Authority is the recognized power or right to enforce rules, make decisions, and command obedience within a specific context or organization. It plays a crucial role in establishing order and guiding behavior by defining who has control and responsibility. Discover how authority shapes leadership and influences your interactions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
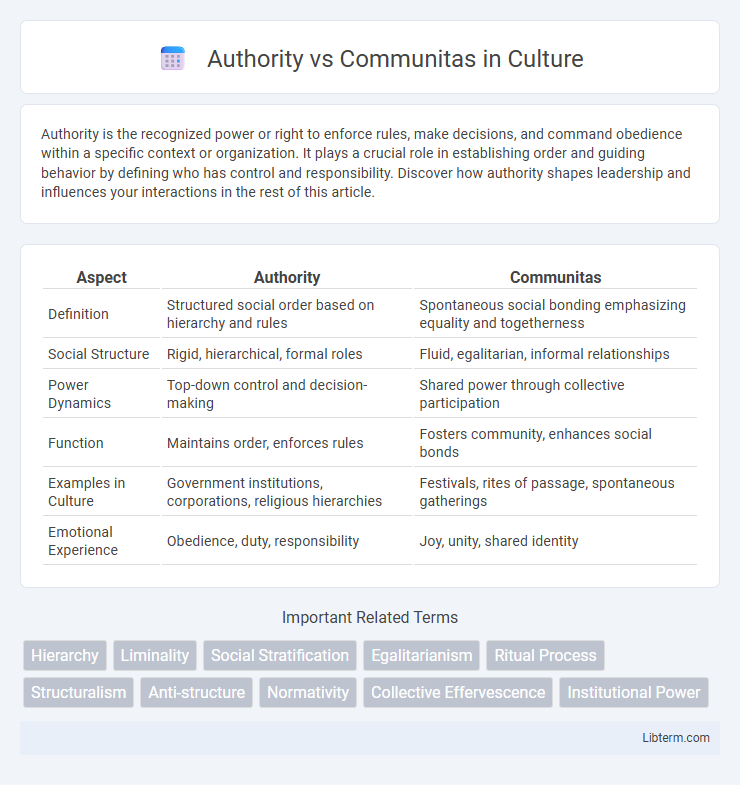
| Aspect | Authority | Communitas |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured social order based on hierarchy and rules | Spontaneous social bonding emphasizing equality and togetherness |
| Social Structure | Rigid, hierarchical, formal roles | Fluid, egalitarian, informal relationships |
| Power Dynamics | Top-down control and decision-making | Shared power through collective participation |
| Function | Maintains order, enforces rules | Fosters community, enhances social bonds |
| Examples in Culture | Government institutions, corporations, religious hierarchies | Festivals, rites of passage, spontaneous gatherings |
| Emotional Experience | Obedience, duty, responsibility | Joy, unity, shared identity |
Understanding Authority: Definition and Origins
Authority refers to the legitimate power or right to command and make decisions within a social structure, often rooted in formal institutions, legal frameworks, or established hierarchies. Its origins trace back to sociological theories by Max Weber, who identified three types of authority: traditional, charismatic, and legal-rational, each deriving legitimacy from cultural customs, personal qualities, or codified laws. This structured power contrasts with communitas, emphasizing ordered control over spontaneous, egalitarian community bonds.
What is Communitas? Exploring Its Meaning
Communitas refers to the intense sense of community and shared experience that emerges among individuals during collective rituals or moments of social equality, transcending structured hierarchies and formal authority. It emphasizes emotional bonds, solidarity, and a temporary suspension of societal roles, fostering a profound feeling of unity and mutual support. Unlike authority, which is based on established power and rules, communitas arises spontaneously, highlighting the human need for connection beyond institutional frameworks.
Historical Perspectives on Authority and Communitas
Historical perspectives on authority emphasize hierarchical structures rooted in formal institutions, where power is often centralized and legitimized through laws, traditions, or religious mandates. In contrast, communitas arises from shared human experiences and collective social bonds, promoting equality and spontaneous community solidarity beyond formal roles. The tension between authority and communitas highlights evolving social dynamics from rigid governance systems to more participatory and egalitarian communal interactions.
Key Differences Between Authority and Communitas
Authority represents structured power and formal roles within established hierarchies, emphasizing control, rules, and responsibility. Communitas embodies spontaneous social bonds and collective equality experienced during shared events or rituals, highlighting emotional connection and unity. The key difference lies in authority's emphasis on order and hierarchy, whereas communitas centers on egalitarian experiences and communal belonging.
The Role of Authority in Social Structures
Authority in social structures establishes formal rules and hierarchies that maintain order and regulate behavior within communities. It provides a framework for decision-making and conflict resolution, ensuring stability and predictable interactions among members. This formalized power contrasts with communitas, which emphasizes spontaneous, egalitarian bonds that arise outside structured authority.
Communitas in Practice: Modern Examples
Communitas in practice manifests in grassroots movements such as community gardens, where individuals collaborate beyond formal hierarchies to foster social bonds and shared purpose. Events like music festivals create temporary spaces of intense communal experience, breaking down social boundaries and emphasizing equality and unity. Digital platforms like online support groups or open-source communities exemplify communitas by enabling collective engagement based on common interests and mutual aid rather than institutional authority.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Authority
Authority provides clear decision-making structures and efficient management, ensuring consistency and accountability within organizations or societies. However, excessive reliance on authority can stifle creativity, reduce individual autonomy, and provoke resistance or dissatisfaction among members. Balancing authority with participatory elements is essential to mitigate drawbacks while maintaining order and effectiveness.
Advantages and Challenges of Communitas
Communitas fosters strong social bonds and shared experiences, enhancing community cohesion and collective identity. It promotes equality and mutual support, encouraging authentic interactions that transcend hierarchical structures. Challenges include difficulties in sustaining long-term organization and potential exclusion of outsiders due to intense in-group solidarity.
Authority vs Communitas in Leadership and Organizations
Authority in leadership relies on formal structures, hierarchical roles, and institutional power to enforce rules and maintain order within organizations. Communitas emphasizes spontaneous, egalitarian connections and shared experiences that foster collaboration, trust, and collective identity among members. Effective organizations balance authority's control with communitas' relational dynamics to enhance innovation, employee engagement, and adaptive capacity.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Authority with Communitas
Striking a balance between authority and communitas involves blending structured leadership with spontaneous community bonding to foster collaboration and innovation. Integrating authority ensures clear decision-making and accountability, while communitas enhances inclusive participation and shared purpose. This synergy promotes resilient organizations where hierarchical guidance supports collective empowerment.
Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com