Integrationism emphasizes the dynamic and context-dependent nature of communication, challenging traditional views that treat language as a fixed code. It focuses on how speakers create meaning through interaction, considering social and situational factors. Discover how integrationism reshapes our understanding of language by exploring the details in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
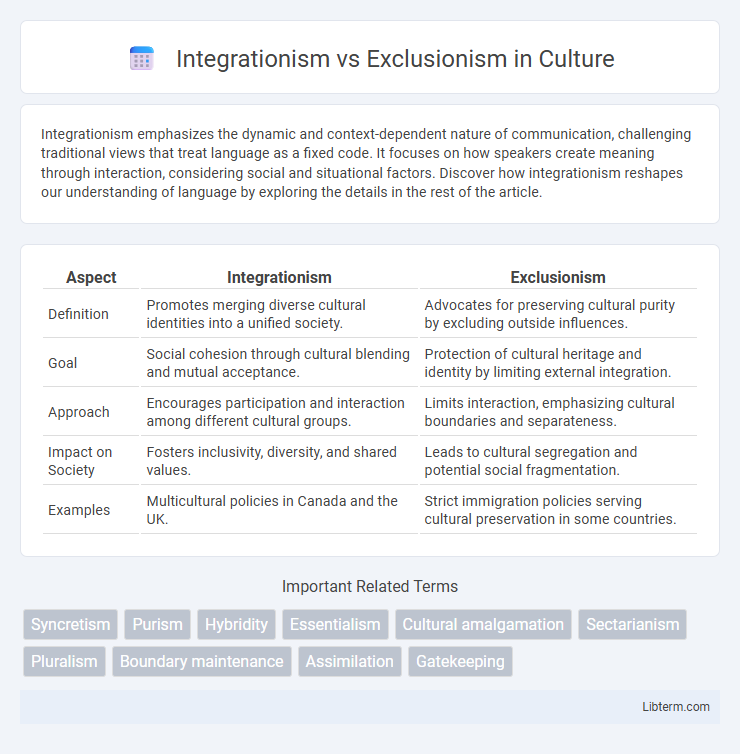
| Aspect | Integrationism | Exclusionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Promotes merging diverse cultural identities into a unified society. | Advocates for preserving cultural purity by excluding outside influences. |
| Goal | Social cohesion through cultural blending and mutual acceptance. | Protection of cultural heritage and identity by limiting external integration. |
| Approach | Encourages participation and interaction among different cultural groups. | Limits interaction, emphasizing cultural boundaries and separateness. |
| Impact on Society | Fosters inclusivity, diversity, and shared values. | Leads to cultural segregation and potential social fragmentation. |
| Examples | Multicultural policies in Canada and the UK. | Strict immigration policies serving cultural preservation in some countries. |
Introduction to Integrationism and Exclusionism
Integrationism emphasizes the blending of diverse cultural, social, and economic groups within a society, promoting inclusivity and equal participation to foster social cohesion and mutual respect. Exclusionism advocates for maintaining distinct boundaries between groups, often prioritizing majority interests and limiting access or influence of minority populations to preserve established norms and control. These contrasting ideologies shape policies on immigration, multiculturalism, and social integration, impacting societal dynamics and governance approaches.
Historical Origins of the Debate
The historical origins of the Integrationism vs Exclusionism debate trace back to early 20th-century sociopolitical theories addressing immigration and national identity. Integrationism advocates for the incorporation of diverse cultural groups into a unified society through policies promoting social cohesion and equal rights. In contrast, Exclusionism emerges from nationalist and protectionist ideologies emphasizing cultural homogeneity and restrictive immigration regulations to preserve perceived ethnic or cultural purity.
Core Principles of Integrationism
Integrationism emphasizes the fluid and dynamic nature of language use, rejecting fixed rules and standardized norms in favor of context-dependent communication practices. It prioritizes the role of social interaction and individual interpretation, viewing meaning as co-constructed rather than pre-determined. Core principles include the belief that linguistic knowledge is inseparable from situational factors and that language evolves through continuous integration of diverse communicative experiences.
Key Tenets of Exclusionism
Exclusionism emphasizes the preservation of distinct cultural, ethnic, or religious identities by restricting social, political, or economic integration with other groups. It advocates for maintaining group boundaries to protect perceived purity, autonomy, and traditional values. Key tenets include limiting immigration, opposing multicultural policies, and promoting social segregation to avoid dilution or assimilation of the in-group's identity.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Integrationism fosters social cohesion by promoting inclusive cultural exchanges and mutual respect among diverse groups, leading to enriched community identities and decreased social tensions. Exclusionism, on the other hand, often results in social fragmentation, marginalization of minority cultures, and heightened cultural conflicts, undermining societal stability and diversity. The contrasting impacts influence national policies, education systems, and intergroup relations, shaping long-term social dynamics and cultural landscapes.
Economic Consequences of Both Approaches
Integrationism promotes inclusive economic policies that enhance labor market participation, boost productivity, and stimulate innovation by leveraging diverse talent and skills. Exclusionism often leads to restricted market access, reduced consumer spending, and increased social welfare costs due to marginalization of certain groups, resulting in slower economic growth. Studies show that integrationist economies typically experience higher GDP growth rates and more robust economic resilience compared to exclusionist counterparts.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Integrationism promotes the inclusion of diverse groups within social, educational, and political frameworks by focusing on collaboration and shared goals, as seen in the successful integration of immigrants in countries like Canada and Sweden. Exclusionism, on the other hand, emphasizes separation or restriction of certain groups, exemplified by policies such as Brexit's impact on European Union nationals or the exclusionary practices faced by minority communities in South Africa during apartheid. Case studies highlight how integrationist approaches lead to greater social cohesion and economic benefit, whereas exclusionism often results in increased social tension and economic disparities.
Critical Arguments: Strengths and Weaknesses
Integrationism emphasizes social cohesion and economic benefits by promoting inclusion of diverse groups, fostering innovation and reducing inequality; however, it may underestimate cultural conflicts and integration challenges in practice. Exclusionism prioritizes preserving cultural or national identity and security by limiting participation of perceived outsiders, which can strengthen social solidarity but often leads to discrimination and economic stagnation. Both approaches face criticism for either oversimplifying complex social dynamics or reinforcing divisive policies that hinder long-term societal progress.
Contemporary Relevance in Global Politics
Integrationism promotes cooperative frameworks and supranational institutions that enhance global governance and economic interdependence, addressing transnational challenges such as climate change and migration. Exclusionism prioritizes national sovereignty and stringent border controls, often fueling nationalism and protectionism in response to globalization's socio-economic disruptions. The tension between these paradigms shapes policies on trade, security alliances, and human rights, influencing the stability and inclusiveness of the international order.
The Future of Integrationism vs Exclusionism
The future of Integrationism vs Exclusionism hinges on shifting societal values towards inclusivity and diversity, emphasizing the benefits of interconnected communities and collaborative problem-solving. Advances in communication technology and globalization continue to challenge exclusionist ideologies by facilitating cross-cultural understanding and cooperation. Policy frameworks promoting equity, access, and cultural recognition are poised to further empower integrationist approaches in social, political, and economic spheres.
Integrationism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com