Phonology is the study of how sounds function within a particular language or languages, focusing on the systematic organization of speech sounds. It analyzes patterns of sounds, including how they interact and change in different linguistic contexts to shape meaning. Dive into the article to explore how phonology impacts communication and enhances your understanding of language structure.
Table of Comparison
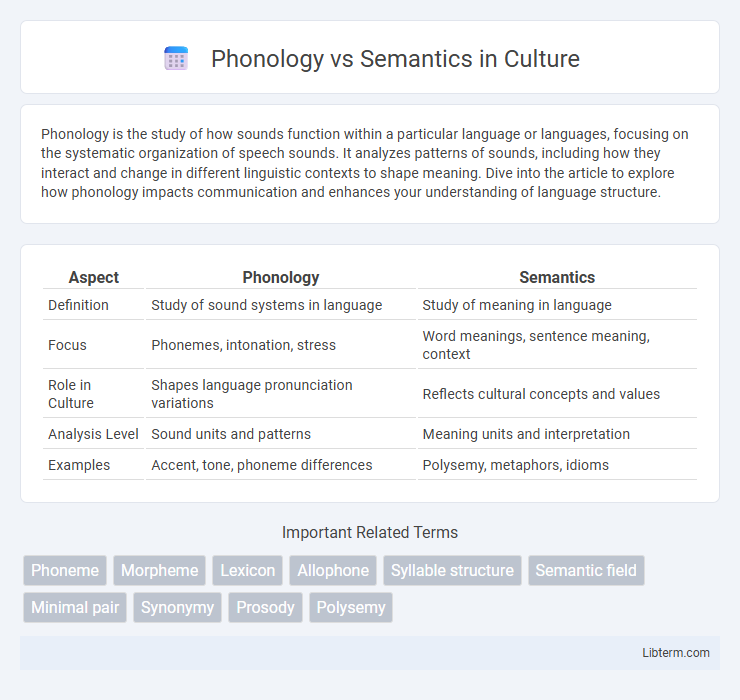
| Aspect | Phonology | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of sound systems in language | Study of meaning in language |
| Focus | Phonemes, intonation, stress | Word meanings, sentence meaning, context |
| Role in Culture | Shapes language pronunciation variations | Reflects cultural concepts and values |
| Analysis Level | Sound units and patterns | Meaning units and interpretation |
| Examples | Accent, tone, phoneme differences | Polysemy, metaphors, idioms |
Introduction to Phonology and Semantics
Phonology studies the systematic organization of sounds in languages, analyzing phonemes, stress patterns, and intonation to understand speech production and perception. Semantics focuses on meaning in language, investigating how words, phrases, and sentences convey concepts and relationships within communication. Both fields are foundational in linguistics, with phonology addressing sound patterns and semantics exploring meaning structures.
Defining Phonology: The Sound System of Language
Phonology examines the systematic organization of sounds in languages, focusing on how phonemes function and interact within a particular language. It involves the study of sound patterns, intonation, stress, and rhythm that shape spoken communication. Unlike semantics, which deals with meaning, phonology centers on the auditory elements that create distinct linguistic units.
Understanding Semantics: The Meaning in Language
Semantics explores the meaning behind words, phrases, and sentences, providing the foundation for understanding language beyond its sound system. While phonology analyzes the sound patterns and structures, semantics delves into how those sounds convey meaning within context. Mastery of semantics enables accurate interpretation and effective communication by connecting linguistic elements to their intended concepts and ideas.
Key Differences Between Phonology and Semantics
Phonology studies the sound systems and patterns in a language, focusing on phonemes, intonation, stress, and rhythm. Semantics deals with meaning, analyzing how words, phrases, and sentences convey ideas and concepts. While phonology addresses the structure of speech sounds, semantics interprets the significance and meaning conveyed by those sounds.
The Role of Phonology in Linguistics
Phonology plays a crucial role in linguistics by analyzing the systematic organization of sounds in languages and how these sound patterns convey meaning. It examines phonemes, syllable structures, stress, and intonation to understand spoken language's underlying sound system and its influence on word formation and comprehension. Unlike semantics, which focuses on meaning, phonology provides the foundation for distinguishing words through sound contrasts and prosodic features essential for effective communication.
The Role of Semantics in Linguistics
Semantics plays a crucial role in linguistics by analyzing meaning in language, contrasting with phonology, which studies sound systems and patterns. While phonology addresses how sounds function and interact, semantics examines how meaning is constructed, interpreted, and conveyed through words, phrases, and sentences. Understanding semantics enables linguists to decode language use, ambiguity, and context, essential for effective communication and language comprehension.
Interactions Between Phonology and Semantics
Interactions between phonology and semantics influence meaning interpretation through phonological cues, such as intonation and stress patterns, which can alter semantic understanding in spoken language. Phonological variations like homophones demonstrate how identical phonetic forms can have multiple semantic representations, requiring contextual disambiguation. Prosodic features contribute to semantic nuances, highlighting the dynamic interplay between sound structure and meaning in linguistic processing.
Applications of Phonology and Semantics in Language Learning
Phonology aids language learners by improving pronunciation, enabling accurate sound recognition, and facilitating listening comprehension through understanding phonetic patterns and phoneme distinctions. Semantics enhances vocabulary acquisition and contextual language use by helping learners grasp word meanings, relationships, and nuanced interpretations in communication. Integrating phonology and semantics in language education supports holistic language proficiency, combining sound accuracy with meaningful expression.
Common Misconceptions: Phonology vs Semantics
Phonology and semantics are often confused, but they address distinct linguistic aspects: phonology studies the sound systems of a language, while semantics focuses on meaning. A common misconception is that similar sounds imply similar meanings, which is false, as phonological similarity does not guarantee semantic relation. Understanding this distinction clarifies language analysis, emphasizing that phonological patterns influence pronunciation without inherently affecting word meaning.
Conclusion: Integrating Phonology and Semantics in Language Studies
Integrating phonology and semantics enhances the comprehensive understanding of language by linking sound patterns with meaning. Phonological analysis informs semantic interpretation by revealing how phonetic variations influence meaning distinctions. This interdisciplinary approach advances linguistics by enabling more accurate modeling of language processing and communication.
Phonology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com