Innovation drives progress by introducing new ideas, technologies, and methods that improve efficiency and solve complex problems. It fosters competitive advantage and opens pathways for growth and transformation in various industries. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your organization can harness innovation for lasting success.
Table of Comparison
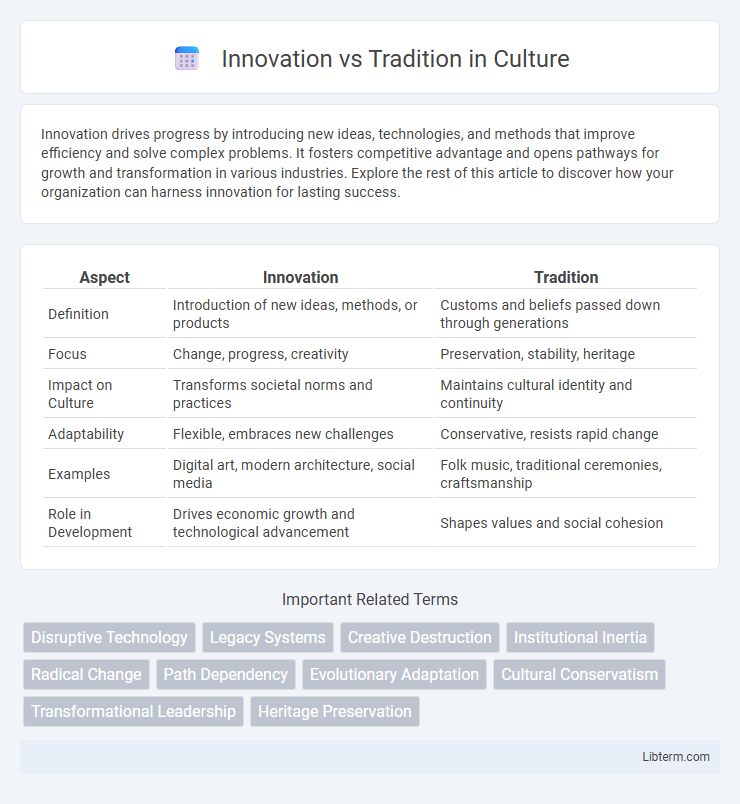
| Aspect | Innovation | Tradition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introduction of new ideas, methods, or products | Customs and beliefs passed down through generations |
| Focus | Change, progress, creativity | Preservation, stability, heritage |
| Impact on Culture | Transforms societal norms and practices | Maintains cultural identity and continuity |
| Adaptability | Flexible, embraces new challenges | Conservative, resists rapid change |
| Examples | Digital art, modern architecture, social media | Folk music, traditional ceremonies, craftsmanship |
| Role in Development | Drives economic growth and technological advancement | Shapes values and social cohesion |
Defining Innovation and Tradition
Innovation refers to the introduction of new ideas, methods, or products that create significant improvements or transformations in a given field. Tradition encompasses established customs, beliefs, and practices passed down through generations that provide cultural continuity and identity. Understanding the dynamic interplay between innovation and tradition is crucial for balancing progress with preservation in society and business.
Historical Perspectives on Progress
Historical perspectives on progress reveal a dynamic tension between innovation and tradition, where civilizations evolved by integrating groundbreaking ideas with established customs. Ancient societies like Mesopotamia advanced through technological inventions such as the wheel while preserving religious rituals, illustrating that progress often depends on a balance between new developments and cultural continuity. The Industrial Revolution exemplifies this interplay by revolutionizing manufacturing and urban life while sparking debates over the preservation of traditional labor structures and social norms.
The Benefits of Innovation
Innovation drives economic growth by introducing cutting-edge technologies that enhance productivity and efficiency. It fosters competitive advantages for businesses, enabling them to adapt to changing markets and meet evolving consumer demands. Embracing innovation also encourages creative problem-solving, leading to breakthroughs in healthcare, sustainability, and communication.
The Enduring Value of Tradition
Tradition preserves cultural identity and provides a stable foundation for communities, fostering a sense of continuity and belonging. It embeds time-tested values and practices that guide behavior and decision-making, ensuring social cohesion. Upholding tradition can enrich innovation by grounding new ideas in meaningful historical context, creating balanced progress.
Areas of Conflict: Innovation vs Tradition
Innovation often challenges established traditions by introducing new technologies and methods that disrupt conventional practices in industries such as manufacturing and education. Conflicts arise when traditional values and cultural norms resist change, fearing loss of identity or control over established systems. These areas of tension highlight the struggle between embracing forward-thinking solutions and preserving historical legacies.
Balancing Change with Continuity
Balancing innovation with tradition requires integrating cutting-edge technologies while preserving core cultural values and practices that define identity and stability. Organizations thriving in dynamic markets emphasize adaptive strategies combining experimental approaches with time-tested principles to foster sustainable growth. Embracing change selectively ensures continuity, allowing innovation to complement rather than disrupt established norms, driving resilience and long-term success.
Case Studies: When Innovation Transformed Traditional Practices
Case studies reveal how innovation has revolutionized traditional practices, such as Toyota's implementation of lean manufacturing, which enhanced efficiency and reduced waste in automobile production. In agriculture, precision farming technologies like drone surveillance and IoT sensors have transformed conventional crop management, boosting yields and sustainability. The retail sector's adoption of e-commerce platforms demonstrates a shift from brick-and-mortar stores to digital marketplaces, reshaping consumer behavior and operational models.
Societal Impacts of Embracing or Resisting Change
Embracing innovation drives societal progress by fostering technological advancements, economic growth, and improved quality of life through new solutions and efficiencies. Resistance to change preserves cultural heritage and social stability but can hinder adaptation to dynamic global challenges and limit access to modern opportunities. Balancing innovation and tradition is crucial for sustainable development, ensuring that societal values coexist with transformative growth.
Navigating Innovation in Traditional Industries
Navigating innovation in traditional industries requires balancing heritage with cutting-edge technologies to drive growth and competitiveness. Integrating digital tools, such as automation and AI, can optimize legacy processes without compromising established quality standards. Embracing adaptive strategies fosters resilience, enabling traditional sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and finance to thrive amid evolving market demands.
Future Outlook: Harmonizing Innovation and Tradition
Balancing innovation with tradition creates resilient strategies that honor cultural heritage while embracing technological advancements. Integrating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and sustainable practices within traditional frameworks fosters long-term growth and societal acceptance. This harmonious approach ensures future development respects historical values while driving progress in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com