Objective reality exists independently of individual perceptions, grounded in measurable and observable facts that remain constant regardless of personal beliefs or opinions. Understanding this concept helps you differentiate between subjective experiences and universal truths. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how objective reality shapes our worldview and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
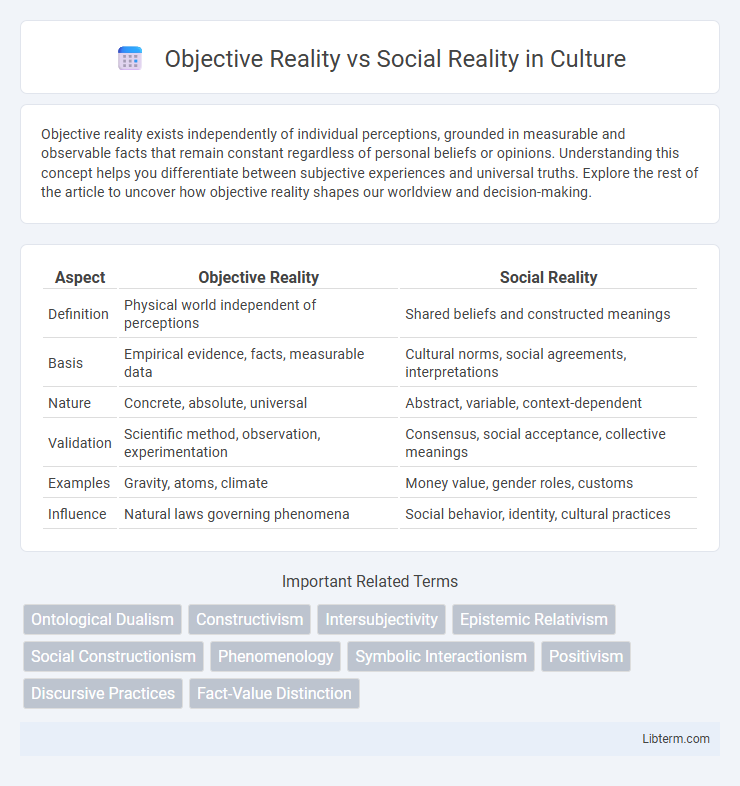
| Aspect | Objective Reality | Social Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical world independent of perceptions | Shared beliefs and constructed meanings |
| Basis | Empirical evidence, facts, measurable data | Cultural norms, social agreements, interpretations |
| Nature | Concrete, absolute, universal | Abstract, variable, context-dependent |
| Validation | Scientific method, observation, experimentation | Consensus, social acceptance, collective meanings |
| Examples | Gravity, atoms, climate | Money value, gender roles, customs |
| Influence | Natural laws governing phenomena | Social behavior, identity, cultural practices |
Defining Objective Reality: Facts Beyond Perception
Objective reality consists of facts and phenomena that exist independently of individual beliefs or perceptions, grounded in measurable, empirical evidence. It encompasses physical laws, natural processes, and observable phenomena that remain constant regardless of subjective interpretation. This contrasts with social reality, which is constructed through collective human agreements, cultural norms, and shared meanings.
Understanding Social Reality: Collective Beliefs and Constructs
Social reality is shaped by collective beliefs, norms, and shared understandings that exist within a society, influencing how individuals perceive and interact with their world. These social constructs, such as culture, language, and institutions, create a framework that defines reality beyond mere physical objects or events. Understanding social reality requires analyzing the ways in which group consensus and social context mold behaviors, values, and meanings accepted as "real" within a community.
Key Differences Between Objective and Social Reality
Objective reality consists of facts and phenomena that exist independently of human perception, grounded in physical evidence and measurable data. Social reality, by contrast, is constructed through collective human agreement, encompassing norms, values, and meanings shaped by cultural and social interactions. The key difference lies in objectivity being universal and verifiable, while social reality is subjective, variable, and context-dependent, influenced by language, beliefs, and social institutions.
Philosophical Foundations: Ontology and Epistemology
Objective reality refers to the existence of entities and truths independent of human perception, grounded in ontological realism asserting that reality has a fixed, mind-independent structure. Social reality, in contrast, emerges from collective human agreement and interpretation, emphasizing constructivist ontology where entities exist through shared beliefs and social practices. Epistemologically, objective reality relies on empirical observation and logical reasoning to acquire knowledge, while social reality is understood through interpretive methods analyzing meanings and social contexts.
The Role of Perception in Shaping Reality
Perception plays a crucial role in shaping both objective and social reality by filtering information through individual experiences and cognitive biases. While objective reality exists independently of human interpretation, social reality emerges from collective agreement and shared meanings constructed through perception. This interplay highlights how subjective perception influences understanding and interaction within social contexts despite the presence of an external objective world.
Social Constructs: Language, Culture, and Meaning
Social constructs such as language, culture, and meaning shape social reality by influencing how individuals interpret and engage with the world around them. Language serves as a tool for communication and conveys shared cultural values, while culture provides the framework through which meaning is created and sustained. These constructs mediate perception and social interaction, differentiating social reality from objective reality, which exists independent of human interpretation.
Science, Evidence, and Objective Truth
Objective reality consists of facts and phenomena that exist independently of human perception, grounded in empirical evidence and scientific methods. Science systematically investigates this reality through observation, experimentation, and verification, aiming to uncover objective truths that remain consistent regardless of social or cultural beliefs. Social reality, shaped by human interactions and shared understandings, often contrasts with objective reality when beliefs or narratives diverge from evidence-based facts.
The Impact of Social Reality on Identity and Behavior
Social reality, shaped by shared beliefs, norms, and cultural contexts, profoundly influences individual identity and behavior by creating frameworks through which people interpret their experiences and interactions. Unlike objective reality, which exists independently of perception, social reality molds self-concept and social roles, guiding behavior to conform with group expectations and societal standards. This dynamic interplay highlights the importance of social constructs in shaping how individuals see themselves and act within their communities.
Conflicts and Overlaps: When Realities Collide
Objective reality, based on measurable facts and independent of human perception, often clashes with social reality, which is constructed through shared beliefs and cultural norms. Conflicts arise when subjective interpretations challenge empirical evidence, leading to disputes in areas like science, law, and ethics. Overlaps occur as social consensus shapes the acceptance of objective findings, influencing policy-making, collective behavior, and societal values.
Implications for Society: Navigating Truth in a Complex World
Objective reality represents facts and events independent of human perception, while social reality consists of shared beliefs and cultural norms shaped by collective agreement. The interplay between these realities influences societal structures, legal systems, and public policies, as communities often base decisions on socially constructed truths rather than empirical evidence alone. Navigating truth in a complex world demands critical thinking and media literacy to discern objective facts amidst powerful social narratives and misinformation.
Objective Reality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com