Homogenization is a mechanical process that breaks down fat molecules in milk to create a uniform texture and prevent separation. This technique improves the consistency, taste, and shelf life of dairy products, making them more appealing and easier to use in cooking. Discover more about how homogenization impacts your favorite dairy items in the rest of this article.
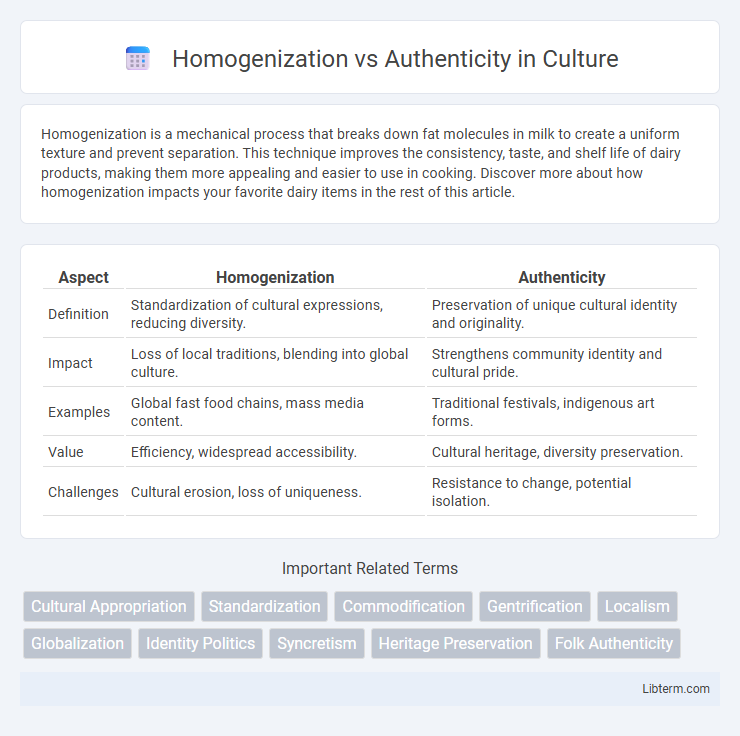
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Homogenization | Authenticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardization of cultural expressions, reducing diversity. | Preservation of unique cultural identity and originality. |
| Impact | Loss of local traditions, blending into global culture. | Strengthens community identity and cultural pride. |
| Examples | Global fast food chains, mass media content. | Traditional festivals, indigenous art forms. |
| Value | Efficiency, widespread accessibility. | Cultural heritage, diversity preservation. |
| Challenges | Cultural erosion, loss of uniqueness. | Resistance to change, potential isolation. |
Understanding Homogenization in a Globalized World
Homogenization in a globalized world refers to the process where diverse cultures, products, and ideas become standardized, often driven by multinational corporations, global media, and technological integration. This phenomenon leads to the widespread adoption of similar consumer behaviors, languages, and cultural practices, diminishing local uniqueness and traditional customs. Understanding homogenization involves analyzing its impact on cultural identity, economic practices, and social interactions within increasingly interconnected societies.
Defining Authenticity in Culture and Identity
Authenticity in culture and identity refers to the genuine expression of traditions, values, and beliefs unique to a particular group or individual, resisting external influences that dilute original characteristics. It emphasizes preserving historical continuity, language, customs, and narratives that shape collective memory and personal sense of self. Authenticity fosters a deep connection to heritage and promotes diversity by valuing distinct cultural identities over homogenized, globalized norms.
Drivers Behind Cultural Homogenization
Globalization, digital communication, and multinational corporations drive cultural homogenization by disseminating uniform cultural products and values worldwide. Media platforms and consumer culture promote standardized lifestyles, diminishing local traditions and ethnic diversity. Economic integration and urbanization further accelerate the convergence of distinct cultural identities into a more homogeneous global culture.
The Value of Preserving Authenticity
Preserving authenticity safeguards cultural heritage, fostering a unique identity that differentiates communities in a globalized world. Authentic expressions in art, language, and customs strengthen social cohesion and promote diversity, enriching collective human experience. Valuing authenticity counters the risks of homogenization, which can dilute meaningful traditions and diminish cultural richness.
Media Influence on Homogenization and Authenticity
Media influence accelerates cultural homogenization by promoting global trends, standardized content, and dominant narratives that overshadow local identities. Simultaneously, media platforms provide spaces for authentic voices to emerge, preserving and sharing diverse cultural expressions despite widespread homogenizing forces. This dual role shapes a dynamic tension where homogenization and authenticity coexist, influenced by the reach and control of media outlets.
Economic Globalization: Catalyst or Threat?
Economic globalization accelerates cultural homogenization by promoting standardized products, media, and consumer behaviors across borders, which can dilute local traditions and identities. However, this integration also provides opportunities for authentic cultural expressions to reach global audiences, fostering cross-cultural understanding and niche markets. Balancing economic benefits with the preservation of unique cultural identities remains a critical challenge in the globalization process.
Social Impacts of Losing Authentic Traditions
The loss of authentic traditions due to cultural homogenization erodes community identity and diminishes social cohesion by replacing unique customs with standardized global practices. This shift often leads to the marginalization of indigenous knowledge systems and disconnects younger generations from their heritage. As traditional values fade, societies face challenges in preserving diversity, fostering belonging, and maintaining social resilience.
Case Studies: Homogenization vs Authenticity in Practice
Case studies on homogenization vs authenticity reveal diverse outcomes in branding and cultural preservation. In global markets, companies like Starbucks exemplify homogenization by standardizing products worldwide, while brands like Patagonia emphasize authenticity through local sourcing and storytelling. These examples demonstrate that balancing uniformity with genuine cultural representation impacts consumer trust and market differentiation.
Balancing Modernization with Cultural Integrity
Balancing modernization with cultural integrity requires a nuanced approach that preserves unique traditions while embracing innovation. Homogenization often leads to the erosion of cultural identities, whereas authenticity reinforces the values and heritage that define communities. Sustainable development strategies integrate modern advancements without compromising cultural distinctiveness, fostering resilience and diversity.
Strategies to Promote Authenticity in a Homogenized Era
Embracing cultural diversity and unique brand identities counters the effects of homogenization by fostering authenticity in marketing strategies. Businesses can promote authenticity by highlighting local traditions, storytelling, and personalized customer experiences that resonate with specific communities. Leveraging user-generated content and transparent communication strengthens trust and differentiates brands in a globalized market dominated by uniformity.
Homogenization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com