Behavioral scripts are mental frameworks that guide expectations and actions in specific social situations, helping individuals predict and interpret others' behaviors. Understanding these cognitive patterns enhances your ability to navigate social interactions more effectively and respond appropriately. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how behavioral scripts influence daily life and improve interpersonal communication.
Table of Comparison
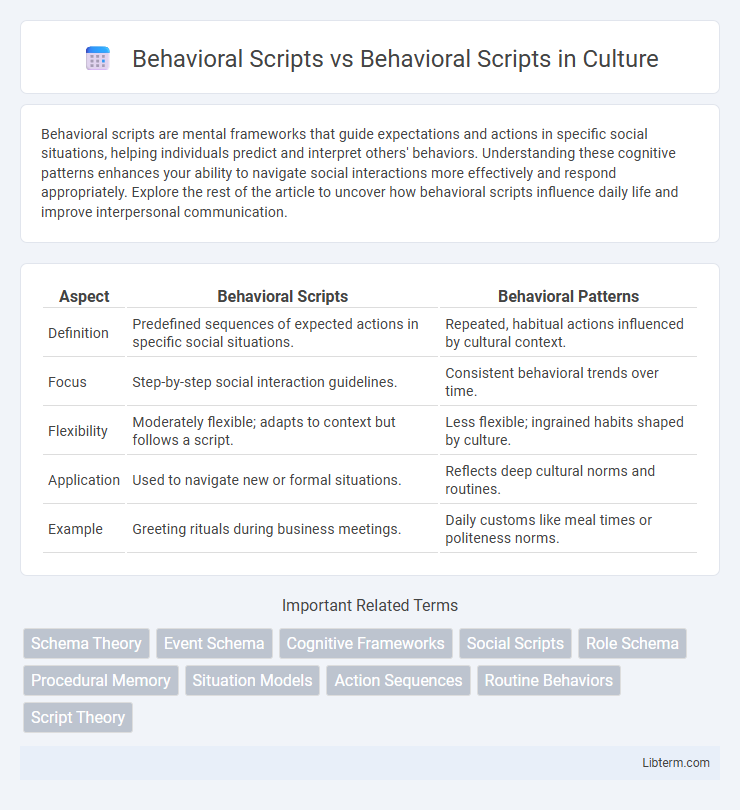
| Aspect | Behavioral Scripts | Behavioral Patterns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predefined sequences of expected actions in specific social situations. | Repeated, habitual actions influenced by cultural context. |
| Focus | Step-by-step social interaction guidelines. | Consistent behavioral trends over time. |
| Flexibility | Moderately flexible; adapts to context but follows a script. | Less flexible; ingrained habits shaped by culture. |
| Application | Used to navigate new or formal situations. | Reflects deep cultural norms and routines. |
| Example | Greeting rituals during business meetings. | Daily customs like meal times or politeness norms. |
Understanding Behavioral Scripts: A Definition
Behavioral scripts are cognitive frameworks that outline expected sequences of actions in specific contexts, guiding individuals' behavior based on past experiences. These scripts help predict outcomes and streamline decision-making by providing a mental template for social interactions and routine activities. Understanding behavioral scripts enables better interpretation of actions and can improve communication by anticipating others' responses.
Types of Behavioral Scripts in Psychology
Behavioral scripts in psychology refer to structured sequences of expected behaviors within specific contexts, such as social interactions or routine activities. Types of behavioral scripts include interpersonal scripts, which guide social exchanges and communication patterns, and event scripts, which outline predictable actions in familiar situations like dining or attending meetings. Understanding these script types helps psychologists analyze behavior patterns, cognitive processes, and social expectations.
The Role of Behavioral Scripts in Daily Life
Behavioral scripts play a crucial role in daily life by providing structured frameworks for routine interactions, enhancing efficiency and predictability in social behavior. These mental representations help individuals anticipate and respond to social cues, reducing cognitive load during complex tasks such as dining, shopping, or workplace communication. By enabling automatic execution of familiar actions, behavioral scripts facilitate smoother social functioning and decision-making processes.
Behavioral Scripts vs. Schemas: Key Differences
Behavioral scripts are specific, sequential actions individuals follow in familiar situations, while schemas are broader cognitive frameworks organizing general knowledge and expectations about the world. Scripts guide routine behaviors by outlining step-by-step procedures, whereas schemas shape perception and interpretation by providing context for various experiences. Understanding these distinctions highlights how scripts facilitate predictable actions and schemas influence overall understanding and memory.
How Behavioral Scripts Influence Decision Making
Behavioral scripts shape decision-making by providing predefined sequences of actions based on past experiences and learned patterns, enabling quicker and often more efficient responses in familiar situations. These mental frameworks reduce cognitive load by guiding expectations and interpretations, thus influencing choices without extensive deliberation. When environmental cues align with established scripts, decisions become more automatic, whereas deviations from scripts may prompt reevaluation and adaptive problem-solving.
Positive vs. Negative Behavioral Scripts
Positive behavioral scripts involve adaptive patterns of thought and action that promote constructive responses to various situations, enhancing social interactions and personal growth. Negative behavioral scripts consist of maladaptive, often automatic responses rooted in past trauma or negative experiences, leading to dysfunctional behaviors and impaired relationships. Understanding the distinction between these scripts aids in cognitive-behavioral therapy, aiming to replace negative scripts with positive ones for improved mental health outcomes.
The Formation and Modification of Behavioral Scripts
Behavioral scripts are formed through repeated exposure and experiences, creating cognitive frameworks that guide expected actions in specific contexts. Modification of these scripts occurs when new information or experiences challenge existing patterns, leading to adaptation or restructuring of behavioral responses. This process involves neural plasticity and cognitive flexibility, allowing individuals to update their behavior according to changing environments or social norms.
Behavioral Scripts in Social Settings
Behavioral scripts in social settings refer to the predictable sequences of actions and reactions individuals follow during interactions, enabling smoother communication and social cohesion. These scripts are shaped by cultural norms, social roles, and contextual cues, facilitating the interpretation of others' behaviors and the anticipation of responses. Understanding behavioral scripts aids in navigating social complexity, reducing misunderstandings, and enhancing interpersonal relationships.
Breaking Unhelpful Behavioral Scripts
Breaking unhelpful behavioral scripts requires identifying automatic patterns shaped by past experiences that influence current responses. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness help disrupt these maladaptive scripts by promoting awareness and deliberate choice-making. Replacing harmful scripts with adaptive behaviors improves emotional regulation and decision-making, fostering psychological resilience.
Applications of Behavioral Scripts in Therapy
Behavioral scripts in therapy serve as structured guides that help clients rehearse and internalize appropriate social responses, enhancing coping mechanisms and emotional regulation. These scripts are utilized in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to modify maladaptive behaviors by providing clear, repeatable patterns for handling specific situations. Implementing behavioral scripts improves skill acquisition in social anxiety treatment, autism spectrum disorder interventions, and habit reversal training.
Behavioral Scripts Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com