Collectivism emphasizes the importance of group goals and social cohesion over individual desires, advocating for shared responsibilities and cooperation to achieve common objectives. This philosophy fosters unity and support within communities, promoting a sense of belonging and collective well-being. Explore the rest of the article to understand how collectivism impacts your daily life and societal structure.
Table of Comparison
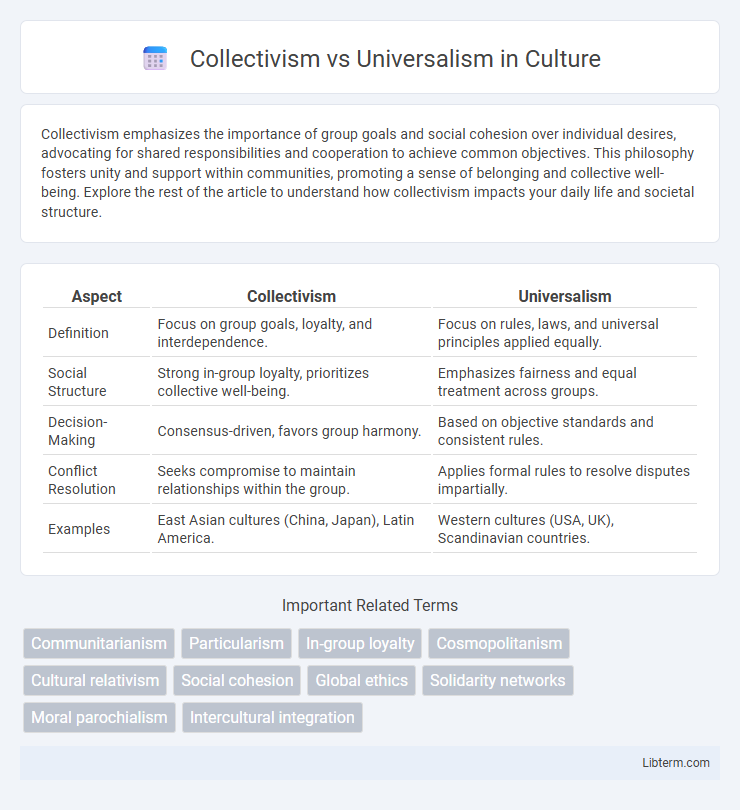
| Aspect | Collectivism | Universalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on group goals, loyalty, and interdependence. | Focus on rules, laws, and universal principles applied equally. |
| Social Structure | Strong in-group loyalty, prioritizes collective well-being. | Emphasizes fairness and equal treatment across groups. |
| Decision-Making | Consensus-driven, favors group harmony. | Based on objective standards and consistent rules. |
| Conflict Resolution | Seeks compromise to maintain relationships within the group. | Applies formal rules to resolve disputes impartially. |
| Examples | East Asian cultures (China, Japan), Latin America. | Western cultures (USA, UK), Scandinavian countries. |
Understanding Collectivism: Core Principles and Values
Collectivism centers on the belief that group goals and community well-being take precedence over individual desires, emphasizing cooperation, mutual support, and interconnectedness. Core principles include prioritizing social harmony, shared responsibility, and collective decision-making to strengthen group cohesion and maintain social order. Values such as loyalty, family orientation, and interdependence are fundamental, fostering environments where individual identities are deeply integrated within the larger community framework.
Defining Universalism: Ideals and Global Perspectives
Universalism emphasizes the application of universal principles and ethical standards that transcend cultural and national boundaries, advocating for equal rights and justice for all individuals regardless of their background. Rooted in global human rights frameworks, universalism promotes ideals such as equality, freedom, and dignity as inherent and universally applicable. This perspective supports international cooperation and policies aimed at addressing global challenges through shared values and comprehensive inclusivity.
Historical Origins of Collectivism and Universalism
Collectivism originated from ancient communal societies and indigenous cultures emphasizing group cohesion and shared responsibilities, evolving through Confucianism in East Asia and Marxist ideologies in Europe. Universalism has roots in ancient Greek philosophy, Christianity, and Enlightenment thought, advocating for universal principles and rights applicable to all individuals regardless of group membership. These historical foundations highlight collectivism's focus on in-group loyalty versus universalism's emphasis on impartiality and equal treatment across diverse populations.
Key Differences Between Collectivism and Universalism
Collectivism emphasizes group goals, social cohesion, and prioritizes the needs of the community over individual desires, whereas Universalism promotes applying consistent moral principles and rules equally to all individuals regardless of their group affiliations. In collectivist cultures, relationships and social contexts heavily influence decision-making, while universalism advocates objective standards and fairness in all situations. Key differences lie in collectivism's focus on in-group loyalty and interdependence versus universalism's commitment to impartiality and equal treatment across diverse groups.
Societal Impact: How Collectivism Shapes Communities
Collectivism prioritizes group goals and social cohesion, fostering strong community bonds through shared responsibilities and mutual support systems. Societal structures in collectivist cultures often emphasize collaboration, leading to greater social stability and reduced individual disparities. This approach enhances communal well-being while influencing social policies that promote inclusivity and collective welfare.
Universalism’s Role in Promoting Human Rights
Universalism plays a crucial role in promoting human rights by advocating for the equal and inherent dignity of all individuals regardless of culture or nationality. It establishes a global framework of universal standards and principles, such as those enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, ensuring protection against discrimination and injustice. This emphasis on common humanity fosters international cooperation and accountability in upholding fundamental freedoms and social justice.
Collectivism in Practice: Real-World Applications
Collectivism emphasizes group goals and interdependence over individual achievement, shaping social, economic, and political frameworks worldwide. In practice, collectivist societies prioritize community welfare, cooperative decision-making, and shared responsibilities, as seen in cooperative business models and social welfare programs in countries like Japan and China. This approach fosters social harmony and collective resilience, especially in environments requiring collaborative problem-solving and resource distribution.
Universalism in Policy and Governance
Universalism in policy and governance emphasizes equal treatment and consistent application of laws across all individuals and groups, promoting fairness and impartiality. This approach seeks to establish standardized regulations and social programs that apply universally rather than tailoring initiatives to specific communities, thereby fostering social cohesion and reducing discrimination. Emphasizing human rights and equality, universalism in governance supports inclusive policies that address broad societal needs while ensuring accountability and transparency.
Debates: Criticisms and Controversies Around Both Concepts
Debates around collectivism versus universalism often highlight tensions between cultural specificity and global ethical standards, with critics arguing that collectivism may undermine individual rights while universalism can impose Western-centric values. Controversies focus on the applicability of universal human rights versus respecting community-based norms, raising questions about moral relativism and ethical imperialism. Scholars emphasize the challenge of balancing collective social responsibilities with personal freedoms, reflecting ongoing disputes in political philosophy and international relations.
Bridging the Divide: Potential for Harmonious Coexistence
Collectivism emphasizes group goals and social cohesion, while universalism prioritizes impartial rules and equal treatment across contexts. Integrating these approaches fosters a balanced social framework where shared cultural values support universal ethical standards. This synergy promotes inclusive decision-making, enabling diverse communities to coexist harmoniously through mutual respect and adaptable norms.
Collectivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com