A norm is a standard or rule that guides behavior within a group or society, shaping expectations and social interactions. Understanding norms helps you navigate social contexts more effectively and avoid misunderstandings. Explore the rest of the article to discover how norms influence daily life and individual choices.
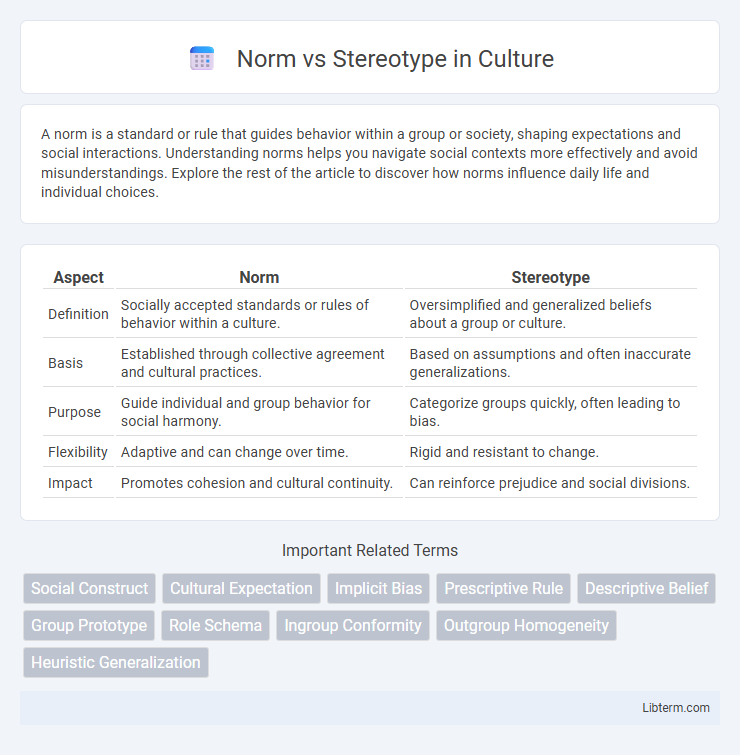
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Norm | Stereotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Socially accepted standards or rules of behavior within a culture. | Oversimplified and generalized beliefs about a group or culture. |
| Basis | Established through collective agreement and cultural practices. | Based on assumptions and often inaccurate generalizations. |
| Purpose | Guide individual and group behavior for social harmony. | Categorize groups quickly, often leading to bias. |
| Flexibility | Adaptive and can change over time. | Rigid and resistant to change. |
| Impact | Promotes cohesion and cultural continuity. | Can reinforce prejudice and social divisions. |
Understanding the Concepts: Norms and Stereotypes
Norms represent the unwritten rules and expected behaviors within a social group, guiding individuals on what is considered acceptable or typical conduct. Stereotypes are widely held but oversimplified and fixed beliefs about a particular group of people, often leading to generalized assumptions. Understanding the concepts of norms and stereotypes is essential for recognizing how social expectations influence behavior and how oversimplified perceptions can perpetuate biases.
Origins: How Norms and Stereotypes Develop
Norms develop through repeated social interactions and cultural transmission, establishing accepted behaviors within groups. Stereotypes originate from cognitive shortcuts that categorize individuals based on perceived group traits, often reinforced by media and social environments. Both emerge from collective experiences but differ as norms guide behavior, whereas stereotypes simplify and generalize social perceptions.
Social Functions of Norms
Norms regulate social behavior by establishing shared expectations that promote group cohesion and predictability in interactions. Unlike stereotypes, which are oversimplified and generalized beliefs about groups, norms function as collective guidelines that help maintain social order and reinforce cultural values. These social functions of norms enable coordination, cooperation, and conformity within communities, reducing uncertainty in social exchanges.
The Role of Stereotypes in Society
Stereotypes serve as simplified cognitive shortcuts that help individuals quickly categorize and make sense of social groups, influencing perceptions and behaviors within society. These generalized beliefs, often based on incomplete or biased information, can reinforce social inequalities and limit opportunities by perpetuating misconceptions about certain groups. Understanding the role of stereotypes is crucial for addressing prejudice and promoting more accurate and inclusive social norms.
Key Differences Between Norms and Stereotypes
Norms represent shared expectations and rules within a social group, guiding acceptable behaviors, whereas stereotypes are oversimplified and generalized beliefs about a group of people. Norms evolve through collective agreement and cultural practices, while stereotypes tend to be fixed, often inaccurate assumptions that reinforce biases. Understanding the distinction is crucial for addressing social interactions and reducing prejudice effectively.
Impacts on Individual Behavior
Norms shape individual behavior by establishing expectations within social groups, guiding actions through implicit or explicit rules. Stereotypes influence behavior by creating fixed, oversimplified perceptions that can lead to biased decision-making and self-fulfilling prophecies. Both norms and stereotypes significantly affect self-identity, social interactions, and conformity pressures, often limiting personal freedom and authenticity.
Influence on Group Dynamics
Norms establish expected behaviors within a group that promote cohesion and predictability, guiding individuals toward collective goals. Stereotypes influence group dynamics by shaping perceptions and interactions, often leading to biased judgments and exclusionary behavior. Together, norms and stereotypes impact conformity, group decision-making, and social identity formation in organizational and social settings.
Cultural Variations: Norms vs Stereotypes
Cultural norms represent shared, accepted behaviors within a specific group that guide social conduct and maintain societal order, while stereotypes are oversimplified and generalized beliefs about a group that often lead to misconceptions and bias. Norms vary significantly across cultures, reflecting unique traditions, values, and social expectations, whereas stereotypes tend to persist across different societies despite a lack of accurate representation. Understanding cultural variations in norms versus stereotypes is critical to promoting intercultural sensitivity and reducing prejudiced judgments in global interactions.
Challenging and Changing Stereotypes
Challenging and changing stereotypes requires actively questioning ingrained beliefs and promoting diverse perspectives that reflect the complexity of individual identities. Social norms often enforce stereotypes by creating expectations for behavior, but education, media representation, and inclusive policies can disrupt these patterns by highlighting varied experiences and achievements. Emphasizing critical thinking and empathy fosters environments where stereotypes lose their influence, enabling societal growth and equity.
Encouraging Healthy Social Norms
Encouraging healthy social norms involves promoting behaviors that benefit community well-being, such as respect, inclusivity, and cooperation, rather than relying on stereotypes that oversimplify or misrepresent groups. Social norms shape individual actions through shared expectations, whereas stereotypes can create harmful biases and limit personal identity. Implementing educational programs and community initiatives fosters positive social norms that challenge stereotypes and support diversity.
Norm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com