Cultural tradition shapes societies by preserving customs, rituals, and beliefs passed down through generations, fostering a sense of identity and community. These traditions influence lifestyles, festivals, and social values, enriching cultural diversity worldwide. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your cultural heritage impacts daily life and social interactions.
Table of Comparison
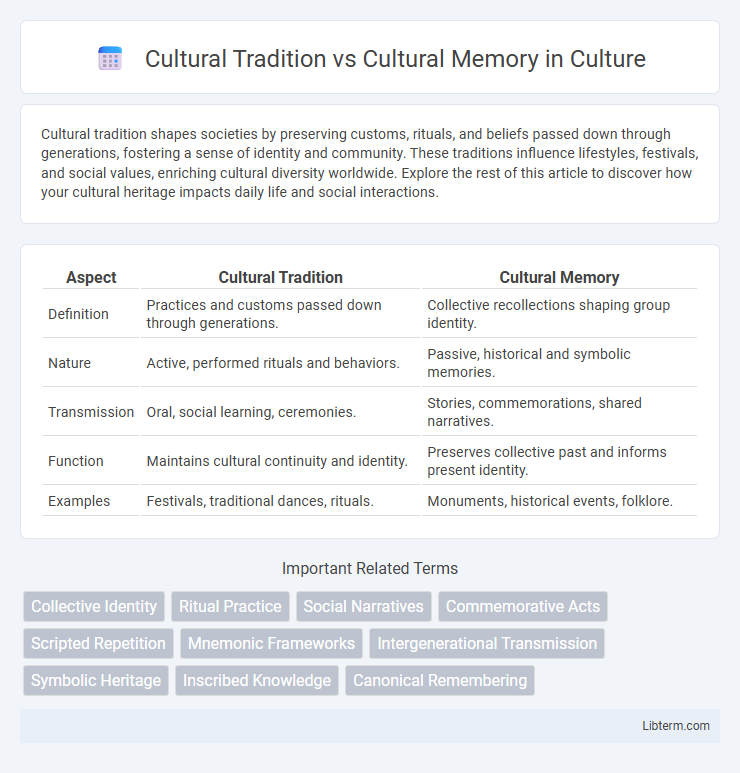
| Aspect | Cultural Tradition | Cultural Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practices and customs passed down through generations. | Collective recollections shaping group identity. |
| Nature | Active, performed rituals and behaviors. | Passive, historical and symbolic memories. |
| Transmission | Oral, social learning, ceremonies. | Stories, commemorations, shared narratives. |
| Function | Maintains cultural continuity and identity. | Preserves collective past and informs present identity. |
| Examples | Festivals, traditional dances, rituals. | Monuments, historical events, folklore. |
Defining Cultural Tradition and Cultural Memory
Cultural tradition refers to the shared practices, rituals, and customs passed down through generations that shape group identity and social cohesion. Cultural memory encompasses the collective recollection of historical events and experiences preserved through stories, symbols, and commemorations within a community. Both concepts underscore the importance of continuity and identity but differ in that tradition is actively practiced, while memory is selectively recalled and interpreted.
Origins and Evolution of Cultural Practices
Cultural tradition originates from established customs and rituals passed down through generations, maintaining continuity within a community. Cultural memory evolves as collective experiences and historical events shape the interpretation and significance of these traditions over time. This dynamic process allows cultural practices to adapt while preserving their foundational meanings.
The Role of Rituals in Tradition and Memory
Rituals serve as crucial mechanisms in both cultural tradition and cultural memory by preserving collective identity and transmitting values across generations. In cultural tradition, rituals function as repeated, codified practices that reinforce social norms and community cohesion. Within cultural memory, rituals act as symbolic reenactments that evoke shared historical experiences, sustaining a community's connection to its past through embodied expression.
Storytelling: Transmitting Memory Across Generations
Storytelling serves as a vital mechanism for transmitting cultural memory across generations by preserving collective experiences, values, and beliefs within oral narratives and rituals. Cultural tradition encompasses the ongoing practices and symbols actively maintained in communal life, while cultural memory functions as the shared repository of historical knowledge sustained through stories and commemorations. This dynamic interplay ensures intergenerational continuity, allowing communities to anchor identity and resilience in evolving social contexts.
Tangible vs. Intangible Heritage
Cultural tradition embodies the tangible heritage of artifacts, monuments, and physical sites that anchor communities to their historical identity. Cultural memory, on the other hand, preserves intangible heritage through oral histories, rituals, and collective practices passed down across generations. The interplay between tangible and intangible heritage ensures the continuity of cultural identity, highlighting the importance of safeguarding both physical relics and lived experiences.
Community Identity: Tradition vs. Collective Memory
Cultural tradition embodies the shared practices and rituals passed down through generations that actively shape community identity by reinforcing collective values and behaviors. Cultural memory, on the other hand, consists of the communal recollections of past events, shaping identity through the selective preservation and interpretation of history. The dynamic interplay between tradition and collective memory fosters a resilient community identity by merging lived experiences with inherited narratives.
The Impact of Modernization on Cultural Memory
Modernization accelerates the loss of cultural memory by prioritizing rapid technological advancements and urbanization over the preservation of traditional practices and oral histories. Digital media and globalization reshape how cultural narratives are transmitted, often diluting local identities and collective memories. The shift from communal experiences to individual digital consumption challenges the intergenerational transmission essential for maintaining cultural memory.
Preservation and Transformation of Traditions
Cultural tradition encompasses practices and customs actively preserved and transmitted across generations to maintain collective identity, while cultural memory involves the dynamic interpretation and reinterpretation of these traditions within societal contexts. Preservation of traditions often relies on rituals, storytelling, and symbolisms that anchor community values, whereas transformation occurs as cultural memory adapts these elements to contemporary realities, enabling evolution without erasing historical significance. This interplay ensures that traditions remain relevant, balancing continuity with innovation in societal cultural expression.
Memory, Trauma, and Cultural Continuity
Cultural memory serves as a collective repository of shared experiences, deeply intertwined with trauma, shaping how societies remember and process historical events. Trauma imprinted in cultural memory influences identity formation and the transmission of values across generations, reinforcing a sense of continuity despite disruption. This dynamic ensures cultural continuity by embedding lessons and emotions from past hardships into communal narratives and rituals.
Bridging Tradition and Memory in the Global Era
Bridging tradition and cultural memory in the global era requires integrating ancient practices with contemporary narratives to maintain cultural identity amidst rapid globalization. Digital platforms and transnational communication facilitate the preservation and reinterpretation of cultural memory, enabling communities to sustain traditions even as they evolve. This dynamic interplay ensures that cultural heritage remains relevant, fostering intergenerational dialogue and global cultural exchange.
Cultural Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com