Orality is the practice and tradition of conveying knowledge, culture, and history through spoken word rather than written texts, deeply rooted in human communication since ancient times. This mode of information transfer emphasizes memory, storytelling, and communal participation, shaping societies and preserving collective identity across generations. Discover how orality continues to influence modern communication and enriches Your understanding of human interaction in the following article.
Table of Comparison
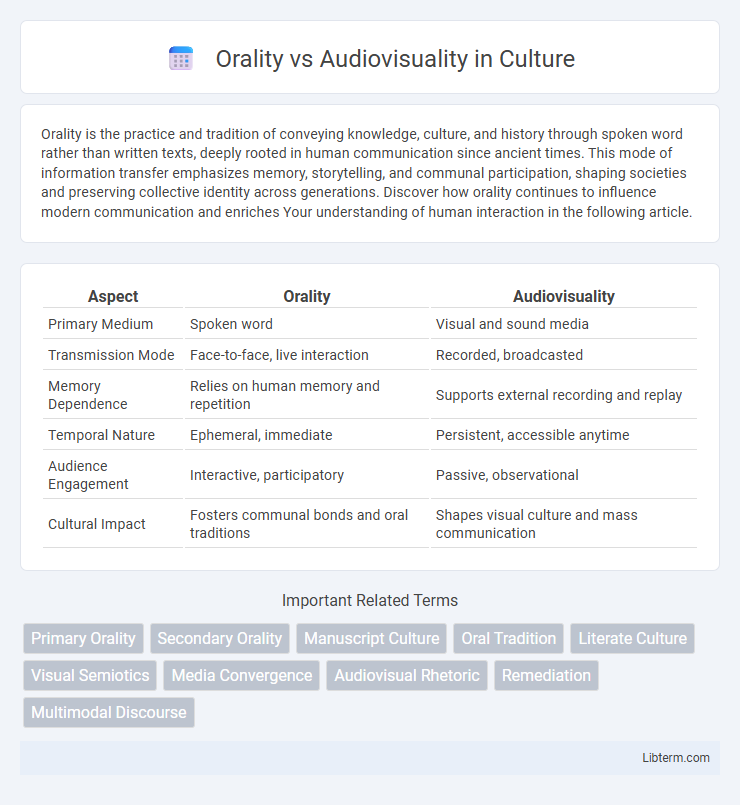
| Aspect | Orality | Audiovisuality |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Spoken word | Visual and sound media |
| Transmission Mode | Face-to-face, live interaction | Recorded, broadcasted |
| Memory Dependence | Relies on human memory and repetition | Supports external recording and replay |
| Temporal Nature | Ephemeral, immediate | Persistent, accessible anytime |
| Audience Engagement | Interactive, participatory | Passive, observational |
| Cultural Impact | Fosters communal bonds and oral traditions | Shapes visual culture and mass communication |
Defining Orality and Audiovisuality
Orality refers to communication primarily based on spoken language and real-time interaction, emphasizing memory, repetition, and collective participation. Audiovisuality combines sound and visual elements, such as images, film, and video, facilitating multisensory engagement and asynchronous communication. These modes differ fundamentally in their reliance on immediacy, sensory channels, and the preservation of information.
Historical Evolution of Communication Modes
Orality, characterized by spoken language and memory-based transmission, dominated human communication for millennia and shaped early cultural and social structures. The advent of audiovisuality introduced a transformative shift, integrating visual and auditory stimuli through technologies like film, television, and digital media, which enabled more immersive and multifaceted information delivery. This historical evolution from orality to audiovisuality reflects a progression from linear, ephemeral communication to complex, multimodal formats impacting cognition, education, and cultural expression.
Cognitive Impacts of Oral vs Audiovisual Media
Orality engages memory and imagination through active listening and verbal interaction, fostering deep cognitive processing and social connectivity. Audiovisual media combine visual and auditory stimuli that enhance information retention by engaging multiple sensory pathways, facilitating faster comprehension but often promoting passive reception. Cognitive impacts of orality emphasize narrative construction and critical thinking, while audiovisuality tends to support immediate understanding and emotional engagement through multisensory integration.
Cultural Transmission through Orality and Audiovisuality
Cultural transmission through orality relies on spoken language, storytelling, and memory, preserving traditions, values, and histories within communities without written records. Audiovisuality enhances cultural transmission by combining images, sound, and motion, enabling dynamic representation and wider dissemination of cultural content across diverse audiences. Both orality and audiovisuality shape cultural identities, but audiovisual media expand reach and sensory engagement, transforming how cultures are shared and preserved.
Memory, Retention, and Learning Styles
Orality relies heavily on oral memory techniques such as repetition and storytelling, which enhance retention through auditory and social engagement. Audiovisuality combines visual and auditory stimuli, supporting diverse learning styles by engaging both the visual and auditory memory pathways for deeper comprehension. Studies show that integrating audiovisual materials improves long-term retention and accommodates learners who benefit from multimodal input, contrasting with the primarily verbal focus of oral traditions.
Technological Advancements Shaping Audiovisuality
Technological advancements such as digital cameras, streaming platforms, and virtual reality have revolutionized audiovisuality by enhancing sensory immersion and accessibility. High-resolution visuals and spatial audio technologies enable more vivid storytelling experiences compared to traditional orality. These innovations continue to shape how audiences consume and engage with content, emphasizing multisensory interaction over purely oral communication.
Social Dynamics and Community Building
Orality fosters immediate, interactive social dynamics through face-to-face communication, reinforcing communal ties and shared cultural memory within groups. Audiovisuality extends these dynamics beyond physical proximity, enabling broader community building through shared visual and auditory experiences across digital platforms. Both forms shape social cohesion differently: orality emphasizes collective participation and embodied presence, while audiovisuality cultivates virtual networks and globalized identities.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Communication
Orality ensures accessibility by engaging listeners through spoken language, which is universally understood and requires minimal technology, fostering inclusivity for individuals with limited literacy or visual impairments. Audiovisuality combines visual and auditory elements, enhancing comprehension for diverse audiences but may exclude those with hearing or sight disabilities without proper accommodations like captions or audio descriptions. Prioritizing accessible design in audiovisual content promotes inclusivity by bridging communication gaps and addressing varied sensory needs.
Challenges in Preserving Oral and Audiovisual Traditions
Preserving oral traditions faces challenges including the risk of language extinction and the difficulty of capturing the dynamic, interactive nature of oral storytelling. Audiovisual traditions encounter issues such as media format obsolescence, degradation of physical recordings, and the need for digital archiving standards to ensure long-term accessibility. Both oral and audiovisual heritage require innovative preservation strategies combining documentation, transcription, and digitization to safeguard cultural memory effectively.
Future Trends: Integrating Orality and Audiovisuality
Future trends in integrating orality and audiovisuality emphasize immersive technologies like virtual and augmented reality, enhancing storytelling by combining spoken word with rich visual experiences. Advances in AI-driven voice synthesis and interactive media facilitate seamless blending of oral narratives with dynamic audiovisual content, promoting engagement and accessibility. This integration supports new forms of education, entertainment, and cultural preservation by leveraging both traditional oral practices and cutting-edge audiovisual tools.
Orality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com