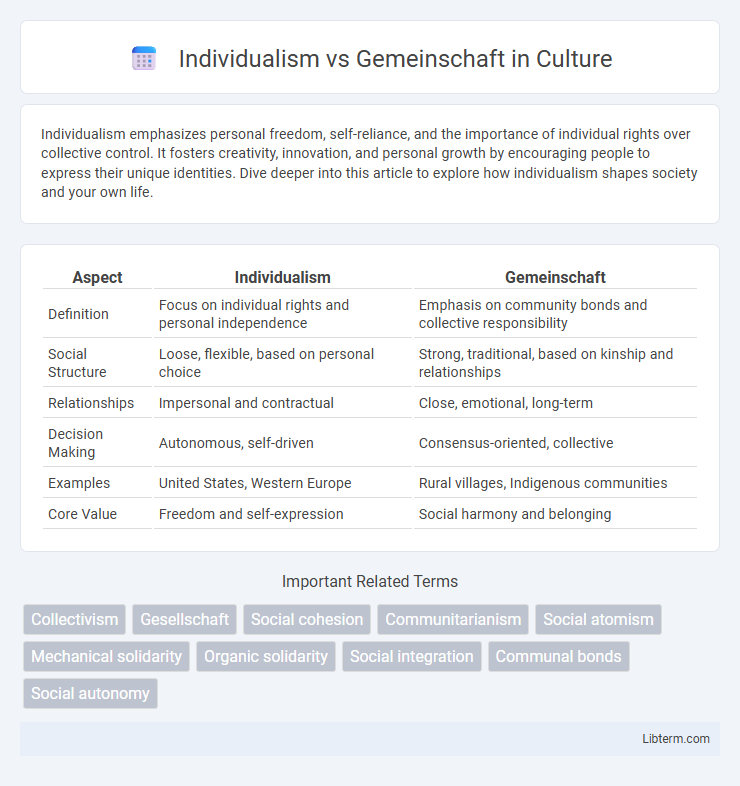
| Aspect | Individualism | Gemeinschaft |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on individual rights and personal independence | Emphasis on community bonds and collective responsibility |
| Social Structure | Loose, flexible, based on personal choice | Strong, traditional, based on kinship and relationships |
| Relationships | Impersonal and contractual | Close, emotional, long-term |
| Decision Making | Autonomous, self-driven | Consensus-oriented, collective |
| Examples | United States, Western Europe | Rural villages, Indigenous communities |
| Core Value | Freedom and self-expression | Social harmony and belonging |
Understanding Individualism: Core Principles and Values
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the pursuit of individual goals, prioritizing individual rights and freedoms over collective constraints. It values independence, personal responsibility, and the belief that individuals inherently possess unique talents and potential to shape their own destiny. Rooted in Enlightenment philosophy, individualism underpins modern liberal democracies and market economies by promoting innovation, personal choice, and individual accountability.
Defining Gemeinschaft: Essence of Community-Centric Living
Gemeinschaft, defined by sociologist Ferdinand Tonnies, emphasizes close-knit, community-centric living where social ties are personal, direct, and grounded in shared values and traditions. This concept contrasts sharply with Individualism, prioritizing collective well-being and mutual cooperation over independent self-interest. The essence of Gemeinschaft lies in fostering strong social cohesion and a sense of belonging within naturally occurring social groups such as families and neighborhoods.
Historical Origins of Individualism and Gemeinschaft
The historical origins of individualism trace back to Renaissance Europe, where humanism emphasized personal autonomy and self-expression, diverging from the collective norms of medieval society. Gemeinschaft, rooted in traditional rural communities, originates from pre-industrial societies characterized by close-knit social ties, shared values, and collective consciousness. These contrasting social structures reflect fundamental differences in how societies organize relationships and prioritize individual versus communal identity.
Key Differences: Individual Autonomy vs Collective Identity
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the prioritization of individual goals and rights over group interests. Gemeinschaft centers on collective identity, strong social bonds, and community cohesion, where relationships are valued for their intrinsic connection and mutual support. These key differences highlight contrasting social structures: individualism fosters independence, while Gemeinschaft nurtures interdependence within tightly-knit communities.
Social Relationships: Personal Freedom or Mutual Obligation?
Individualism emphasizes personal freedom and autonomy in social relationships, prioritizing self-expression and independent decision-making. Gemeinschaft centers on mutual obligation, fostering close-knit community bonds where social roles and collective responsibility shape interactions. These contrasting frameworks influence how societies balance individual rights with communal duties in maintaining social cohesion.
Economic Implications: Market Societies vs Traditional Communities
Market societies driven by individualism prioritize personal economic freedom, fostering competition and innovation while emphasizing private property and contractual exchanges. Traditional Gemeinschaft communities rely on shared values and social obligations, promoting economic cooperation, collective ownership, and mutual support over profit maximization. These economic implications influence social cohesion, resource distribution, and the development of institutional frameworks within each societal type.
Modern Society: The Shift from Gemeinschaft to Individualism
Modern society experiences a pronounced shift from Gemeinschaft's close-knit, community-oriented relationships towards individualism characterized by personal autonomy and self-expression. Urbanization, technological advancements, and economic development amplify this transformation, fostering social networks based on personal choice rather than communal obligation. This transition reshapes social structures, influencing identity, social cohesion, and the nature of interpersonal connections in contemporary life.
Cultural Perspectives: East vs West on Self and Community
In Western societies, individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-expression, and independence, shaping cultural values around individual rights and personal achievement. Eastern cultures, reflecting Gemeinschaft principles, prioritize community, harmony, and social interconnectedness, placing collective well-being above individual desires. These cultural perspectives influence social behaviors, decision-making, and identity formation, highlighting the contrast between self-oriented Western norms and community-centered Eastern traditions.
Advantages and Limitations of Individualistic Cultures
Individualistic cultures promote personal autonomy, self-expression, and innovation, fostering creativity and individual achievement. These cultures emphasize individual rights and responsibilities, enabling people to pursue personal goals without excessive social constraints. However, individualism can lead to social isolation, weakened community bonds, and reduced collective support, which may impact emotional well-being and social cohesion.
Relevance Today: Balancing Individualism and Gemeinschaft in a Globalized World
Balancing individualism and Gemeinschaft remains crucial as globalization intensifies cultural exchanges and social interdependencies across societies. Modern communities navigate the tension between personal autonomy and collective belonging by fostering inclusive networks that respect individual rights while promoting social cohesion. This dynamic equilibrium supports resilient societies capable of adapting to rapid technological and economic changes without eroding cultural identities.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com