Formal rituals establish structured practices that reinforce cultural values and social bonds through symbolic actions. They often involve prescribed ceremonies, specific attire, and designated roles, creating a shared experience that fosters community identity and continuity. Discover how formal rituals shape your social interactions and cultural understanding in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
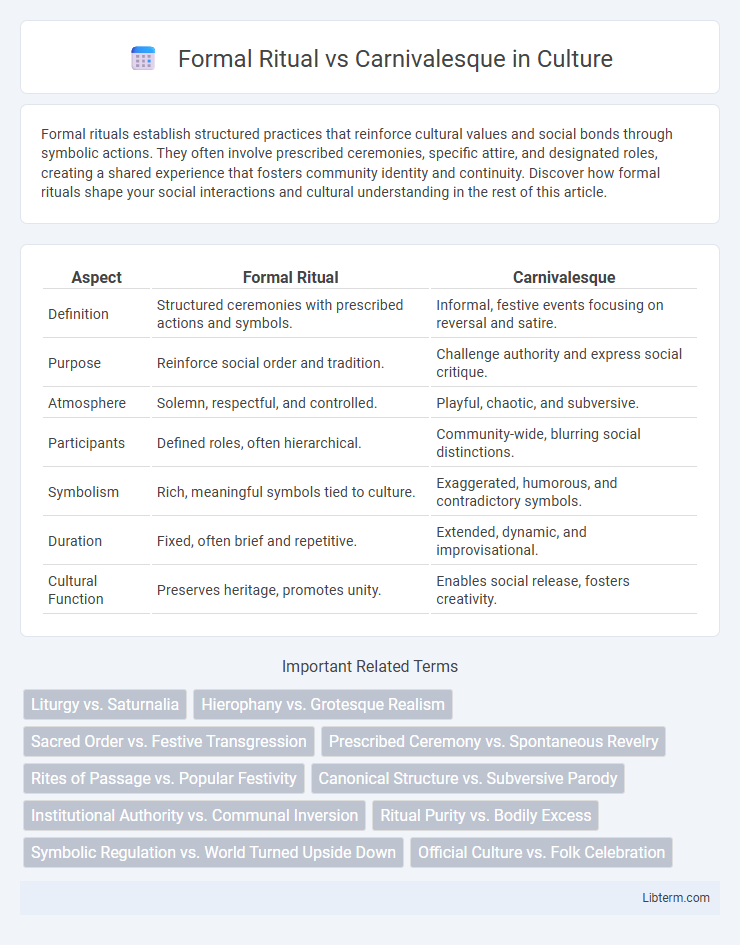
| Aspect | Formal Ritual | Carnivalesque |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured ceremonies with prescribed actions and symbols. | Informal, festive events focusing on reversal and satire. |
| Purpose | Reinforce social order and tradition. | Challenge authority and express social critique. |
| Atmosphere | Solemn, respectful, and controlled. | Playful, chaotic, and subversive. |
| Participants | Defined roles, often hierarchical. | Community-wide, blurring social distinctions. |
| Symbolism | Rich, meaningful symbols tied to culture. | Exaggerated, humorous, and contradictory symbols. |
| Duration | Fixed, often brief and repetitive. | Extended, dynamic, and improvisational. |
| Cultural Function | Preserves heritage, promotes unity. | Enables social release, fosters creativity. |
Defining Formal Ritual and Carnivalesque
Formal ritual is a structured, repetitive practice often rooted in religious or cultural traditions, characterized by prescribed actions, specific roles, and solemn significance that reinforce social hierarchies and communal values. Carnivalesque, coined by Mikhail Bakhtin, describes moments of subversion and inversion within society where norms and hierarchies are temporarily suspended, allowing for humor, chaos, and freedom of expression. These contrasting concepts highlight the tension between order and disorder, authority and liberation in cultural performances.
