Corporate culture shapes employee behavior, drives organizational values, and influences overall business success by fostering a shared sense of purpose and collaboration. Strong corporate culture enhances productivity, retention, and innovation, creating an environment where employees feel valued and motivated. Discover how you can harness the power of corporate culture to elevate your organization's performance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
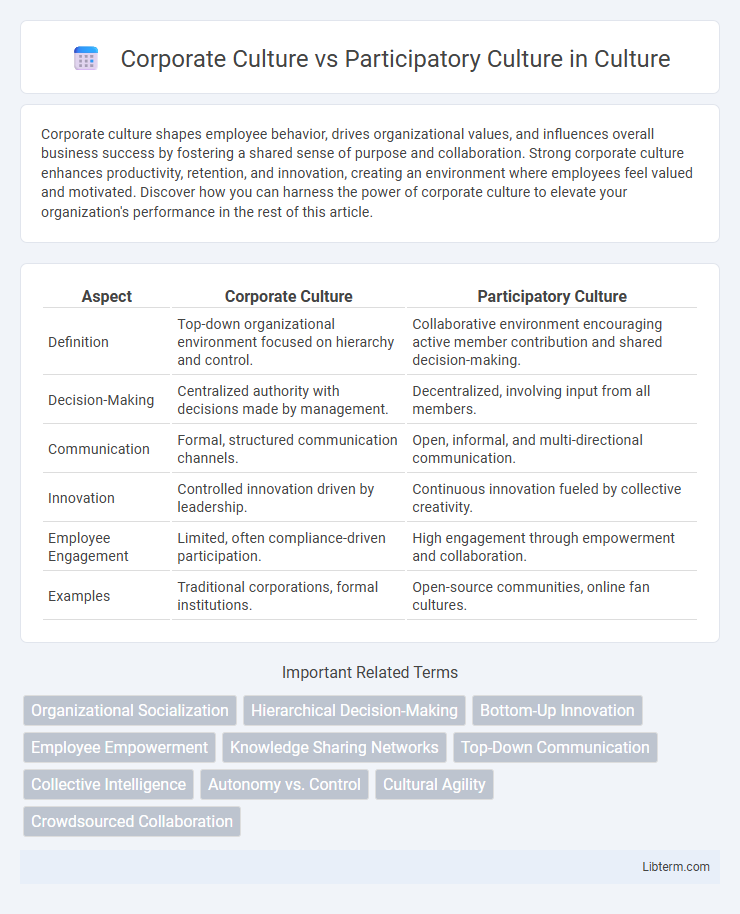
| Aspect | Corporate Culture | Participatory Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Top-down organizational environment focused on hierarchy and control. | Collaborative environment encouraging active member contribution and shared decision-making. |
| Decision-Making | Centralized authority with decisions made by management. | Decentralized, involving input from all members. |
| Communication | Formal, structured communication channels. | Open, informal, and multi-directional communication. |
| Innovation | Controlled innovation driven by leadership. | Continuous innovation fueled by collective creativity. |
| Employee Engagement | Limited, often compliance-driven participation. | High engagement through empowerment and collaboration. |
| Examples | Traditional corporations, formal institutions. | Open-source communities, online fan cultures. |
Defining Corporate Culture
Corporate culture defines an organization's shared values, beliefs, and behaviors shaping employee interactions and decision-making processes. It influences organizational identity, guiding how goals are pursued and how members communicate and collaborate. A strong corporate culture creates consistency and alignment, fostering productivity and employee engagement within hierarchical structures.
Understanding Participatory Culture
Participatory culture emphasizes active engagement, collaboration, and shared authority among members, contrasting with traditional corporate culture's hierarchical structure and controlled communication. This culture fosters creativity, innovation, and community-building by encouraging individuals to contribute ideas and take initiative. Understanding participatory culture requires recognizing its foundation in trust, openness, and the democratization of content and decision-making.
Key Differences Between Corporate and Participatory Cultures
Corporate culture emphasizes hierarchical structures, formal communication, and top-down decision-making, whereas participatory culture fosters open collaboration, shared ownership, and decentralized authority. Corporate environments prioritize efficiency and control through established policies, while participatory cultures encourage creativity, inclusivity, and active user engagement. The contrast lies in how power dynamics and employee involvement shape organizational behavior and innovation.
Origins and Evolution of Each Culture
Corporate culture originated in early 20th-century industrial organizations, shaped by hierarchical management principles and standardized workflows to optimize efficiency and control. Participatory culture emerged with the rise of digital technology and social media in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, promoting collaboration, user-generated content, and decentralized decision-making. The evolution of corporate culture reflects structured, top-down communication, while participatory culture emphasizes egalitarian interaction and community-driven innovation.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Corporate culture typically features hierarchical decision-making processes where authority flows top-down, emphasizing structured roles and formal approval chains. In contrast, participatory culture fosters collaborative decision-making with input from diverse stakeholders, promoting inclusivity and shared ownership of outcomes. This participatory approach accelerates innovation and responsiveness by leveraging collective expertise and decentralized authority.
Impact on Employee Engagement
Corporate culture shapes employee engagement by establishing clear values, norms, and expectations that align workforce behavior with organizational goals, fostering a sense of belonging and purpose. Participatory culture enhances engagement through collaboration, open communication, and employee empowerment, which promotes creativity and ownership of work outcomes. Research indicates that participatory cultures often lead to higher job satisfaction, increased motivation, and improved retention compared to traditional hierarchical corporate cultures.
Communication Styles in Both Cultures
Corporate culture communication style is typically top-down, formal, and structured, emphasizing clear hierarchies and controlled information flow to maintain organizational efficiency. Participatory culture favors open, collaborative, and informal communication, encouraging feedback and dialogue across all levels to foster innovation and collective decision-making. Effective communication in participatory culture enhances employee engagement, while corporate culture prioritizes message consistency and authority.
Innovation and Adaptability Factors
Corporate culture often emphasizes hierarchical structures and standardized processes, which can limit innovation and adaptability by constraining employee autonomy. Participatory culture fosters open communication, collaboration, and shared decision-making, enhancing innovation through diverse viewpoints and rapid adaptation to change. Organizations embracing participatory culture tend to outperform in dynamic markets by continuously evolving their strategies and products.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies reveal that corporate culture in companies like Google emphasizes innovation through structured collaboration and clear hierarchy, fostering productivity and goal alignment. Participatory culture examples such as Wikipedia illustrate decentralized content creation driven by community engagement and collective knowledge sharing, resulting in dynamic and constantly evolving resources. Comparative analysis shows corporate culture thrives in controlled environments, while participatory culture excels in open, user-driven platforms promoting creativity and inclusivity.
Choosing the Right Culture for Your Organization
Selecting the right culture for your organization involves evaluating the dynamics between corporate culture and participatory culture. Corporate culture emphasizes hierarchy, formal rules, and top-down decision-making, ideal for organizations requiring clear authority and consistency. Participatory culture fosters collaboration, open communication, and employee empowerment, benefiting innovative environments that thrive on collective input and agility.
Corporate Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com