Dramatization enhances storytelling by bringing scenes to life through expressive acting, dialogue, and vivid imagery. It deepens audience engagement and emotional connection by transforming written narratives into compelling visual or performative experiences. Discover how dramatization can elevate your storytelling by exploring the techniques discussed in the rest of this article.
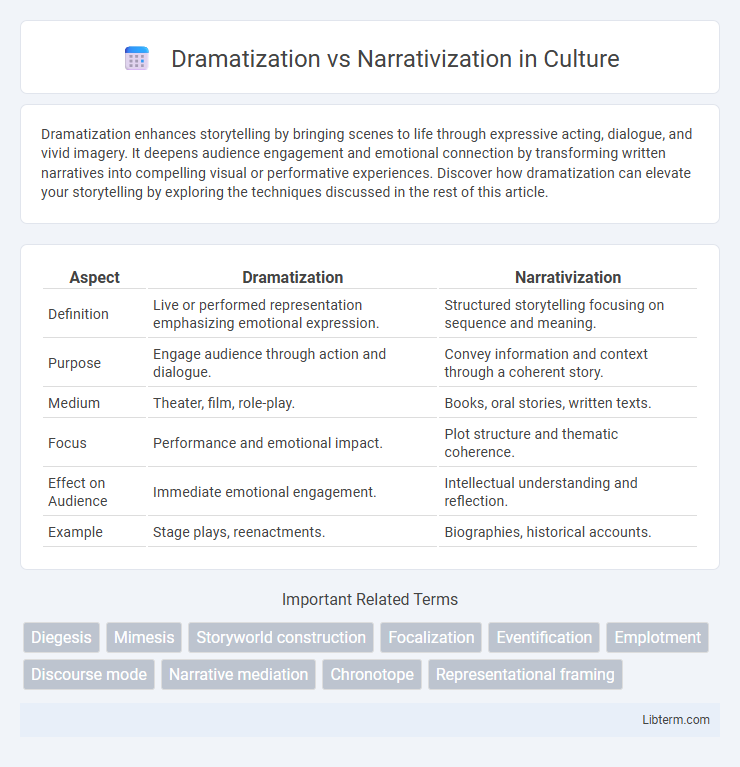
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dramatization | Narrativization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Live or performed representation emphasizing emotional expression. | Structured storytelling focusing on sequence and meaning. |
| Purpose | Engage audience through action and dialogue. | Convey information and context through a coherent story. |
| Medium | Theater, film, role-play. | Books, oral stories, written texts. |
| Focus | Performance and emotional impact. | Plot structure and thematic coherence. |
| Effect on Audience | Immediate emotional engagement. | Intellectual understanding and reflection. |
| Example | Stage plays, reenactments. | Biographies, historical accounts. |
Understanding Dramatization: Definition and Scope
Dramatization involves transforming real-life events or abstract concepts into vivid, emotionally engaging scenes that emphasize conflict, characters, and tension to enhance audience engagement. It extends beyond mere storytelling by incorporating theatrical techniques such as dialogue, pacing, and visual imagery to create immersive experiences. Understanding its scope reveals its use in education, media, and psychology to convey complex messages more effectively through experiential learning and empathy development.
What Is Narrativization? An Analytical Overview
Narrativization refers to the process of structuring events or information into a coherent narrative, emphasizing cause-and-effect relationships, temporal sequences, and character development to enhance understanding. It transforms raw data or fragmented incidents into meaningful stories that provide context and engage the audience cognitively and emotionally. This technique is crucial in fields such as media studies, psychology, and communication, where constructing a narrative helps to interpret and convey complex experiences effectively.
Core Differences Between Dramatization and Narrativization
Dramatization involves presenting events through performance, emphasizing emotional expression and visual spectacle to engage audiences, while narrativization structures events into coherent stories by organizing facts and experiences into a meaningful sequence. The core difference lies in dramatization's focus on action and dialogue to evoke immediacy, contrasting with narrativization's emphasis on causality, context, and thematic development. Dramatization often relies on theatrical techniques and character interactions, whereas narrativization uses storytelling frameworks to interpret and convey information.
The Role of Structure in Dramatization vs Narrativization
Dramatization relies on a structured sequence of events emphasizing conflict, tension, and resolution to engage audiences emotionally and heighten suspense. Narrativization organizes information into a coherent storyline that connects events with cause-and-effect relationships for clarity and meaning. The role of structure in dramatization centers on dynamic pacing and character-driven moments, while narrativization depends on logical flow and thematic coherence.
Emotional Impact: Dramatization Compared to Narrativization
Dramatization intensifies emotional impact by vividly portraying conflicts and emotions through dynamic scenes, characters, and dialogue, creating an immersive experience that evokes stronger feelings. Narrativization provides emotional resonance by structuring events into a coherent story, allowing audiences to connect with the underlying meaning and themes over time. The immediate, heightened emotional engagement seen in dramatization contrasts with the reflective, interpretive emotional response nurtured by narrativization.
Techniques Employed in Dramatization
Dramatization employs techniques such as dialogue enactment, character impersonation, and expressive body language to convey emotions and conflicts vividly. It integrates visual and auditory elements like stage props, costume, and tone modulation to create immersive storytelling experiences. These methods enhance audience engagement by transforming narrative content into dynamic, performative expressions.
Storytelling Strategies in Narrativization
Narrativization in storytelling strategies emphasizes structured plots, character development, and temporal sequences to convey meaning and engage audiences. This approach prioritizes coherence and causal relationships, allowing listeners to infer themes and emotions through enacted events rather than mere description. Unlike dramatization, which relies heavily on performative expression, narrativization leverages linguistic and narrative techniques to create immersive and relatable stories.
Real-World Examples: Dramatization vs Narrativization
Dramatization emphasizes emotional engagement through vivid scenes and dialogues, as seen in films like "The Social Network," which highlights conflicts and character dynamics surrounding Facebook's origin. Narrativization organizes information into coherent storylines, exemplified by documentaries like "Inside Bill's Brain," which chronologically explores Bill Gates's life and philanthropic efforts. Both approaches enhance understanding but differ in technique: dramatization immerses viewers emotionally, while narrativization provides structured, informative storytelling.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Dramatize or Narrativize
Choosing between dramatization and narrativization depends on the desired emotional engagement and clarity of the message. Dramatization works best for immersive storytelling that highlights conflict and character emotions, while narrativization suits conveying complex information or sequences with clear, concise summaries. Analyzing audience preferences and content goals ensures the most effective communication strategy.
Implications for Writers and Content Creators
Dramatization emphasizes vivid, action-driven scenes that engage audiences emotionally by showing events in real-time, while narrativization involves structured storytelling and thematic coherence through explanation and reflection. Writers and content creators must balance these techniques to enhance audience immersion and understanding, leveraging dramatization for emotional impact and narrativization for clarity and context. Mastering this balance unlocks deeper engagement, improves message retention, and broadens creative expression in multimedia and literary works.
Dramatization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com