Solarpunk envisions a future where technology and nature coexist harmoniously through sustainable energy, green architecture, and community-driven innovations. Emphasizing renewable resources like solar power, it encourages a lifestyle that reduces environmental impact while promoting social equity and resilience. Explore the rest of this article to discover how solarpunk principles can inspire Your journey towards a brighter, eco-conscious future.
Table of Comparison
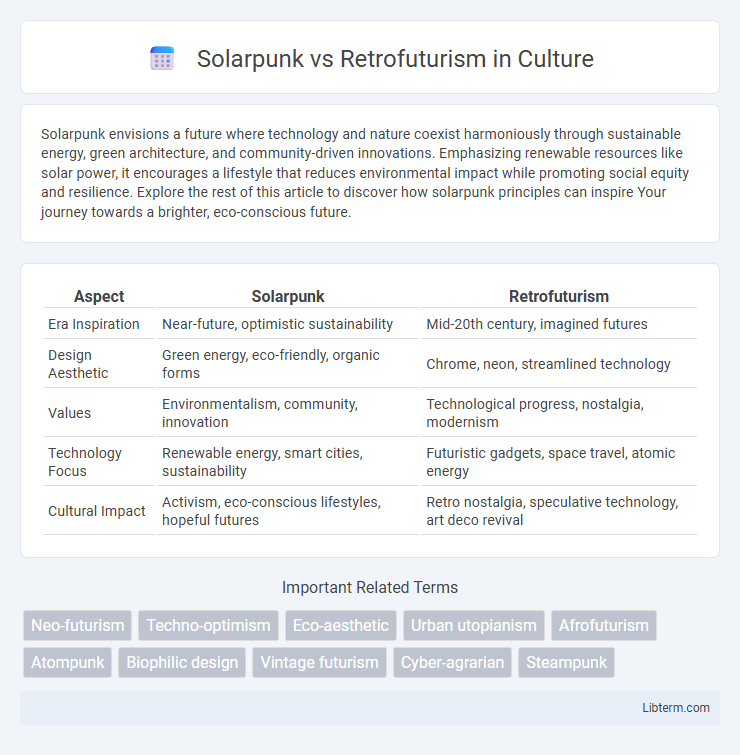
| Aspect | Solarpunk | Retrofuturism |
|---|---|---|
| Era Inspiration | Near-future, optimistic sustainability | Mid-20th century, imagined futures |
| Design Aesthetic | Green energy, eco-friendly, organic forms | Chrome, neon, streamlined technology |
| Values | Environmentalism, community, innovation | Technological progress, nostalgia, modernism |
| Technology Focus | Renewable energy, smart cities, sustainability | Futuristic gadgets, space travel, atomic energy |
| Cultural Impact | Activism, eco-conscious lifestyles, hopeful futures | Retro nostalgia, speculative technology, art deco revival |
Introduction to Solarpunk and Retrofuturism
Solarpunk envisions a sustainable future powered by renewable energy, combining advanced technology with ecological harmony to inspire community resilience and environmental stewardship. Retrofuturism revisits past eras' visions of the future, blending vintage aesthetics with speculative technology to critique modernity and nostalgia through design, literature, and art. Both movements explore contrasting relationships between technology, society, and the environment, offering unique cultural narratives and visions of what the future might hold.
Origins and Historical Context
Solarpunk emerged in the early 2010s as a response to climate change and a desire for sustainable futures, blending ecological awareness with technology rooted in renewable energy and community resilience. Retrofuturism originated in the mid-20th century, reflecting optimism about the future through the lens of past eras, particularly the 1950s and 1960s, shaped by space race ambitions and industrial progress. These movements contrast in their historical context, with Solarpunk focused on ecological balance and social equity, while Retrofuturism channels nostalgic visions of technological advancement and modernity from earlier decades.
Core Aesthetics and Visual Themes
Solarpunk emphasizes vibrant greenery, sustainable architecture, and bright, optimistic color palettes that blend nature with advanced technology, highlighting eco-friendly solutions and community harmony. Retrofuturism features sleek, streamlined designs inspired by mid-20th-century visions of the future, incorporating chrome, neon lights, and bold geometric shapes that reflect a nostalgic yet imaginative take on technology. Both aesthetics visually explore humanity's relationship with technology but diverge in tone--Solarpunk fosters hope and environmental integration, while Retrofuturism evokes a retro-modern blend of optimism and futurism grounded in historical design.
