Psychopolitics explores the intersection of psychology and political power, focusing on how psychological techniques influence public opinion and behavior. Understanding these mechanisms can reveal how leaders manipulate emotions and beliefs to maintain control. Discover how psychopolitics shapes societies and affects your perception in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
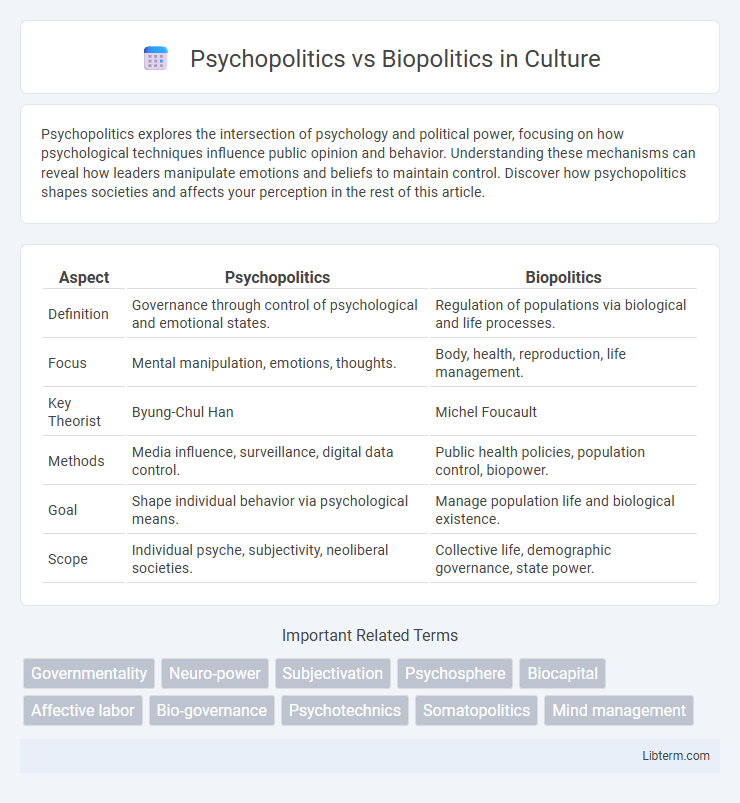
| Aspect | Psychopolitics | Biopolitics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance through control of psychological and emotional states. | Regulation of populations via biological and life processes. |
| Focus | Mental manipulation, emotions, thoughts. | Body, health, reproduction, life management. |
| Key Theorist | Byung-Chul Han | Michel Foucault |
| Methods | Media influence, surveillance, digital data control. | Public health policies, population control, biopower. |
| Goal | Shape individual behavior via psychological means. | Manage population life and biological existence. |
| Scope | Individual psyche, subjectivity, neoliberal societies. | Collective life, demographic governance, state power. |
Introduction to Psychopolitics and Biopolitics
Psychopolitics examines how psychological techniques and emotional manipulation are used to influence political behavior and maintain power, emphasizing control over mental states and individual subjectivity. Biopolitics focuses on managing populations through regulatory mechanisms related to health, life processes, and biological factors, highlighting governance of bodies and collective life. Both concepts intersect in analyzing power dynamics but differ in their focus on mental versus corporeal control within political systems.
Historical Origins and Theoretical Foundations
Psychopolitics originates from the strategic use of psychological techniques to influence populations, tracing back to post-World War II developments in propaganda and mass media control, while biopolitics, rooted in Michel Foucault's analysis, examines how states regulate populations through biopower, managing life, health, and bodies. Theoretical foundations of psychopolitics emphasize the manipulation of individual subjectivity and consumer behavior via digital technologies, contrasting with biopolitics' focus on governing population dynamics through institutions and public health policies. Both concepts reveal different modalities of power: psychopolitics targets the psyche, shaping desires and identities, whereas biopolitics governs biological processes and collective life.
Key Thinkers and Influential Texts
Michel Foucault's foundational works, particularly "Discipline and Punish" and "The History of Sexuality," illuminate the concept of biopolitics by analyzing how power regulates populations through institutions and societal norms. By contrast, Byung-Chul Han's "Psychopolitics: Neoliberalism and New Technologies of Power" explores psychopolitics, emphasizing the manipulation of individual subjectivities and emotions in digital and neoliberal contexts. These key thinkers and texts critically map the evolution from biopolitical governance focused on bodies and populations to psychopolitical control that engages psychological and affective dimensions.
Defining Biopolitics: Power Over Life
Biopolitics refers to the practice of modern states exercising control over populations through policies and regulations that manage life processes such as health, reproduction, and mortality. It encompasses governance strategies that regulate biological existence, including public health measures, demographic management, and surveillance. This form of power operates by shaping life itself, aiming to optimize and control the biological capacities of individuals and populations for political objectives.
Understanding Psychopolitics: Power Over Minds
Psychopolitics explores how power structures manipulate and control individual and collective minds through psychological techniques, shaping beliefs, desires, and behaviors to maintain dominance. This approach contrasts with biopolitics, which governs populations through regulation of bodies, health, and biological processes. Understanding psychopolitics reveals the strategic use of media, rhetoric, and surveillance to influence cognitive freedom and social conformity in contemporary societies.
Mechanisms of Control: Surveillance, Discipline, and Influence
Psychopolitics employs mechanisms of control by manipulating individual psyches through surveillance, psychological discipline, and influence tactics, targeting emotions, beliefs, and desires to shape behavior covertly. Biopolitics exerts control by regulating populations via surveillance of health, reproduction, and life processes, enforcing discipline through public policies, medical norms, and demographic management. Both approaches utilize surveillance and discipline but differ in focus: psychopolitics targets the mind and subjectivity, while biopolitics governs biological life and collective bodies.
Psychopolitics in the Digital Era
Psychopolitics in the Digital Era explores how digital technologies and big data analytics manipulate human psychology to influence political behavior and public opinion. Unlike biopolitics, which governs populations through biological and bodily control, psychopolitics targets emotions, cognition, and digital identities using algorithms on social media platforms. This paradigm exploits personalized information streams to engineer consent, shape desires, and maintain power in an increasingly connected and surveilled society.
Biopolitical Governance: Healthcare, Population, and the Body
Biopolitical governance centers on managing healthcare systems, regulating populations, and controlling the body through policies that influence biological life and health outcomes. It involves state interventions in public health, reproduction, and disease prevention, reflecting power structures that prioritize population well-being and discipline individual bodies. Key concepts include surveillance, healthcare accessibility, and the regulation of bodily autonomy within sociopolitical contexts.
Intersection, Overlap, and Conflict between Psychopolitics and Biopolitics
Psychopolitics and biopolitics intersect in their governance of human behavior, where psychopolitics manipulates individual subjectivity and emotions, while biopolitics regulates populations through biological and demographic control. The overlap emerges in techniques that simultaneously target mental states and physical bodies, such as surveillance, public health policies, and social norms enforcement. Conflict arises when the focus on individual psychological autonomy in psychopolitics challenges or undermines the systemic population-level strategies central to biopolitical power structures.
Future Implications for Society and Individual Agency
Psychopolitics leverages psychological insights and media strategies to influence individual behavior and opinions, potentially leading to more covert forms of social control compared to biopolitics, which traditionally manages populations through regulation of biology and health. The future implications for society include increased manipulation of personal identities and desires, raising ethical concerns about autonomy and consent within digital and political realms. Individual agency may be undermined as technological advancements enable more sophisticated surveillance and behavioral interventions, challenging notions of freedom and self-determination.
Psychopolitics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com