Localization ensures that your content, products, or services are culturally and linguistically tailored to meet the needs of a specific target market, enhancing user experience and engagement. By adapting language, currency, date formats, and cultural references, localization helps your brand resonate more deeply with local audiences, increasing trust and conversion rates. Discover how effective localization strategies can transform your global outreach by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
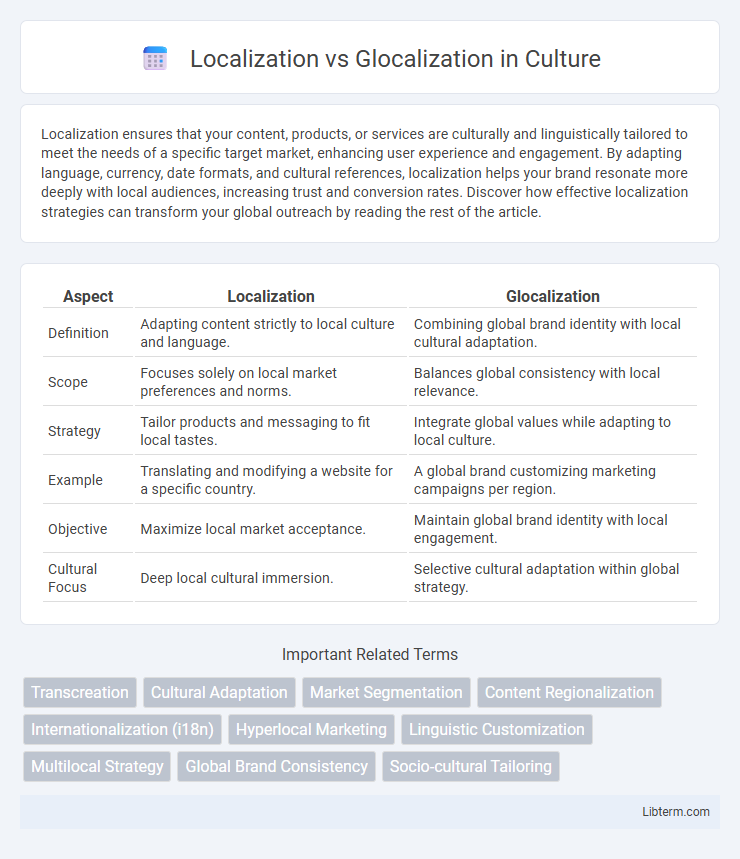
| Aspect | Localization | Glocalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting content strictly to local culture and language. | Combining global brand identity with local cultural adaptation. |
| Scope | Focuses solely on local market preferences and norms. | Balances global consistency with local relevance. |
| Strategy | Tailor products and messaging to fit local tastes. | Integrate global values while adapting to local culture. |
| Example | Translating and modifying a website for a specific country. | A global brand customizing marketing campaigns per region. |
| Objective | Maximize local market acceptance. | Maintain global brand identity with local engagement. |
| Cultural Focus | Deep local cultural immersion. | Selective cultural adaptation within global strategy. |
Introduction to Localization and Glocalization
Localization involves adapting products or content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and regulatory requirements of a specific local market, ensuring relevance and user engagement. Glocalization combines global reach with local adaptation by maintaining a core global brand identity while customizing marketing, products, or services to fit local preferences and cultural nuances. Both strategies aim to enhance market penetration, with localization focusing on individual markets and glocalization balancing global consistency and local relevance.
Defining Localization: Tailoring for Local Markets
Localization involves adapting products, services, and content to meet the specific cultural, linguistic, and regulatory requirements of individual local markets. It includes modifying language, currency, date formats, and marketing messages to resonate with local consumer behavior and preferences. Effective localization enhances user experience and brand relevance by addressing the unique characteristics of each target market.
Glocalization Explained: Global Strategies, Local Adaptations
Glocalization combines global strategies with local adaptations to create products and marketing approaches that resonate with diverse cultural preferences while maintaining brand consistency. This approach tailors global business models by integrating local languages, customs, and consumer behaviors, enhancing relevance and competitive advantage in various markets. By leveraging glocalization, companies can efficiently address regional demands without sacrificing the scalability and coherence of global operations.
Key Differences Between Localization and Glocalization
Localization involves tailoring products, content, and marketing strategies specifically to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regulatory needs of a single target market or region. Glocalization combines global branding with local adaptations, balancing standardized global strategies with localized elements to appeal to diverse markets simultaneously. The key difference lies in localization's deep customization for one market versus glocalization's hybrid approach that maintains global consistency while incorporating local relevance.
Benefits of Localization for Businesses
Localization enhances customer experience by tailoring products and marketing to specific cultural preferences, leading to increased brand loyalty and higher conversion rates. It improves market penetration and competitive advantage by addressing local regulations, languages, and consumer behaviors more effectively than global strategies. Businesses benefit from reduced communication barriers and stronger local partnerships, fostering trust and long-term growth in diverse markets.
Advantages of Glocalization in a Global Marketplace
Glocalization enhances business competitiveness by combining global brand consistency with local market adaptation, allowing companies to meet specific cultural preferences and consumer behaviors effectively. It increases customer engagement and loyalty by delivering tailored products and marketing strategies that resonate with local audiences while leveraging global resources and scale. This approach reduces market entry risks and improves responsiveness to regional trends and regulations, driving sustained growth in diverse international markets.
Real-World Examples of Localization Success
Localization success is evident in companies like McDonald's tailoring menus to cultural tastes in India by offering vegetarian options, or Netflix adapting content libraries and subtitles to local languages, increasing viewer engagement worldwide. IKEA's product designs consider local space constraints and lifestyle preferences, reflecting effective localization strategies that enhance customer experience in diverse markets. These real-world examples demonstrate how deep market understanding and cultural adaptation drive higher acceptance and brand loyalty.
Glocalization Case Studies: Global Brands, Local Impact
Glocalization strategies enable global brands like McDonald's and Coca-Cola to adapt their products and marketing to local cultures while maintaining their core identity, driving deeper consumer engagement and brand loyalty. Case studies reveal how McDonald's menu variations in India, such as the McAloo Tikki burger, and Coca-Cola's localized advertising campaigns successfully resonate with regional tastes and cultural values. These examples demonstrate that combining global consistency with local relevance boosts market penetration and fosters sustainable growth in diverse markets.
Choosing Between Localization and Glocalization Strategies
Choosing between localization and glocalization strategies depends on the target market's cultural nuances and the brand's global objectives. Localization involves adapting products or content specifically to fit the local culture, language, and consumer preferences, ensuring relevance and acceptance. Glocalization balances global brand consistency with local customization, optimizing market penetration by integrating worldwide standards while addressing regional differences.
Future Trends in Localization and Glocalization
Future trends in localization emphasize AI-driven automation and real-time language adaptation to enhance global user experiences efficiently. Glocalization strategies increasingly integrate culturally nuanced content with scalable technology platforms to balance global brand consistency and local relevance. Emerging markets will drive the demand for hyper-localized solutions, blending advanced machine learning with human expertise for precise, context-aware communication.
Localization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com