Philosophical Ideals and Worldviews
Solarpunk embodies an eco-centric philosophy emphasizing sustainability, community resilience, and harmonious integration with nature, envisioning a future where technology and environment coexist symbiotically. Retrofuturism reflects a nostalgic yet speculative worldview, blending past cultural aesthetics with futuristic technology, often critiquing modernity by reimagining alternative historical progressions. Both philosophies explore human relationships with technology and environment, but Solarpunk prioritizes ecological balance and equitable societies, whereas Retrofuturism interrogates historical narratives and cultural identity through a lens of speculative imagination.
Technology in Solarpunk vs Retrofuturism
Solarpunk technology emphasizes sustainable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, integrated into eco-friendly urban designs that promote green living and community resilience. Retrofuturism showcases technology inspired by mid-20th-century visions of the future, featuring steam-powered machines, analog gadgets, and bulky mechanical devices often powered by fossil fuels. Solarpunk prioritizes renewable innovations and environmental harmony, while retrofuturism reflects nostalgic technological aesthetics with less emphasis on sustainability.
Environmental Perspectives and Sustainability
Solarpunk envisions a sustainable future by integrating renewable energy, green architecture, and eco-friendly technologies into harmonious communities that prioritize environmental stewardship and climate resilience. Retrofuturism reflects past visions of the future, often emphasizing technological innovation but frequently lacking a strong focus on sustainability or ecological impact, highlighting a contrast with Solarpunk's green ideals. The environmental perspective in Solarpunk promotes circular economies and biodiversity preservation, while Retrofuturism serves more as an aesthetic homage than a blueprint for sustainable living.
Social Structures and Community Portrayals
Solarpunk envisions social structures rooted in decentralized, cooperative communities emphasizing sustainability, equality, and direct participation, portraying inclusive neighborhoods intertwined with green technology. Retrofuturism often reflects hierarchical or industrial social orders inspired by mid-20th century aesthetics, highlighting centralized power structures and technological optimism within urban or mechanical landscapes. Both genres explore community dynamics but contrast in their values--Solarpunk promotes ecological harmony and grassroots governance, while Retrofuturism nostalgically idealizes progress through technological dominance and structured authority.
Literary and Artistic Influences
Solarpunk embraces themes of sustainability and community, drawing inspiration from utopian literature and eco-centric art that emphasize harmony between technology and nature. Retrofuturism channels mid-20th century visions of the future, reflecting the aesthetics of classic sci-fi literature, vintage advertisements, and industrial design with a nostalgic yet speculative approach. Both movements influence contemporary creative works by blending historical context with futuristic aspirations, yet Solarpunk foregrounds ecological optimism while Retrofuturism revisits past futurism with stylistic nostalgia.
Representation in Popular Media
Solarpunk and Retrofuturism both offer distinctive visual aesthetics in popular media, with Solarpunk emphasizing sustainable technology, green urban environments, and optimistic futures powered by renewable energy. Retrofuturism portrays futures imagined from past perspectives, often featuring neon lights, chrome, and a blend of 1950s-1980s technology and culture, reflecting societal hopes and anxieties of those eras. Media such as films, video games, and graphic novels showcase Solarpunk through vibrant, eco-conscious cityscapes, while Retrofuturism appears in cyberpunk genres and vintage sci-fi, highlighting contrasting visions of human progress.
Future Trends and Cultural Impact
Solarpunk envisions a sustainable future powered by renewable energy, emphasizing community resilience and ecological harmony, while Retrofuturism blends nostalgic aesthetics with futuristic technology, reflecting cultural hopes and anxieties from past decades. Future trends in Solarpunk prioritize green infrastructure, decentralized energy systems, and social equity, driving innovations in urban planning and environmental policy. Retrofuturism influences design, media, and fashion by revisiting mid-20th century visions of the future, shaping cultural identity through reinterpretation of technological optimism and critique.
Solarpunk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com