Auditory culture shapes how societies interpret sound, music, and communication, influencing human interaction and cultural identity deeply. Understanding the nuances of auditory experiences reveals the profound impact of sound on memory, emotion, and social cohesion. Explore the rest of the article to discover how auditory culture shapes your perception and daily life.
Table of Comparison
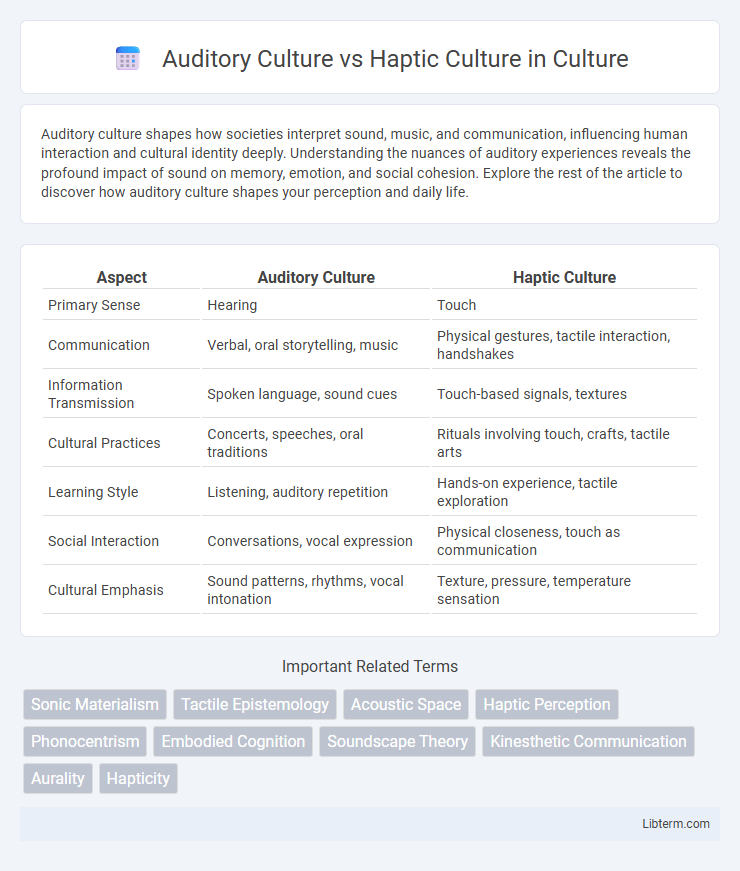
| Aspect | Auditory Culture | Haptic Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Sense | Hearing | Touch |
| Communication | Verbal, oral storytelling, music | Physical gestures, tactile interaction, handshakes |
| Information Transmission | Spoken language, sound cues | Touch-based signals, textures |
| Cultural Practices | Concerts, speeches, oral traditions | Rituals involving touch, crafts, tactile arts |
| Learning Style | Listening, auditory repetition | Hands-on experience, tactile exploration |
| Social Interaction | Conversations, vocal expression | Physical closeness, touch as communication |
| Cultural Emphasis | Sound patterns, rhythms, vocal intonation | Texture, pressure, temperature sensation |
Introduction to Auditory and Haptic Cultures
Auditory culture centers on sound as the primary medium for communication, memory, and social interaction, emphasizing listening and oral traditions in human experience. Haptic culture, by contrast, prioritizes touch and tactile sensations, shaping behavior and cognition through physical contact and sensory engagement with the environment. Understanding these cultures reveals how sensory modalities influence perception, communication styles, and cultural identity across different societies.
Defining Auditory Culture
Auditory culture centers on the primacy of sound in communication, perception, and social interaction, emphasizing listening as a key sensory experience. It shapes how communities interpret meaning through spoken language, music, and environmental sounds, influencing cognitive processes and memory. This culture contrasts with haptic culture by prioritizing acoustic signals over tactile or visual cues, highlighting the significance of auditory stimuli in human behavior and cultural expression.
Understanding Haptic Culture
Haptic culture emphasizes tactile experiences and physical interactions as primary means of communication and knowledge transmission, contrasting with auditory culture's reliance on spoken language and sound. Understanding haptic culture involves recognizing how touch, texture, and bodily engagement shape social practices, identity, and memory within communities. This sensory-based approach reveals the deep connections between materiality and meaning that auditory-dominant frameworks often overlook.
Historical Perspectives on Sensory Dominance
Auditory culture, dominant in ancient oral societies, emphasized hearing as the primary mode of communication, shaping traditions and social interactions through spoken language and sound-based rituals. In contrast, haptic culture prioritized touch and physical sensation, evident in societies relying on tactile knowledge, crafts, and embodied practices before widespread literacy. Historical shifts, such as the advent of writing and print technology, marked transitions from predominantly auditory to more visually and haptically oriented cultures, reflecting changing sensory hierarchies over time.
Communication Modes in Auditory and Haptic Cultures
Auditory culture emphasizes communication through spoken language, tone, rhythm, and sound patterns, enabling rapid information exchange and emotional expression in social interactions. Haptic culture relies on touch as a primary mode of communication, using physical contact such as handshakes, hugs, and gestures to convey meaning, establish trust, and create social bonds. These distinct communication modes shape cognitive processing and the interpretation of social cues, influencing how individuals experience and relate to their environment.
Social Interactions: Listening vs Touch
Auditory culture emphasizes social interactions through listening, where verbal communication and sound cues shape relationships and community bonds. Haptic culture prioritizes touch as a fundamental mode of social connection, using physical contact to convey emotions, trust, and social hierarchies. Understanding these sensory-based communication methods highlights how societies organize social behavior and intimacy differently based on dominant sensory experiences.
Impacts on Learning and Education
Auditory culture emphasizes listening and verbal communication, fostering skills in language acquisition, memory retention, and oral instruction, which benefits auditory learners in traditional classroom settings. Haptic culture prioritizes touch and physical interaction, enhancing kinesthetic learning and experiential knowledge through hands-on activities and tactile exploration, critical in vocational training and early childhood education. Integrating both cultures in education promotes cognitive diversity, improving engagement and comprehension by addressing different sensory processing preferences.
Technological Influences on Sensory Experience
Technological advancements have profoundly reshaped auditory culture by enhancing sound reproduction through devices like high-fidelity speakers and headphones, expanding the way people engage with music and spoken word. In contrast, haptic culture has been transformed by innovations such as haptic feedback in smartphones and virtual reality systems, which simulate tactile sensations and create immersive experiences. These technologies bridge the gap between sensory input and digital interaction, altering how users perceive and interact with their environments.
Cultural Identity and Sensory Preferences
Auditory culture, shaped by oral traditions and spoken language, emphasizes listening and vocal expression as central to cultural identity, fostering strong community bonds through shared sounds and speech patterns. In contrast, haptic culture prioritizes touch and physical interaction, influencing sensory preferences by valuing tactile experiences in social rituals and communication. These differing sensory emphases create distinct cultural identities by shaping how individuals perceive, interpret, and engage with their social environments.
Future Trends in Sensory Cultures
Future trends in sensory cultures highlight the growing integration of auditory and haptic experiences, driven by advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. Emerging sensory interfaces prioritize multisensory engagement, blending soundscapes with tactile feedback to create immersive environments for education, entertainment, and communication. Increasing research in neuroscience emphasizes the transmodal perception of auditory and haptic stimuli, shaping innovations that redefine human interaction with digital and physical spaces.
Auditory Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com