Ideology shapes the core beliefs and values that influence social, political, and cultural systems worldwide. Understanding different ideologies helps you critically evaluate policies and behaviors that impact various communities. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how ideology affects your daily life and societal structures.
Table of Comparison
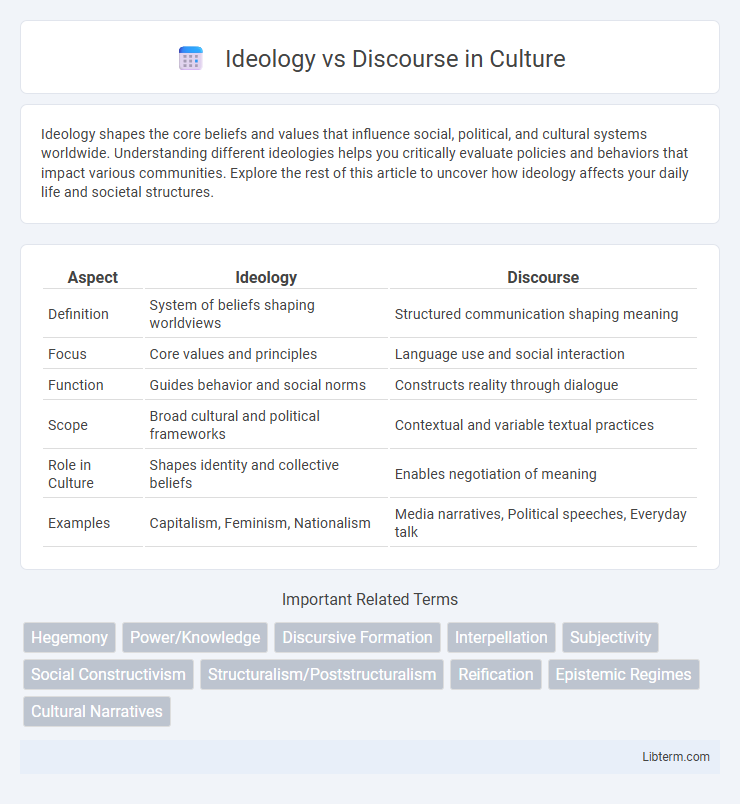
| Aspect | Ideology | Discourse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System of beliefs shaping worldviews | Structured communication shaping meaning |
| Focus | Core values and principles | Language use and social interaction |
| Function | Guides behavior and social norms | Constructs reality through dialogue |
| Scope | Broad cultural and political frameworks | Contextual and variable textual practices |
| Role in Culture | Shapes identity and collective beliefs | Enables negotiation of meaning |
| Examples | Capitalism, Feminism, Nationalism | Media narratives, Political speeches, Everyday talk |
Defining Ideology: Core Concepts
Ideology consists of a system of ideas and beliefs that shape social norms, values, and power structures within a culture. It functions as a framework influencing individual and collective perceptions, guiding behavior and legitimizing social institutions. Core concepts include hegemony, false consciousness, and the reproduction of dominant social relations through symbolic practices.
Understanding Discourse: Key Principles
Understanding discourse involves analyzing language use in social contexts, emphasizing how power relations and ideologies are embedded within communication patterns. Discourse shapes perceptions and constructs social realities by framing knowledge, identities, and norms through specific linguistic practices. Key principles include recognizing discourse as both a product and a driver of societal structures, highlighting its role in perpetuating or challenging dominant ideologies.
Historical Roots of Ideology and Discourse
Ideology stems from the Enlightenment era, rooted in structured belief systems that shape political, social, and economic perspectives, often serving as frameworks for power and control. Discourse originates from linguistic and philosophical traditions, emphasizing language practices and communication as mechanisms through which knowledge, truth, and social realities are constructed and maintained. Both concepts intersect in critical theory, where ideology reveals underlying power in discourse, and discourse unveils how ideology is reproduced through language over time.
The Relationship Between Ideology and Discourse
Ideology shapes discourse by providing the underlying beliefs and values that influence language use and communication patterns within a society. Discourse, in turn, reinforces and reproduces ideology through repeated narratives, symbols, and rhetorical strategies embedded in texts and conversations. This reciprocal relationship highlights how power dynamics and social structures are maintained and challenged through ideological discourse practices.
Ideological Influence on Discourse Formation
Ideological frameworks shape discourse by framing how ideas are expressed and understood within cultural and social contexts, guiding the selection of language, themes, and narratives. This influence determines which perspectives are emphasized or marginalized, effectively controlling meaning production and social power dynamics. As a result, discourse formation becomes a strategic process where ideology reinforces dominant values and structures through communicative practices.
Discourse as a Tool for Ideological Power
Discourse functions as a powerful tool for ideological control by shaping perceptions, beliefs, and social norms through language and communication practices. It constructs and reinforces dominant ideologies by controlling narratives, framing reality, and marginalizing alternative viewpoints. Consequently, discourse not only reflects ideological power but actively sustains and reproduces it across social institutions.
Analyzing Examples: Ideology vs Discourse in Media
Media often reflects ideology by promoting specific belief systems, such as nationalism or consumerism, through repetitive themes and imagery. Discourse shapes how these ideologies are communicated, influencing public perception by framing narratives around power, identity, and social norms. Analyzing news coverage of political events reveals ideological bias embedded in discourse patterns, highlighting the media's role in constructing social reality.
Ideology in Political Discourse
Ideology in political discourse shapes how power structures, social norms, and collective identities are constructed and maintained through language. It influences the framing of political issues, guiding public opinion and legitimizing policies by embedding specific beliefs and values into communication. Understanding ideological underpinnings reveals how political actors manipulate discourse to reinforce authority and control societal narratives.
Discursive Strategies for Challenging Ideology
Discursive strategies for challenging ideology involve critically analyzing language use to expose underlying power structures and assumptions embedded within dominant ideologies. Techniques such as deconstruction, counter-narratives, and reframing enable the disruption of hegemonic discourses by revealing contradictions and marginalized perspectives. These strategies empower individuals and groups to resist ideological control by fostering alternative meanings and promoting critical awareness in social communication.
Implications for Critical Thinking and Social Change
Ideology shapes perception by embedding a set of beliefs and values that influence how individuals interpret information, often leading to confirmation bias that hinders critical thinking. Discourse, as the medium through which ideas are communicated and contested, facilitates the negotiation of meaning and can either reinforce or challenge prevailing ideologies. Understanding the dynamic interplay between ideology and discourse is crucial for fostering critical thinking skills and driving social change by promoting reflexivity and opening spaces for alternative voices.
Ideology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com