Antonymy refers to the relationship between words that have opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold" or "happy" and "sad." This linguistic concept is essential for understanding contrast and nuance in language, helping you enhance your vocabulary and communication skills. Explore the rest of the article to discover the different types of antonyms and their practical uses.
Table of Comparison
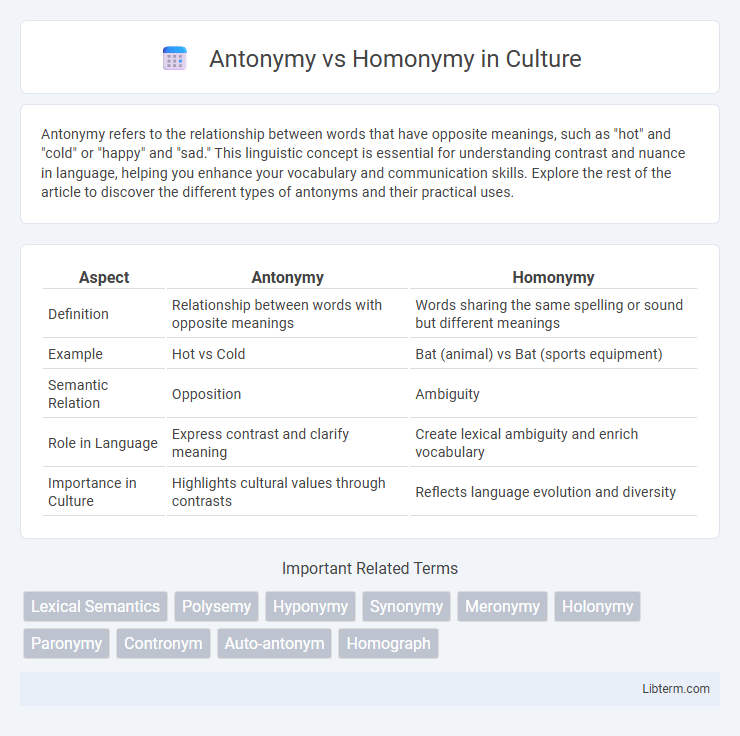
| Aspect | Antonymy | Homonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relationship between words with opposite meanings | Words sharing the same spelling or sound but different meanings |
| Example | Hot vs Cold | Bat (animal) vs Bat (sports equipment) |
| Semantic Relation | Opposition | Ambiguity |
| Role in Language | Express contrast and clarify meaning | Create lexical ambiguity and enrich vocabulary |
| Importance in Culture | Highlights cultural values through contrasts | Reflects language evolution and diversity |
Understanding Antonymy: Definition and Examples
Antonymy refers to the semantic relationship between words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold" or "light" and "dark." Understanding antonymy involves recognizing gradable pairs that allow varying degrees, like "tall" versus "short," as well as complementary pairs that are mutually exclusive, such as "alive" and "dead." Examples of antonyms help clarify how this lexical opposition functions in language, enhancing vocabulary precision and communication effectiveness.
Exploring Homonymy: Meaning and Types
Homonymy refers to the phenomenon where two or more words share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, such as "bat" (an animal) and "bat" (a sports equipment). It is categorized into two main types: homographs, which are words spelled the same but pronounced differently or similarly, and homophones, which are words pronounced the same but spelled differently, like "flour" and "flower." Understanding homonymy is crucial for semantic analysis and language processing, as it helps clarify meaning in context.
Key Differences Between Antonymy and Homonymy
Antonymy involves words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," while homonymy refers to words that share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, like "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (used in sports). Antonyms contribute to semantic contrast, aiding in language clarity and precision, whereas homonyms require contextual cues for disambiguation due to their lexical ambiguity. Understanding the distinction is crucial for effective communication, vocabulary development, and natural language processing tasks.
Semantic Roles of Antonyms in Language
Antonymy involves pairs of words with opposite meanings serving distinct semantic roles such as gradable, complementary, or relational opposites, which clarify contrast and define boundaries in language. Homonymy refers to words sharing the same form but differing in meaning, often causing ambiguity without contributing to semantic opposition. The semantic roles of antonyms enhance language precision by structuring meaning through opposition, aiding comprehension and effective communication.
Types of Antonyms: Gradable, Complementary, and Relational
Antonymy involves words with opposite meanings, categorized into gradable, complementary, and relational antonyms. Gradable antonyms represent opposite ends of a continuous spectrum, such as "hot" and "cold," allowing intermediate states. Complementary antonyms, like "alive" and "dead," exhibit mutually exclusive states with no middle ground, while relational antonyms, including "teacher" and "student," express symmetrical relationships dependent on each other.
Homonyms in English: Homographs, Homophones, and Homonyms
Homonyms in English encompass homographs, homophones, and true homonyms, each differing by spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. Homographs are words spelled identically but with different meanings and sometimes different pronunciations, such as "lead" (to guide) and "lead" (a metal). Homophones share pronunciation but differ in spelling and meaning, like "to," "two," and "too," while true homonyms overlap in both spelling and pronunciation but possess unrelated meanings, exemplified by "bat" (an animal) and "bat" (a sports implement).
Ambiguity and Meaning: The Impact of Homonymy
Homonymy significantly contributes to linguistic ambiguity by presenting words that share spelling or pronunciation but possess entirely different meanings, complicating comprehension and context interpretation. Antonymy, defined by words with opposite meanings, generally reduces ambiguity through clear semantic opposition. The impact of homonymy on meaning requires speakers and listeners to rely heavily on context to disambiguate word sense and avoid misunderstandings in communication.
Usage of Antonyms and Homonyms in Communication
Antonyms enhance clarity in communication by providing precise contrasts that help define concepts and ideas, making messages easier to understand and interpret. Homonyms, with their multiple meanings, can introduce ambiguity or humor, requiring context to ensure accurate comprehension and effective interaction. Both antonyms and homonyms play crucial roles in language, with antonyms emphasizing difference and homonyms enriching expression through lexical diversity.
Cognitive Processing of Antonymy vs Homonymy
Antonymy involves understanding words with opposite meanings, engaging the brain's semantic network to distinguish contrasting concepts, which enhances categorical differentiation and cognitive flexibility. Homonymy requires recognizing a single word form with multiple unrelated meanings, demanding context-dependent disambiguation and increased reliance on contextual cues during lexical access. Cognitive processing of antonymy emphasizes binary semantic differentiation, while homonymy challenges the mental lexicon with polysemy resolution and flexible interpretive mechanisms.
Practical Applications in Linguistics and Language Learning
Antonymy and homonymy play crucial roles in practical linguistics and language learning by enhancing vocabulary comprehension and communication clarity. Antonymy aids learners in understanding semantic oppositions, improving their ability to distinguish meanings and use words precisely in context. Homonymy challenges learners to interpret words based on context, fostering skills in disambiguation and increasing linguistic flexibility essential for advanced language proficiency.
Antonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com