Political authority defines the legitimate power that enables governments to create and enforce laws, maintaining social order and security. This authority is often derived from constitutions, legal frameworks, and the consent of the governed, ensuring that power is exercised responsibly. Explore the rest of the article to understand how political authority shapes societies and impacts your daily life.
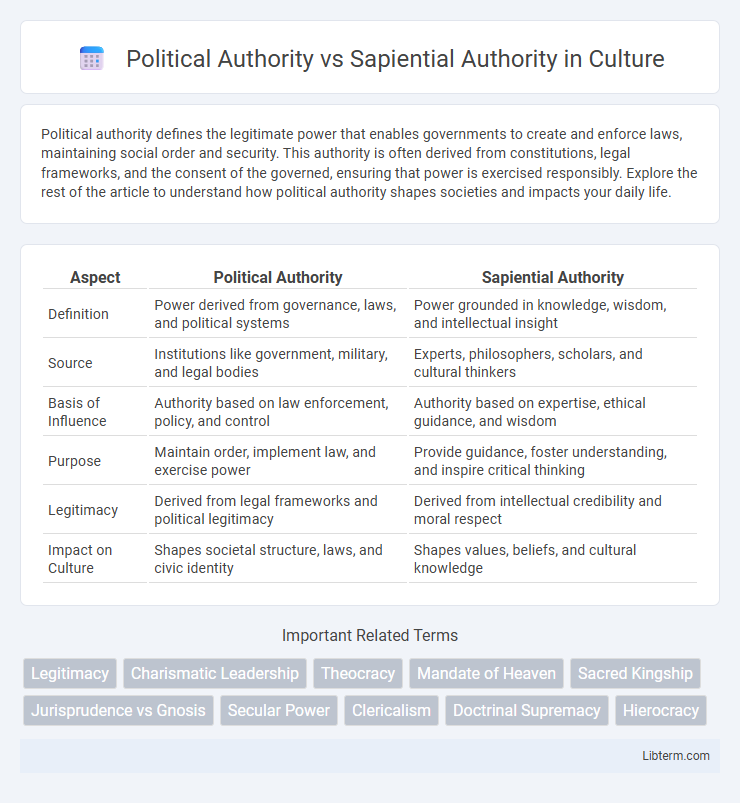
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Authority | Sapiential Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power derived from governance, laws, and political systems | Power grounded in knowledge, wisdom, and intellectual insight |
| Source | Institutions like government, military, and legal bodies | Experts, philosophers, scholars, and cultural thinkers |
| Basis of Influence | Authority based on law enforcement, policy, and control | Authority based on expertise, ethical guidance, and wisdom |
| Purpose | Maintain order, implement law, and exercise power | Provide guidance, foster understanding, and inspire critical thinking |
| Legitimacy | Derived from legal frameworks and political legitimacy | Derived from intellectual credibility and moral respect |
| Impact on Culture | Shapes societal structure, laws, and civic identity | Shapes values, beliefs, and cultural knowledge |
Defining Political Authority: Power and Governance
Political authority refers to the legitimate power vested in institutions or individuals to create, enforce, and interpret laws within a defined political framework. It involves governance mechanisms that regulate the behavior of citizens and maintain social order through policies and administrative control. Unlike sapiential authority, which is based on knowledge and expertise, political authority derives its strength from legal-rational legitimacy and institutional structures.
Understanding Sapiential Authority: Wisdom and Knowledge
Sapiential authority derives its legitimacy from accumulated wisdom and deep knowledge, emphasizing insight over formal power structures. It often manifests in cultural, spiritual, or academic contexts where experiences and intellectual depth guide decision-making. Unlike political authority, which is anchored in governance and law enforcement, sapiential authority commands respect through expertise and moral understanding.
Historical Perspectives on Authority Types
Historical perspectives on political authority reveal its foundation in laws, governance structures, and coercive power, often linked to rulers, governments, and state institutions. Sapiential authority, rooted in wisdom, knowledge, and moral insight, has traditionally been embodied by philosophers, religious leaders, and scholars, influencing societies through intellectual and ethical guidance. Distinctions between these authority types are evident in historical shifts, such as the decline of feudal monarchies' political power versus the rise of Enlightenment thinkers' sapiential influence on modern democratic principles.
Political Leadership vs. Scholarly Influence
Political leadership wields power through formal institutions and governance structures, directing public policy and societal order. Scholarly influence stems from intellectual expertise and the production of knowledge, shaping societal values and ideas through research and education. While political authority enforces decisions via laws and regulations, sapiential authority guides through moral and epistemic credibility within academic and cultural spheres.
Sources and Legitimacy of Political Authority
Political authority derives its legitimacy primarily from institutional frameworks such as constitutions, legal systems, and electoral processes established by the state, which grant rulers the formal right to govern. Sapiential authority, in contrast, is grounded in recognized wisdom, expertise, or moral insight, often emanating from religious, philosophical, or scholarly traditions rather than codified legal institutions. The source of political authority is thus external and procedural, relying on consent and law, while sapiential authority is internal and cognitive, depending on the perceived knowledge and ethical integrity of the individual or group.
The Foundations of Sapiential Authority
Sapiential authority is grounded in knowledge, wisdom, and expertise, drawing legitimacy from intellectual and moral understanding rather than coercive power. It relies on the trust in an individual's or institution's ability to provide insightful guidance, ethical judgment, and profound comprehension of complex issues. This form of authority contrasts with political authority, which is based on formal structures, legal frameworks, and the capacity to enforce rules through power.
Conflicts Between Political and Sapiential Authorities
Conflicts between political authority and sapiential authority often arise when governing bodies impose policies that contradict established expert knowledge or ethical norms. Political leaders may prioritize power retention or popular support, while sapiential authorities emphasize wisdom, scientific evidence, and moral considerations. This tension can lead to public distrust, policy gridlock, and challenges in balancing effective governance with informed decision-making.
Case Studies: When Wisdom Challenges Power
Political authority often derives legitimacy from institutional power and governance structures, while sapiential authority stems from recognized wisdom and moral insight. Case studies, such as the civil disobedience led by Mahatma Gandhi against British colonial rule, highlight how sapiential authority can challenge and reshape political authority by appealing to ethical principles and popular conscience. In contemporary contexts, figures like Nelson Mandela illustrate the transformative power of wisdom challenging entrenched political systems to achieve justice and societal reform.
Reconciling Political and Sapiential Roles in Society
Reconciling political authority and sapiential authority requires understanding their distinct but complementary roles: political authority governs societal order and public policy, while sapiential authority offers ethical guidance and wisdom rooted in cultural or philosophical traditions. Effective governance emerges when political leaders integrate sapiential insights to inform just decision-making, fostering legitimacy and societal cohesion. This synthesis facilitates a balance where political power is exercised with moral responsibility, enhancing trust and stability within communities.
The Future of Authority: Wisdom in Political Decision-Making
Political authority derives from institutional power and legal legitimacy, whereas sapiential authority is grounded in wisdom and ethical insight. Future political decision-making demands integrating sapiential authority to foster informed policies that anticipate long-term societal impacts. Emphasizing wisdom within governance can enhance legitimacy and public trust by aligning political actions with ethical and sustainable principles.
Political Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com