Direct communication enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings by conveying messages straightforwardly. It fosters trust and efficiency in both personal and professional interactions, ensuring your intentions are clearly understood. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for mastering direct communication.
Table of Comparison
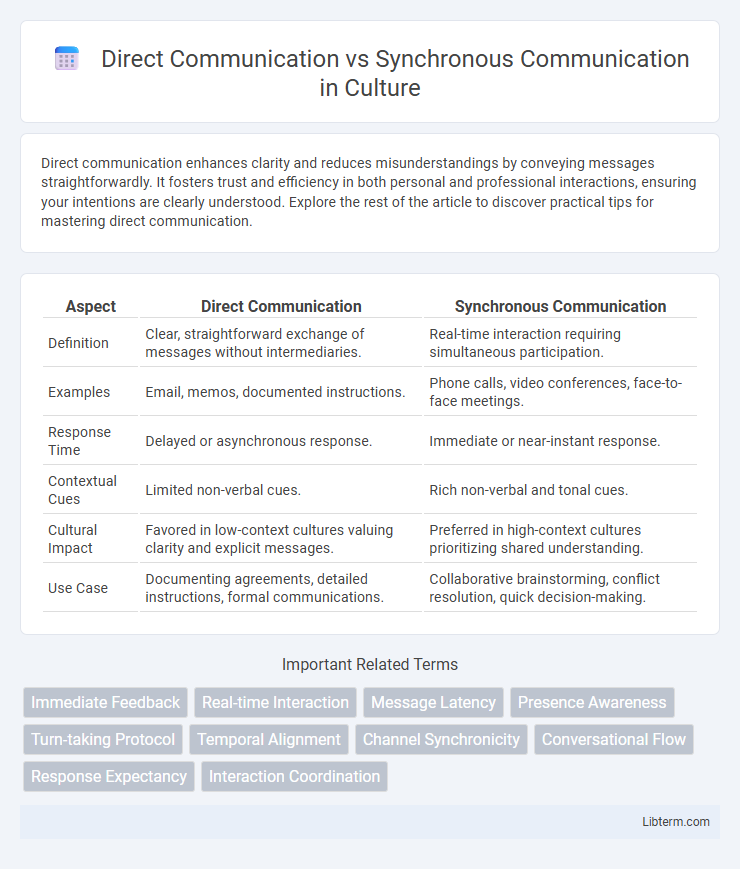
| Aspect | Direct Communication | Synchronous Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clear, straightforward exchange of messages without intermediaries. | Real-time interaction requiring simultaneous participation. |
| Examples | Email, memos, documented instructions. | Phone calls, video conferences, face-to-face meetings. |
| Response Time | Delayed or asynchronous response. | Immediate or near-instant response. |
| Contextual Cues | Limited non-verbal cues. | Rich non-verbal and tonal cues. |
| Cultural Impact | Favored in low-context cultures valuing clarity and explicit messages. | Preferred in high-context cultures prioritizing shared understanding. |
| Use Case | Documenting agreements, detailed instructions, formal communications. | Collaborative brainstorming, conflict resolution, quick decision-making. |
Understanding Direct Communication
Direct communication involves the immediate exchange of information between parties without intermediaries, ensuring clarity and reducing misunderstandings. It enables real-time feedback, fostering stronger relationships and efficient decision-making. Understanding direct communication is essential for improving interpersonal skills and enhancing collaboration in both personal and professional settings.
Defining Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication is defined as real-time interaction where all participants engage simultaneously, such as phone calls, video conferences, or live chats. This mode ensures immediate feedback and dynamic exchange, enhancing clarity and collaboration efficiency. Unlike direct communication, which emphasizes personal or one-on-one interaction, synchronous communication includes both personal and group engagements dependent on real-time responsiveness.
Key Features of Direct Communication
Direct communication involves immediate, face-to-face or real-time interactions where messages are exchanged without intermediaries, ensuring clarity and prompt feedback. Key features include personal engagement, verbal and non-verbal cues, and reduced chances of misinterpretation, enhancing the effectiveness of information transfer. This communication style is crucial in high-stakes environments such as crisis management and collaborative teamwork where swift decisions are necessary.
Core Characteristics of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication involves real-time interaction where participants exchange information simultaneously, facilitating immediate feedback and collaborative decision-making. Core characteristics include direct engagement, often through verbal or video channels, enabling instantaneous clarification and dynamic dialogue. This mode enhances responsiveness and builds stronger interpersonal connections by allowing participants to interpret nonverbal cues and adapt messages accordingly.
Advantages of Direct Communication
Direct communication enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings by enabling immediate feedback between participants. It accelerates decision-making processes through real-time interaction, minimizing delays caused by message transmission. This approach fosters stronger personal connections and trust, improving collaboration and overall team dynamics.
Benefits of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication ensures real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and clarification, which enhances collaboration and decision-making efficiency. It fosters stronger team cohesion and reduces misunderstandings by allowing participants to interpret tone and non-verbal cues. This communication style is ideal for complex discussions and urgent problem-solving in dynamic work environments.
Challenges in Direct Communication
Direct communication often faces challenges such as misunderstandings due to lack of non-verbal cues, leading to misinterpretation of tone or intent. The immediacy required can create pressure, hindering thoughtful responses and increasing the risk of conflict. Differences in communication styles and cultural backgrounds further complicate clarity, making effective direct communication difficult to achieve consistently.
Limitations of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication demands real-time interaction, which can cause scheduling challenges across different time zones and limit flexibility for participants. The necessity for immediate responses increases pressure, potentially reducing message clarity and thoughtful decision-making. Technical issues like connectivity problems can further disrupt synchronous exchanges, impacting productivity and collaboration efficiency.
Choosing the Right Communication Method
Choosing the right communication method depends on the context, urgency, and complexity of the information being exchanged. Direct communication, such as face-to-face conversations or phone calls, ensures immediate feedback and clarity, making it ideal for resolving complex issues or sensitive topics quickly. Synchronous communication methods like video conferencing or instant messaging facilitate real-time collaboration while allowing teams to maintain a structured workflow, especially in remote or hybrid work environments.
Future Trends in Communication Methods
Future trends in communication methods emphasize the integration of direct communication through AI-driven platforms enabling real-time interactions without intermediaries. Synchronous communication is evolving with advancements in augmented reality and immersive virtual environments, facilitating more engaging, face-to-face digital experiences. Hybrid models combining direct and synchronous techniques are expected to enhance collaboration efficiency in remote and distributed workforces.
Direct Communication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com