Glocalization integrates global strategies with local adaptations to ensure business success in diverse markets. By tailoring products and marketing efforts to local cultures while maintaining a global brand identity, companies enhance customer engagement and competitive advantage. Explore the article to discover how glocalization can transform Your approach to global business.
Table of Comparison
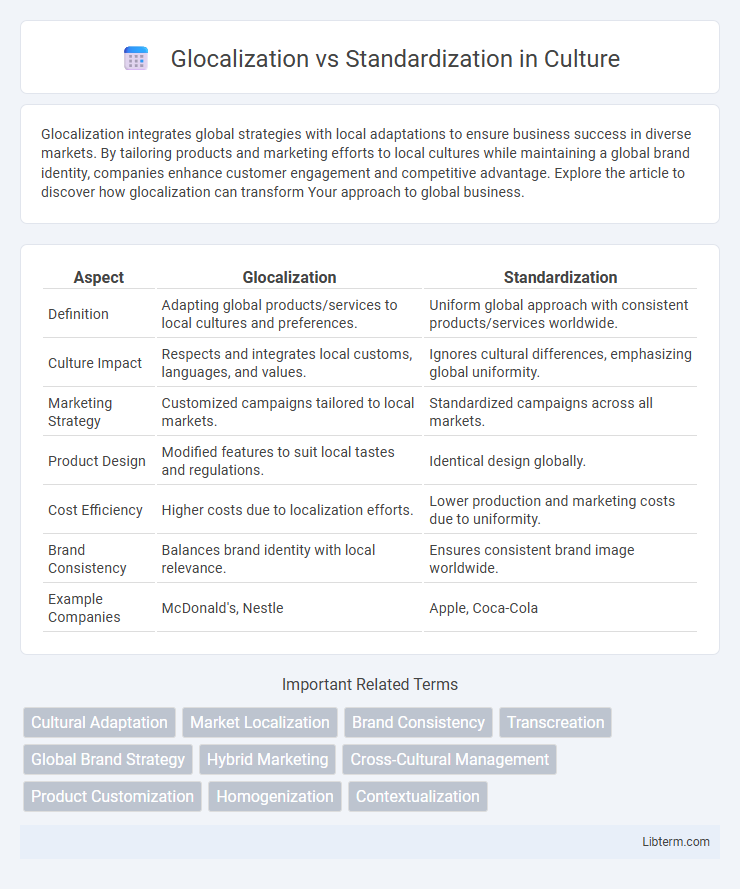
| Aspect | Glocalization | Standardization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting global products/services to local cultures and preferences. | Uniform global approach with consistent products/services worldwide. |
| Culture Impact | Respects and integrates local customs, languages, and values. | Ignores cultural differences, emphasizing global uniformity. |
| Marketing Strategy | Customized campaigns tailored to local markets. | Standardized campaigns across all markets. |
| Product Design | Modified features to suit local tastes and regulations. | Identical design globally. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs due to localization efforts. | Lower production and marketing costs due to uniformity. |
| Brand Consistency | Balances brand identity with local relevance. | Ensures consistent brand image worldwide. |
| Example Companies | McDonald's, Nestle | Apple, Coca-Cola |
Understanding Glocalization and Standardization
Glocalization involves adapting global products or services to fit local cultures, preferences, and regulations, ensuring relevance and acceptance in diverse markets. Standardization focuses on maintaining uniformity in products, branding, and marketing strategies across all regions to achieve consistency and cost efficiency. Understanding these concepts helps businesses balance global integration with local responsiveness for optimal market performance.
Key Differences Between Glocalization and Standardization
Glocalization tailors products and marketing strategies to meet local cultural, economic, and regulatory needs, enhancing customer relevance and engagement. Standardization emphasizes uniformity in products and branding across global markets to achieve cost efficiency and consistent brand identity. Key differences include flexibility, with glocalization adapting to local preferences, while standardization seeks operational simplicity through uniform offerings.
Advantages of Glocalization in Global Markets
Glocalization enhances brand relevance by adapting products and marketing strategies to local cultures, increasing customer engagement and loyalty. It allows companies to respond swiftly to regional preferences and regulatory requirements, minimizing risks and maximizing market penetration. This strategy supports sustainable growth by balancing global efficiency with local responsiveness in diverse markets.
Benefits of Standardization for Multinational Companies
Standardization enables multinational companies to achieve cost efficiencies through uniform production and marketing processes across diverse markets. Consistent brand messaging strengthens global brand recognition and customer trust, enhancing competitive advantage. Streamlined operations and centralized control reduce complexity, allowing faster decision-making and scalability in international markets.
Challenges of Implementing Glocalization Strategies
Implementing glocalization strategies presents challenges such as balancing global brand consistency with local cultural adaptation, which requires extensive market research and agile marketing approaches. Companies often face increased costs and complexity in supply chain management and product customization to meet diverse regional preferences. Furthermore, navigating varied regulatory environments and consumer behaviors demands localized expertise while maintaining overall corporate objectives.
Drawbacks of Full Standardization Approaches
Full standardization approaches in global marketing often lead to a lack of cultural sensitivity, resulting in products and campaigns that fail to resonate with local consumers. Ignoring regional preferences and social norms can cause reduced customer engagement and brand loyalty. Moreover, standardization limits flexibility, making it difficult for companies to adapt to diverse market dynamics and regulatory environments.
Industry Examples: Glocalization vs Standardization
McDonald's exemplifies glocalization by adapting menus to local tastes, such as offering the McSpicy Paneer in India, while Coca-Cola employs standardization with its uniform branding and product formula globally. Toyota balances both by maintaining core vehicle designs but tailoring marketing strategies and features to regional preferences like hybrid models popular in Europe. Fast fashion brands like Zara implement glocalization by quickly adapting collections to local trends, whereas luxury brands like Rolex rely on standardization to preserve exclusivity and consistent brand identity worldwide.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between Glocalization and Standardization
The choice between glocalization and standardization hinges on factors such as cultural differences, market diversity, and consumer preferences, which demand tailored marketing strategies for local relevance. Economic conditions and regulatory environments also drive companies to adapt products and services locally to comply with varying laws and optimize cost-efficiency. Brand consistency and scalability pressures, alongside technological capabilities and competitive dynamics, further influence whether a firm leans toward a global standardized approach or a localized, customized strategy.
Balancing Glocalization and Standardization: Best Practices
Balancing glocalization and standardization requires integrating global brand consistency with local market adaptation to maximize consumer relevance and operational efficiency. Best practices include conducting thorough market research to understand cultural preferences, implementing flexible marketing strategies that allow customization without compromising core brand identity, and leveraging technology platforms to streamline localized content management. Companies adopting this approach optimize product offerings while maintaining scalable processes, driving both global brand equity and local market success.
The Future of Global Business: Glocalization or Standardization?
The future of global business hinges on balancing glocalization and standardization strategies to maximize market reach and local relevance. Glocalization enables companies to tailor products and marketing to cultural nuances, enhancing customer engagement and brand loyalty in diverse regions. Standardization drives cost efficiency and consistent brand identity across borders, but integrating adaptive elements ensures competitiveness in dynamic global markets.
Glocalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com