Historical Origins of Ritual and Carnival
The historical origins of formal ritual trace back to ancient religious and social ceremonies designed to reinforce communal values and hierarchical structures, often codified through symbolism and prescribed actions. Carnivalesque traditions stem from medieval festival practices, such as the Roman Saturnalia and European Carnival, which temporarily subverted social norms and allowed for collective revelry and mockery of authority. Both formal rituals and carnivalesque events function as cultural mechanisms but differ significantly in their approaches to social order and expression throughout history.
Core Characteristics of Formal Ritual
Formal rituals are characterized by structured sequences of actions performed with precision and consistency, often rooted in religious or cultural traditions. These rituals emphasize symbolism, hierarchy, and solemnity, reinforcing social norms and shared values within a community. Their core features include prescribed roles, repetitive enactment, and an atmosphere of reverence or disciplined comportment.
Elements of the Carnivalesque
The carnivalesque features elements such as subversion of social hierarchies, grotesque humor, and the temporary suspension of norms, creating a space where traditional authority and order are inverted. It thrives on bodily excess, chaos, and collective participation, contrasting sharply with the structured, rule-bound nature of formal rituals designed to reinforce social stability and hierarchy. These characteristics foster a liberating atmosphere where the grotesque body and festive misrule challenge dominant cultural narratives and conventions.
Social Functions and Cultural Impact
Formal rituals reinforce social hierarchies and collective identity by promoting conformity, tradition, and shared values within a structured framework. Carnivalesque practices subvert established norms, enabling temporary social liberation, satire, and creative expression that challenge authority and encourage cultural renewal. Both serve crucial social functions by balancing order with resistance, fostering community cohesion, and driving cultural evolution through contrasting modes of participation.
Order, Structure, and Authority in Ritual
Formal rituals emphasize strict order, clear structure, and the reinforcement of authority through prescribed actions and hierarchical roles, ensuring social cohesion and stability. Carnivalesque rituals subvert these norms by embracing chaos, inversion of roles, and playful disorder, temporarily challenging established power and social hierarchies. The tension between formal ritual's rigidity and carnivalesque's fluidity highlights contrasting approaches to authority and communal identity within cultural practices.
Subversion and Inversion in the Carnivalesque
The carnivalesque subverts traditional social hierarchies by inverting established norms, allowing temporary freedom from authority often rigidly maintained in formal rituals. This inversion celebrates chaos, humor, and bodily excess, contrasting the solemnity and order typical of formal rituals that reinforce societal control. By embracing parody and ambiguity, the carnivalesque destabilizes power structures, fostering a space for social critique and renewal.
Rituals in Religious and Secular Contexts
Formal rituals in religious contexts often follow strict, codified procedures that reinforce communal beliefs and sacred traditions, emphasizing order, symbolism, and reverence. In secular contexts, rituals can maintain social cohesion and mark significant life events like weddings or graduations, focusing on shared cultural values and collective identity. Both forms utilize repetition and symbolism but differ in purpose, with religious rituals seeking spiritual connection and secular rituals fostering social bonds.
Carnival as a Space for Freedom and Laughter
Carnival operates as a carnivalesque space where traditional social hierarchies and formal rituals are temporarily suspended, creating an atmosphere of freedom and collective laughter. This liminal period allows participants to subvert norms, express creativity, and engage in role reversals, fostering a sense of communal joy and liberation. The carnivalesque challenges rigid structures by emphasizing spontaneity, parody, and the celebration of the body's vitality, contrasting sharply with the solemnity and orderliness of formal ritual.
Interplay and Tension between Ritual and Carnival
Formal rituals embody structured, symbolic actions that reinforce social hierarchies and collective norms, while carnivalesque moments invert these norms through playful chaos and subversion. The interplay between ritual and carnival creates a dynamic tension where order and disorder coexist, allowing cultural renewal and social critique within traditional frameworks. This dialectic fosters a space where authority is both challenged and reaffirmed, highlighting the fluid boundaries between control and freedom in societal practices.
Formal Ritual Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com