Cultural dynamism represents the continuous evolution and adaptation of cultural practices, beliefs, and expressions within societies. It drives social innovation and fosters resilience by blending tradition with change, influencing identity and community cohesion. Explore the rest of this article to understand how cultural dynamism shapes your world and the future of societies globally.
Table of Comparison
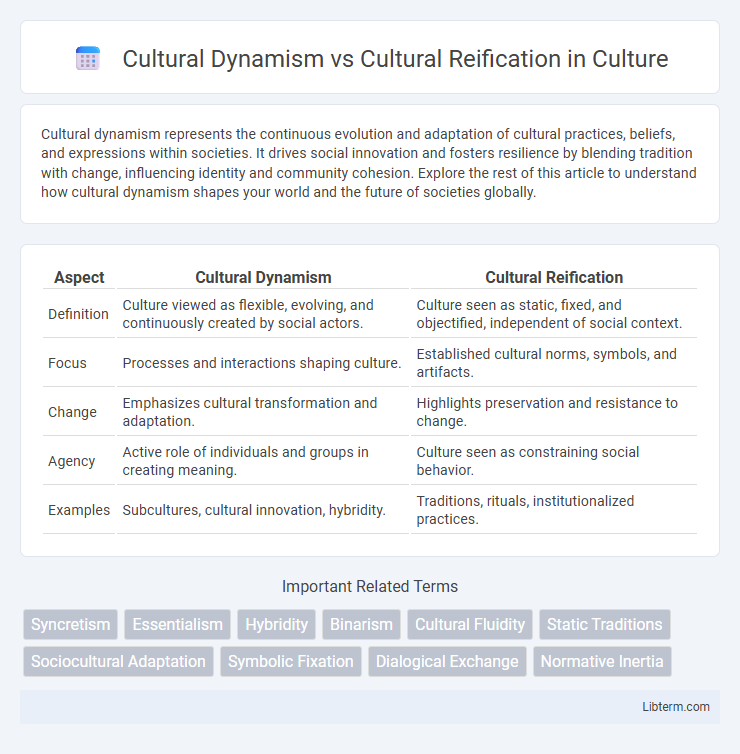
| Aspect | Cultural Dynamism | Cultural Reification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture viewed as flexible, evolving, and continuously created by social actors. | Culture seen as static, fixed, and objectified, independent of social context. |
| Focus | Processes and interactions shaping culture. | Established cultural norms, symbols, and artifacts. |
| Change | Emphasizes cultural transformation and adaptation. | Highlights preservation and resistance to change. |
| Agency | Active role of individuals and groups in creating meaning. | Culture seen as constraining social behavior. |
| Examples | Subcultures, cultural innovation, hybridity. | Traditions, rituals, institutionalized practices. |
Understanding Cultural Dynamism
Cultural dynamism refers to the continuous process of change, adaptation, and innovation within cultures, driven by social interaction, technology, and globalization. This concept emphasizes culture as fluid and evolving, contrasting with cultural reification, which treats culture as static and unchanging. Understanding cultural dynamism is crucial for recognizing how identities, practices, and meanings transform over time in response to internal and external influences.
Defining Cultural Reification
Cultural reification refers to the process of treating culture as a fixed, concrete entity rather than a fluid, evolving phenomenon shaped by social interactions. This concept emphasizes how cultural symbols, values, and practices become objectified and perceived as immutable, limiting the recognition of cultural dynamism and transformation. Understanding cultural reification is essential for analyzing how societies often resist change by solidifying traditions into rigid frameworks.
Historical Roots of Cultural Evolution
Historical roots of cultural evolution reveal a dynamic interplay between cultural dynamism and cultural reification, where societies continuously adapt traditions while some practices become rigidly fixed through institutionalization. Anthropological studies trace cultural dynamism to fluid exchanges and innovations in response to environmental and social changes, contrasting with cultural reification's preservation of norms as immutable symbols of identity. Understanding these historical patterns enables deeper insights into how civilizations balance adaptation and stability in their cultural development.
The Dangers of Viewing Culture as Static
Viewing culture as static leads to cultural reification, which oversimplifies dynamic social practices into fixed, unchanging entities. This perspective risks marginalizing evolving identities and stifling innovation within multicultural societies. Emphasizing cultural dynamism acknowledges continuous transformation, fostering inclusivity and adaptability in global interactions.
Agents of Cultural Change
Agents of cultural change drive cultural dynamism by introducing innovations, challenging existing norms, and facilitating adaptation within societies. These agents include individuals, social groups, institutions, and environmental factors that actively reshape cultural meanings and practices, fostering continuous evolution. In contrast, cultural reification occurs when cultural elements are rigidly fixed and treated as immutable, undermining the fluidity that agents of change promote.
Reification’s Impact on Social Stereotypes
Cultural reification solidifies social stereotypes by transforming fluid cultural practices into fixed, unchangeable norms, leading to the perpetuation of biased and oversimplified group identities. This process reinforces existing power structures by limiting individual and collective identities to rigid categories, which stifles cultural innovation and diversity. Social stereotypes rooted in cultural reification contribute to discrimination and social exclusion by promoting homogeneous cultural interpretations.
Cultural Dynamism in the Age of Globalization
Cultural dynamism in the age of globalization reflects the continuous evolution and hybridization of cultural practices driven by increased cross-cultural interactions and technology. Global networks enable the rapid exchange of ideas, languages, and traditions, fostering innovation and cultural fluidity that challenge static cultural definitions. This dynamic process enhances cultural diversity while promoting adaptive identities within interconnected global societies.
The Role of Education in Shaping Cultural Perceptions
Education acts as a critical catalyst for cultural dynamism by encouraging critical thinking and fostering adaptability to evolving social norms. It challenges cultural reification by deconstructing fixed stereotypes and promoting inclusive narratives that reflect diverse identities. Through curricula that emphasize intercultural competence and historical context, educational systems reshape cultural perceptions and support a fluid understanding of cultural identities.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies in cultural dynamism reveal how societies continuously adapt traditions, such as Japan's evolving tea ceremony reflecting modern influences while preserving heritage. In contrast, cultural reification is evident in museums that freeze indigenous artifacts as static exhibits, often detaching them from living cultures. These real-world applications highlight the tension between culture as a living process versus culture as a fixed identity.
Moving Toward a Dynamic Cultural Perspective
Moving toward a dynamic cultural perspective emphasizes culture as an evolving, fluid process shaped by ongoing social interactions rather than a fixed set of static traits. This approach highlights cultural dynamism, where identities and practices continuously adapt to changing contexts, contrasting with cultural reification that solidifies culture into unchanging stereotypes. Embracing cultural dynamism enables more accurate analysis of social behaviors and promotes inclusivity by recognizing diversity within cultures.
Cultural Dynamism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com