Collectivism emphasizes the importance of group goals and social cohesion over individual desires, fostering cooperation and shared responsibility within communities. This philosophy often shapes political systems, social organizations, and cultural values by prioritizing collective well-being over personal gain. Explore the rest of the article to understand how collectivism influences both society and your everyday life.
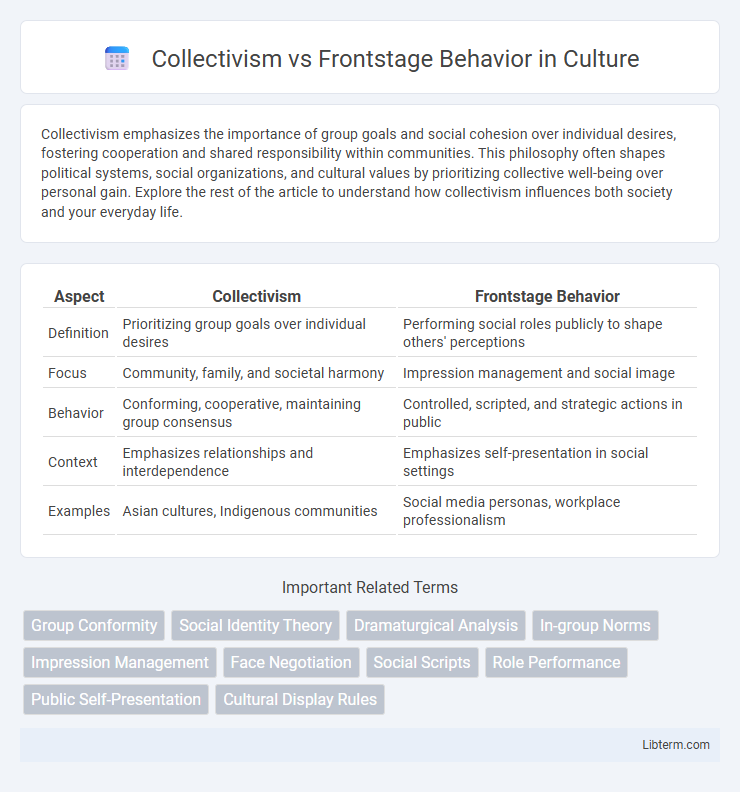
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Collectivism | Frontstage Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prioritizing group goals over individual desires | Performing social roles publicly to shape others' perceptions |
| Focus | Community, family, and societal harmony | Impression management and social image |
| Behavior | Conforming, cooperative, maintaining group consensus | Controlled, scripted, and strategic actions in public |
| Context | Emphasizes relationships and interdependence | Emphasizes self-presentation in social settings |
| Examples | Asian cultures, Indigenous communities | Social media personas, workplace professionalism |
Understanding Collectivism: Core Principles
Collectivism emphasizes group goals, social harmony, and interdependence over individual desires, shaping behaviors and decision-making processes. In collectivist cultures, frontstage behavior often involves conforming to social norms and maintaining group cohesion, reflecting respect and responsibility towards the community. Understanding these core principles helps interpret social interactions where public personas are crafted to support collective identity and relational roles.
Defining Frontstage Behavior in Social Contexts
Frontstage behavior refers to the actions and presentations individuals display in social contexts where they are consciously performing or managing impressions for others. It involves adhering to social norms, roles, and expectations to influence how one is perceived in public settings. This concept contrasts with collectivism, which emphasizes group harmony over individual expression, often shaping the nature of frontstage performances.
The Interplay Between Group Identity and Public Persona
Collectivism emphasizes group identity, shaping individuals' public personas to align with shared values and norms, enhancing social cohesion. Frontstage behavior reflects this interplay by showcasing carefully curated actions and appearances that uphold group reputation in public settings. This dynamic reinforces conformity while allowing subtle negotiation of personal identity within communal expectations.
Collectivist Cultures: Influence on Social Interactions
Collectivist cultures prioritize group harmony and interdependence, shaping social interactions through a strong emphasis on context, relationships, and social roles. In these cultures, frontstage behavior often involves carefully managing impressions to uphold group cohesion, reflecting shared norms and expectations rather than individual expression. Social interactions are guided by collective goals, with individuals frequently engaging in indirect communication and nonverbal cues to maintain harmony and avoid conflict.
Rituals and Norms: Shaping Frontstage Conduct
Collectivism emphasizes shared rituals and norms that reinforce group cohesion and guide frontstage behavior, ensuring individuals display socially acceptable conduct aligned with community values. These rituals act as culturally embedded scripts that dictate appropriate expressions of identity and interaction during public performances. Norms within collectivist societies create predictable frontstage behavior by prioritizing harmony, respect, and conformity over individual expression.
Conformity and Impression Management in Collectivist Societies
In collectivist societies, conformity plays a crucial role in maintaining social harmony and group cohesion, leading individuals to prioritize group norms and expectations. Frontstage behavior is meticulously managed through impression management to project an idealized image that aligns with collective values and social roles. This dynamic reinforces social bonds by ensuring actions and expressions support communal goals while minimizing personal deviation.
Navigating Authenticity: Backstage vs Frontstage in Groups
Navigating authenticity in group settings requires understanding the contrast between collectivism and frontstage behavior, where individuals often perform roles aligned with group norms to maintain harmony and social order. Backstage behavior reveals true attitudes and feelings, offering a space for genuine self-expression free from the scrutiny of the collective audience. Balancing these dynamics involves managing the tension between conforming to expectant group identities and preserving personal authenticity behind the scenes.
Social Harmony and Conflict Avoidance Behaviors
Collectivism prioritizes social harmony by emphasizing group cohesion and interdependence, leading individuals to engage in frontstage behavior that aligns with communal expectations. Frontstage behavior in collectivist cultures often involves managing impressions carefully to avoid conflict and maintain face within the group. Conflict avoidance behaviors manifest through indirect communication and deference, ensuring that social bonds remain intact and group stability is preserved.
Collectivism’s Impact on Communication Styles
Collectivism profoundly shapes communication styles by emphasizing group harmony, indirectness, and context-rich interactions to maintain social cohesion. In collectivist cultures, speakers prioritize relationship-building and use nonverbal cues, implicit messages, and high-context communication to avoid conflict and show respect. This contrasts with more direct and individualistic communication, as collectivist communication often relies on shared understanding within the group rather than explicit verbal expression.
Evolving Dynamics: Individualism Amidst Collectivist Frontstages
Evolving dynamics reveal how individualism subtly asserts itself within collectivist frontstages, where social harmony often dictates public behavior. Individuals navigate group expectations by performing socially acceptable roles while expressing unique identities through nuanced gestures and selective self-disclosure. This complex interplay highlights the tension between collective norms and personal authenticity in contemporary social interactions.
Collectivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com